
How to Use SOCKET: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with SOCKET in Cirkit Designer
Design with SOCKET in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A socket is a device that provides a connection point for electrical components, enabling the easy insertion and removal of plugs or connectors. Sockets are widely used in electronic circuits to facilitate modularity, simplify maintenance, and allow for the replacement of components without soldering. They are commonly found in applications such as microcontroller programming, IC mounting, and power distribution.
Explore Projects Built with SOCKET
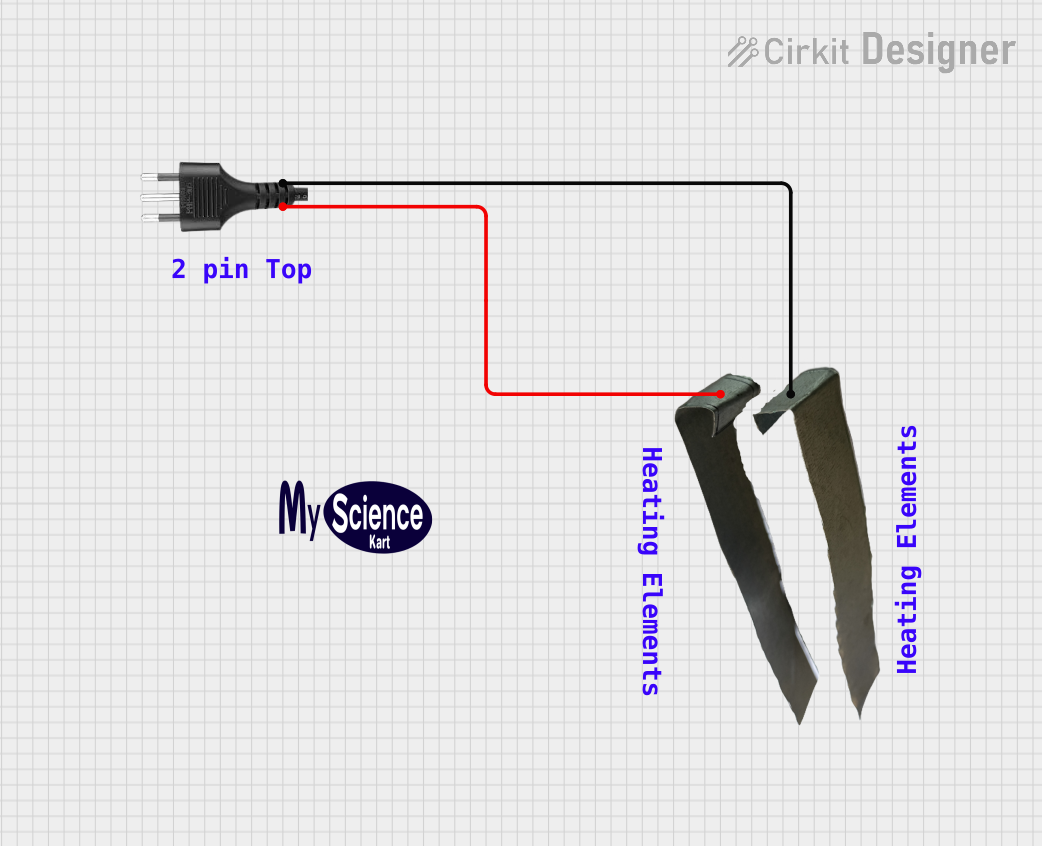
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer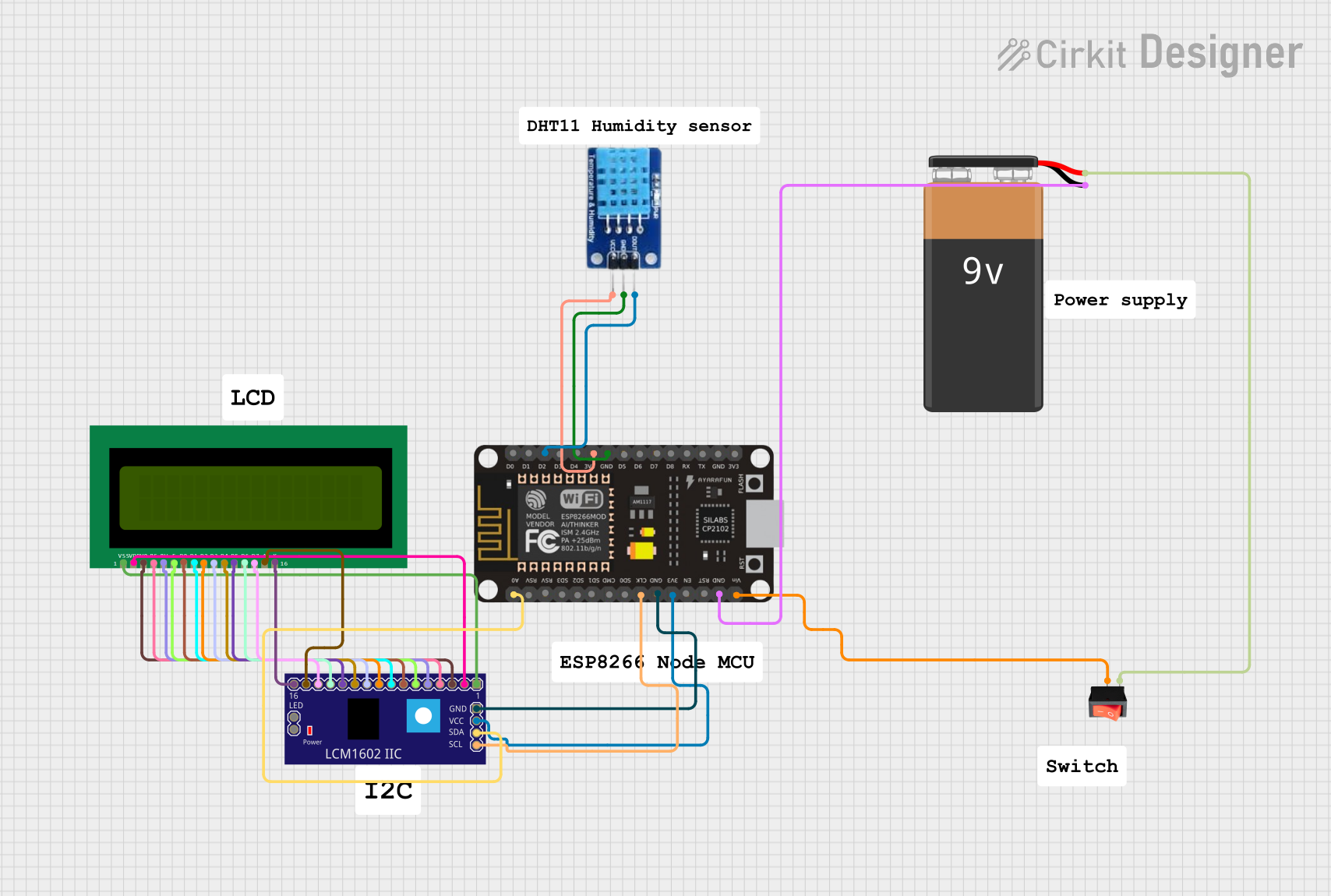
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer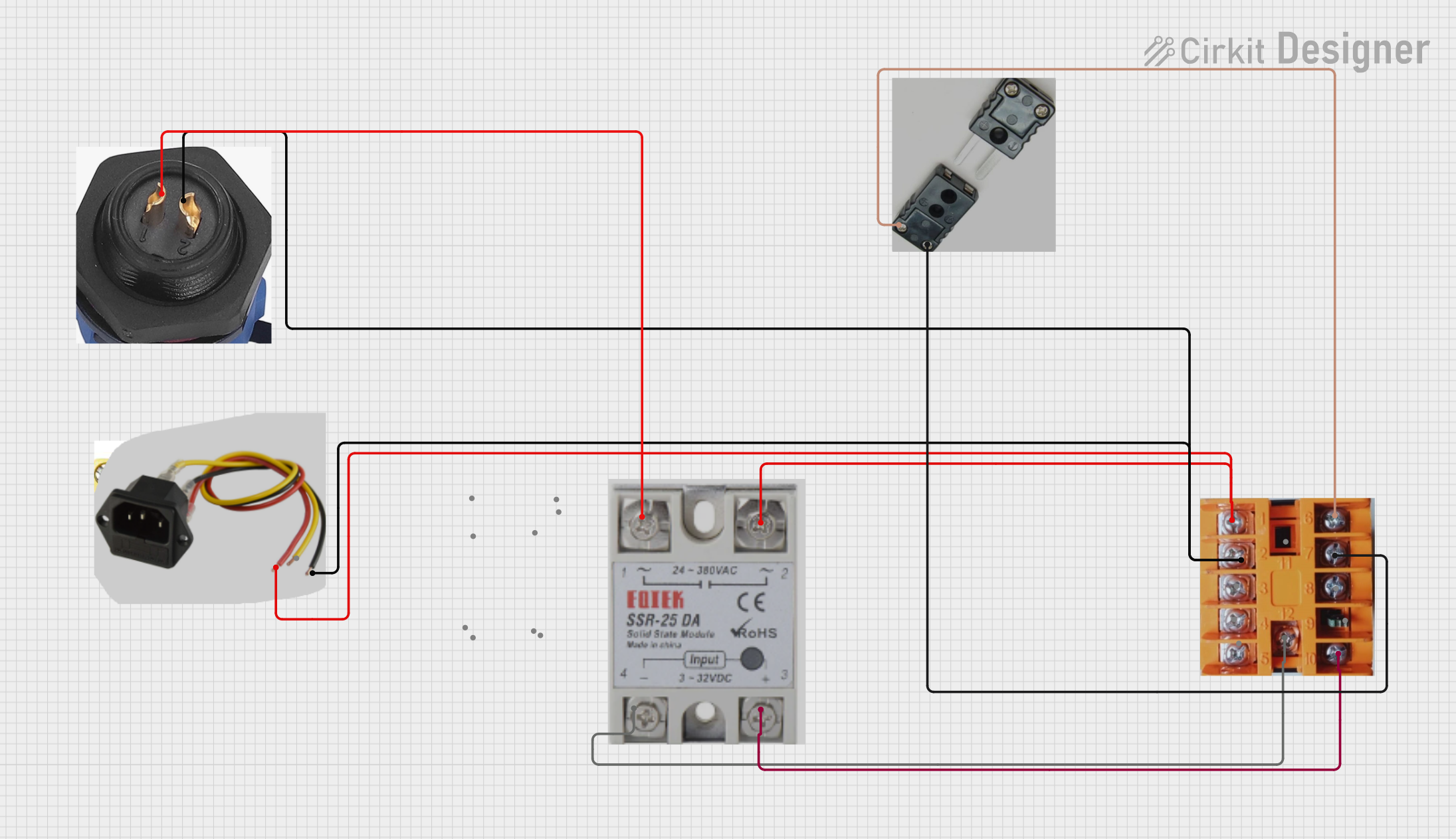
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer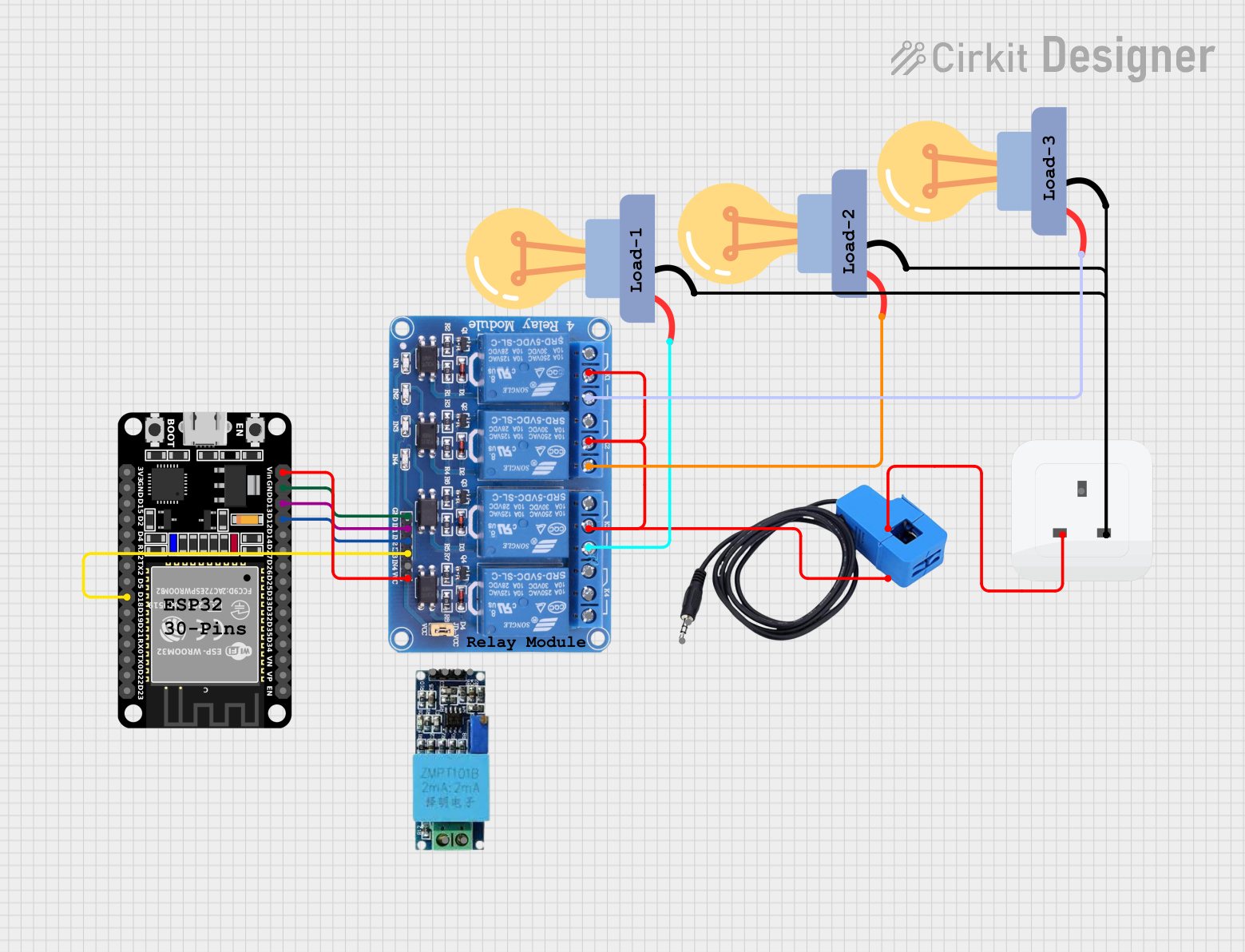
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SOCKET

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Integrated Circuit (IC) Mounting: Sockets are used to hold ICs, allowing for easy replacement or upgrades.
- Microcontroller Programming: Sockets provide a reliable connection for programming microcontrollers.
- Power Distribution: Power sockets are used to connect devices to power sources.
- Prototyping: Sockets allow for quick assembly and disassembly of circuits during development.
Technical Specifications
Sockets come in various types and sizes, depending on their intended use. Below are the general technical specifications for common socket types:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 5V to 250V (varies by type) |
| Current Rating | 1A to 15A (varies by type) |
| Material | Plastic (insulator), metal (conductors) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
| Contact Resistance | < 20 mΩ |
| Durability | 500 to 10,000 insertion cycles |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration of a socket depends on its type. Below is an example for a DIP (Dual Inline Package) IC Socket:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 to N | IC pin connections (N = total pins) |
| - | No additional pins; all are IC-specific |
For power sockets, the pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Connects to the live wire |
| Neutral (N) | Connects to the neutral wire |
| Ground (G) | Connects to the ground wire |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Select the Appropriate Socket: Choose a socket that matches the pin configuration and size of the component you intend to connect.
- Insert the Socket into the PCB: Place the socket into the designated holes on the printed circuit board (PCB) and solder it in place.
- Insert the Component: Carefully align the pins of the component with the socket and press it in gently.
- Connect External Wires (if applicable): For power sockets, connect the live, neutral, and ground wires to the corresponding terminals.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure Compatibility: Verify that the socket's voltage and current ratings match the requirements of your circuit.
- Avoid Overheating: When soldering the socket to a PCB, avoid excessive heat to prevent damage to the plastic housing.
- Check Pin Alignment: Ensure that the pins of the component align correctly with the socket to avoid short circuits or damage.
- Use Proper Tools: Use a socket insertion/extraction tool for ICs to prevent bending or breaking pins.
Example: Using a DIP Socket with an Arduino UNO
DIP sockets are often used to mount ICs like the ATmega328P microcontroller in Arduino UNO boards. Below is an example of how to connect an external DIP socket to an Arduino UNO for prototyping:
// Example: Blinking an LED using an ATmega328P in a DIP socket
// Ensure the ATmega328P is programmed with the Arduino bootloader
int ledPin = 13; // Pin 13 is connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Loose Connections: The component may not make proper contact with the socket.
- Solution: Ensure the component is fully inserted and the socket pins are clean.
- Bent or Broken Pins: Pins may bend or break during insertion.
- Solution: Use a pin straightener or replace the damaged component.
- Overheating During Soldering: Excessive heat can deform the socket.
- Solution: Use a temperature-controlled soldering iron and work quickly.
- Incorrect Pin Alignment: Misaligned pins can cause short circuits or damage.
- Solution: Double-check the pin alignment before inserting the component.
FAQs
Q: Can I reuse a socket after desoldering it from a PCB?
A: Yes, but inspect the socket for damage or wear before reusing it.
Q: How do I clean a socket?
A: Use compressed air or a small brush to remove dust and debris. For stubborn dirt, use isopropyl alcohol and a cotton swab.
Q: Are sockets suitable for high-frequency applications?
A: Some sockets may introduce parasitic capacitance or resistance, which can affect high-frequency signals. Use low-profile or specialized sockets for such applications.
Q: Can I use a socket for power connections?
A: Yes, but ensure the socket's current and voltage ratings are sufficient for the application.