
How to Use ESC BLDC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
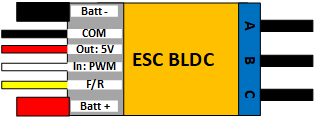
 Design with ESC BLDC in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESC BLDC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) for Brushless DC (BLDC) motors is a critical component in modern motor control systems. It regulates the motor's speed, direction, and start/stop functions by varying the voltage and current supplied to the motor. ESCs are widely used in applications requiring precise motor control, such as drones, electric vehicles, robotics, and RC (radio-controlled) devices.
Explore Projects Built with ESC BLDC
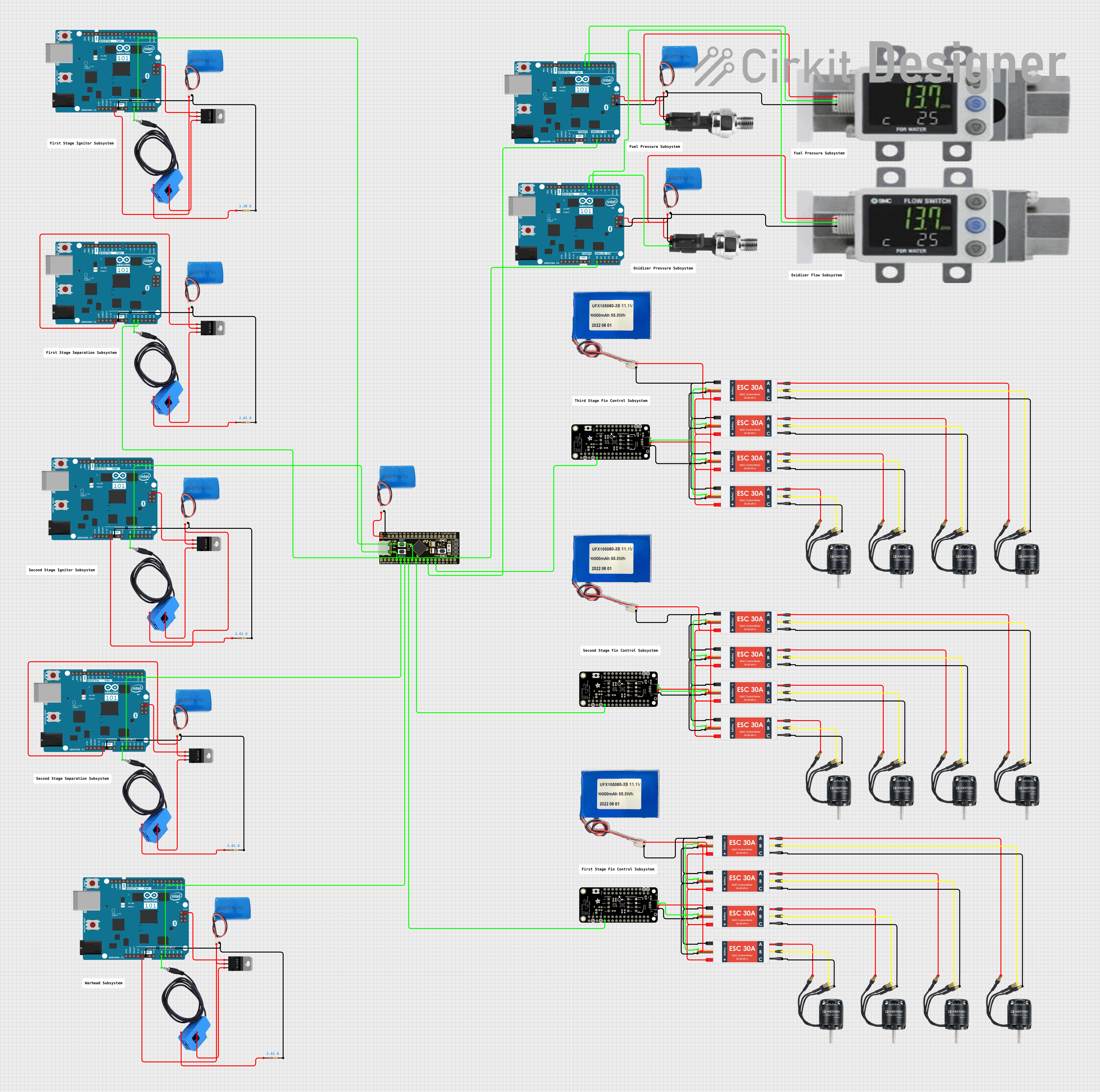
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer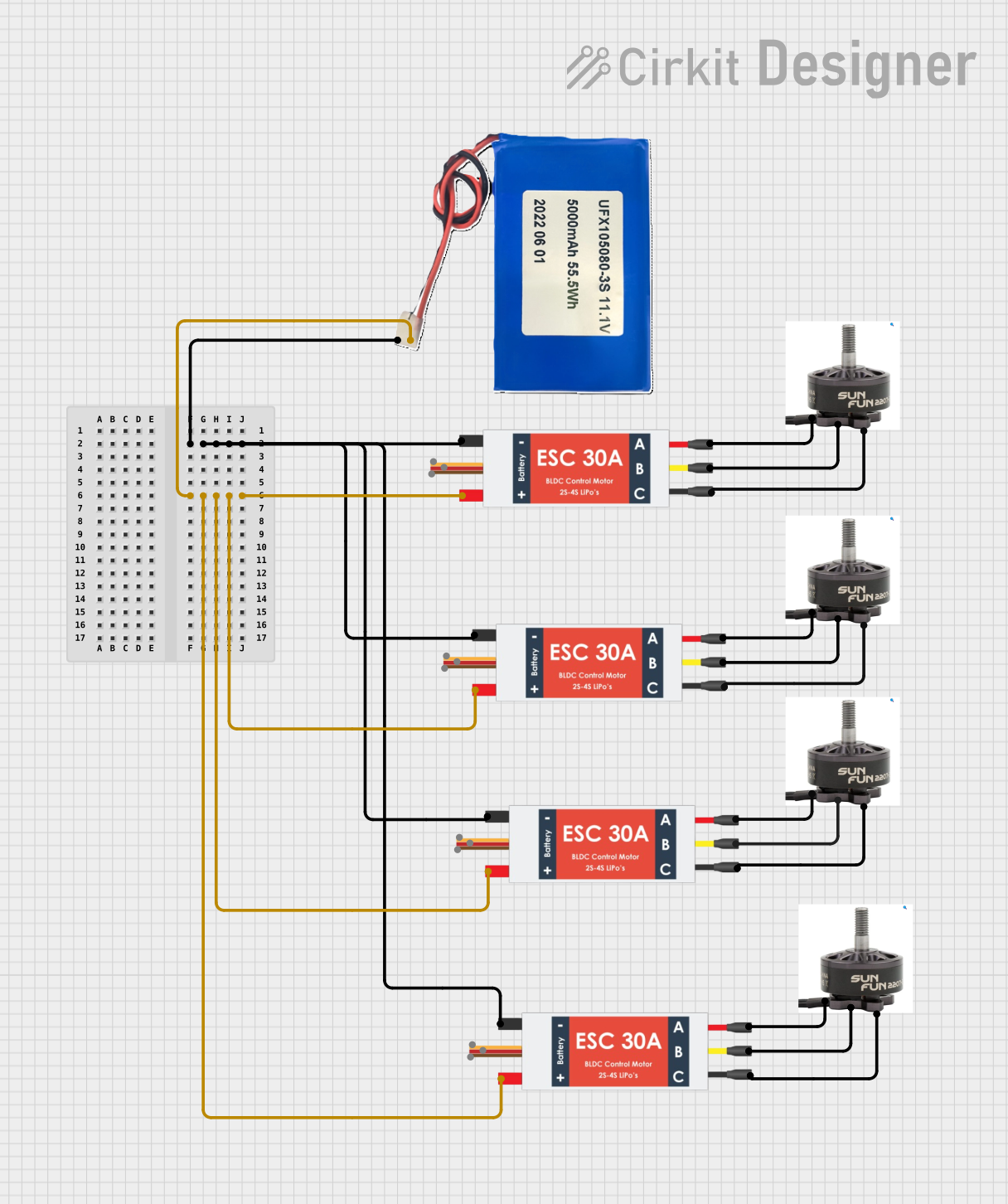
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer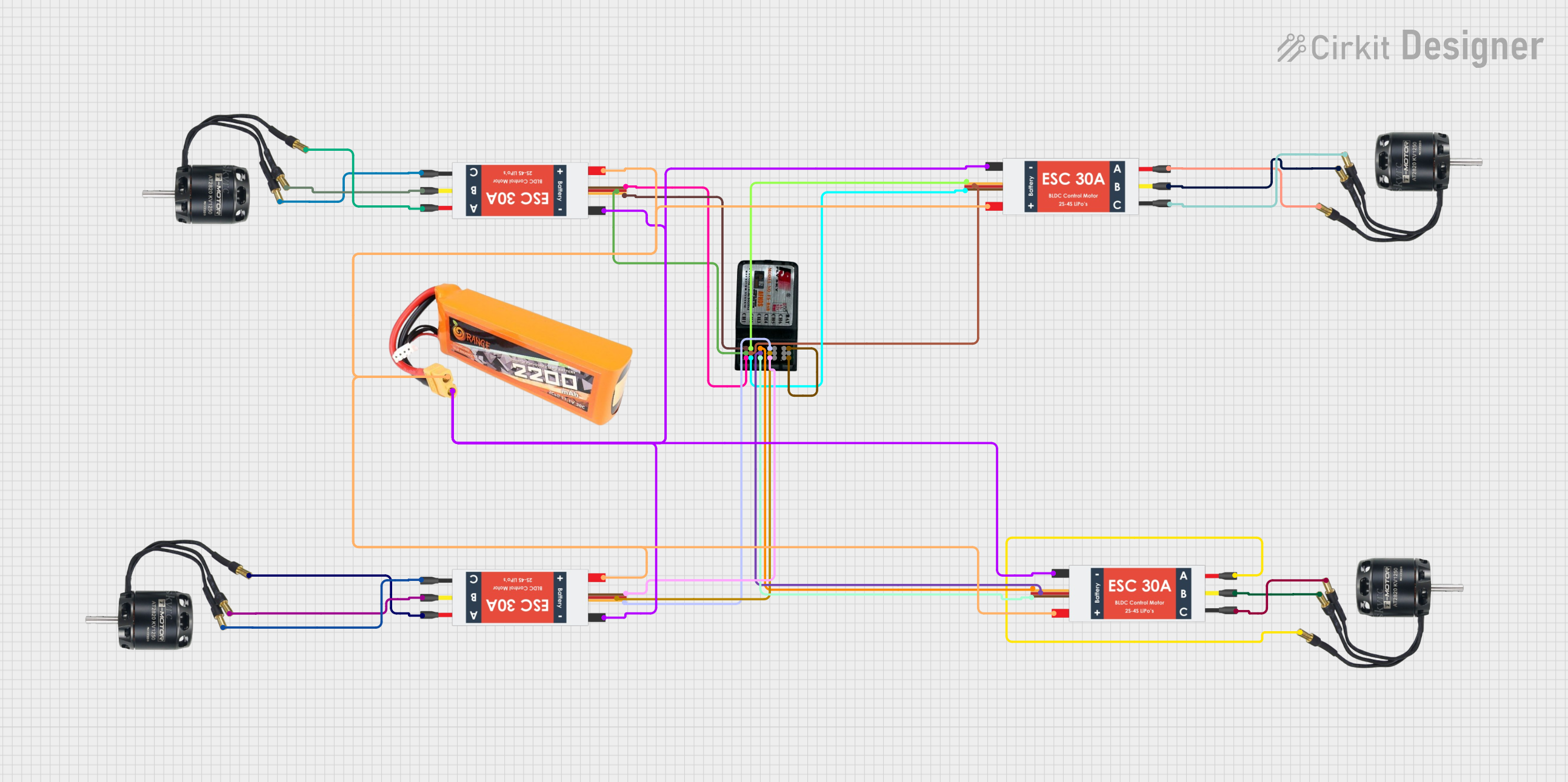
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer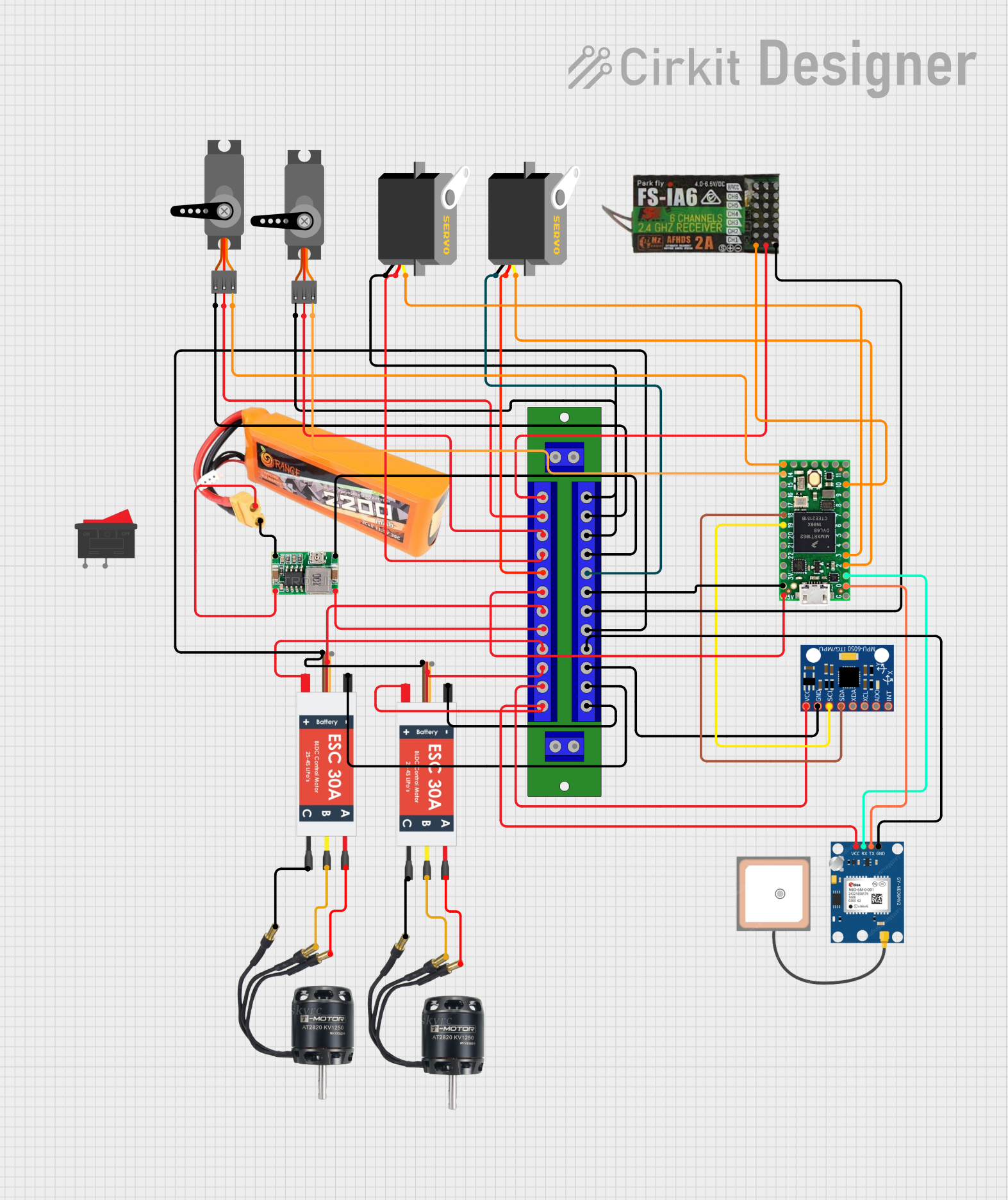
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESC BLDC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Drones and UAVs: For controlling the speed of propeller motors.
- Electric Vehicles: To manage motor speed and torque.
- Robotics: For precise movement and control of robotic arms or wheels.
- RC Devices: In cars, boats, and planes for speed and direction control.
- Industrial Automation: For conveyor belts and other motorized systems.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical ESC designed for BLDC motors:
General Specifications
- Input Voltage Range: 6V to 24V (depending on the model)
- Continuous Current Rating: 20A to 60A (varies by model)
- Peak Current Rating: Up to 100A (for short durations)
- Supported Motor Types: 3-phase Brushless DC (BLDC) motors
- Control Signal Input: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, typically 1ms to 2ms pulse width
- BEC (Battery Eliminator Circuit): 5V or 6V output for powering external devices (optional, depending on model)
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 60°C
- Weight: 20g to 50g (varies by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESC typically has three main connection groups: motor output, power input, and control signal input. Below is a table describing the pin configuration:
| Pin/Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| Motor Phase A | Connects to one of the three motor windings (phase A). |
| Motor Phase B | Connects to one of the three motor windings (phase B). |
| Motor Phase C | Connects to one of the three motor windings (phase C). |
| Power Input (+) | Positive terminal for the power supply (battery). |
| Power Input (-) | Negative terminal for the power supply (battery). |
| Signal Input | Receives the PWM signal from the microcontroller or receiver. |
| Ground (GND) | Ground connection for the control signal (shared with the power supply ground). |
| BEC Output (optional) | Provides regulated 5V or 6V power for external devices like microcontrollers. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESC in a Circuit
- Connect the Motor: Attach the three motor phase wires (A, B, C) to the corresponding ESC motor output terminals. The order of connection determines the motor's rotation direction, which can be adjusted later if needed.
- Connect the Power Supply: Connect the positive and negative terminals of the battery to the ESC's power input terminals. Ensure the voltage and current ratings of the battery match the ESC's specifications.
- Connect the Control Signal: Use a PWM-capable microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) or an RC receiver to send control signals to the ESC's signal input pin. Connect the ground pin of the ESC to the ground of the microcontroller or receiver.
- Calibrate the ESC: Many ESCs require calibration to match the PWM signal range. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for calibration.
- Test the Setup: Gradually increase the PWM signal to test the motor's response. Ensure the motor spins smoothly without unusual noise or vibration.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Use a battery or power source that matches the ESC's voltage and current requirements. Overloading the ESC can cause overheating or damage.
- Cooling: Ensure proper ventilation or cooling for the ESC, especially in high-current applications.
- Signal Range: Verify the PWM signal range (e.g., 1ms for minimum throttle, 2ms for maximum throttle) and configure your microcontroller accordingly.
- Reverse Polarity Protection: Check if the ESC has built-in reverse polarity protection. If not, double-check connections to avoid damage.
- Motor Compatibility: Ensure the motor is a 3-phase BLDC motor compatible with the ESC.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control an ESC using an Arduino UNO:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library to generate PWM signals
Servo esc; // Create a Servo object to control the ESC
void setup() {
esc.attach(9); // Attach the ESC signal wire to pin 9 on the Arduino
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Send minimum throttle (1ms pulse width)
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds to allow the ESC to initialize
}
void loop() {
esc.writeMicroseconds(1500); // Set throttle to mid-range (1.5ms pulse width)
delay(5000); // Run the motor at this speed for 5 seconds
esc.writeMicroseconds(2000); // Set throttle to maximum (2ms pulse width)
delay(5000); // Run the motor at this speed for 5 seconds
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Set throttle to minimum (1ms pulse width)
delay(5000); // Stop the motor for 5 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Does Not Spin:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or no PWM signal.
- Solution: Verify motor and power connections. Ensure the microcontroller is sending a valid PWM signal.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction:
- Cause: Incorrect motor phase wiring.
- Solution: Swap any two of the three motor phase wires to reverse the direction.
ESC Overheats:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Use a higher-rated ESC or improve cooling with a heat sink or fan.
ESC Does Not Initialize:
- Cause: Incorrect PWM signal range or calibration issue.
- Solution: Calibrate the ESC according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure the PWM signal is within the expected range.
Motor Stutters or Vibrates:
- Cause: Poor connections or incompatible motor.
- Solution: Check all connections and ensure the motor is compatible with the ESC.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an ESC with a brushed DC motor?
A: No, ESCs for BLDC motors are specifically designed for 3-phase brushless motors. Use a brushed motor controller instead.Q: How do I know if my ESC has a BEC?
A: Check the ESC's specifications or look for a dedicated output labeled "BEC" or "5V/6V."Q: Can I control multiple ESCs with one Arduino?
A: Yes, you can control multiple ESCs by connecting their signal wires to different PWM-capable pins on the Arduino.Q: What happens if I exceed the ESC's current rating?
A: Exceeding the current rating can cause the ESC to overheat, shut down, or fail permanently. Always use an ESC with a sufficient current margin for your application.