
How to Use DIP Switch (2 Position): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with DIP Switch (2 Position) in Cirkit Designer
Design with DIP Switch (2 Position) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A DIP (Dual Inline Package) switch is a manual electrical switch packaged in a standard dual in-line configuration. The 2-position DIP switch allows for a simple on-off configuration in digital circuits, providing a convenient way to set or change options. These switches are often used for setting device addresses, configuration settings for computer peripherals, or as general-purpose input selectors in various electronic projects.
Explore Projects Built with DIP Switch (2 Position)
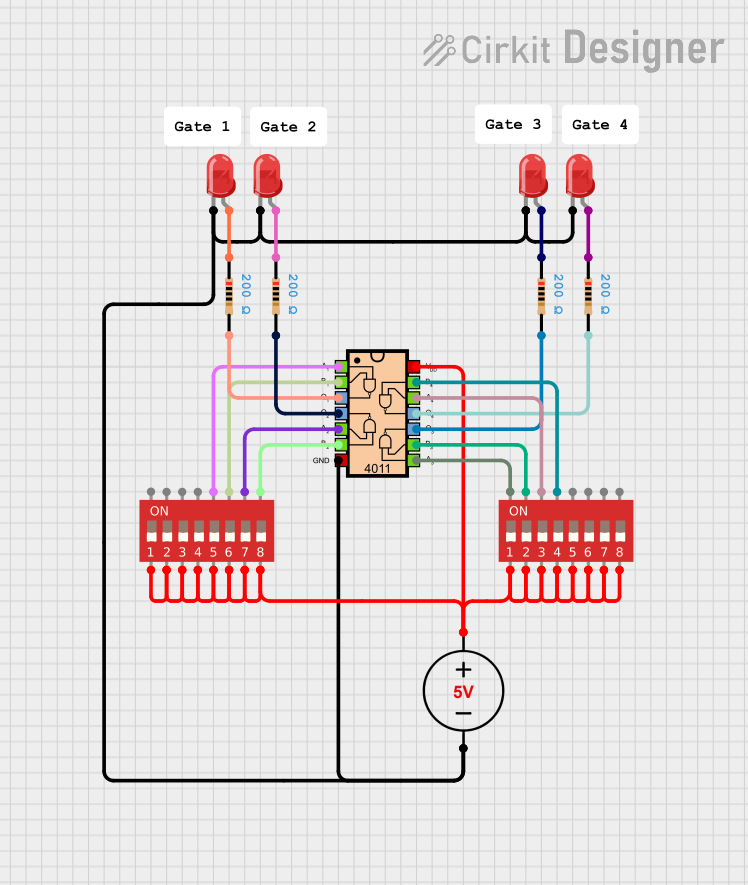
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer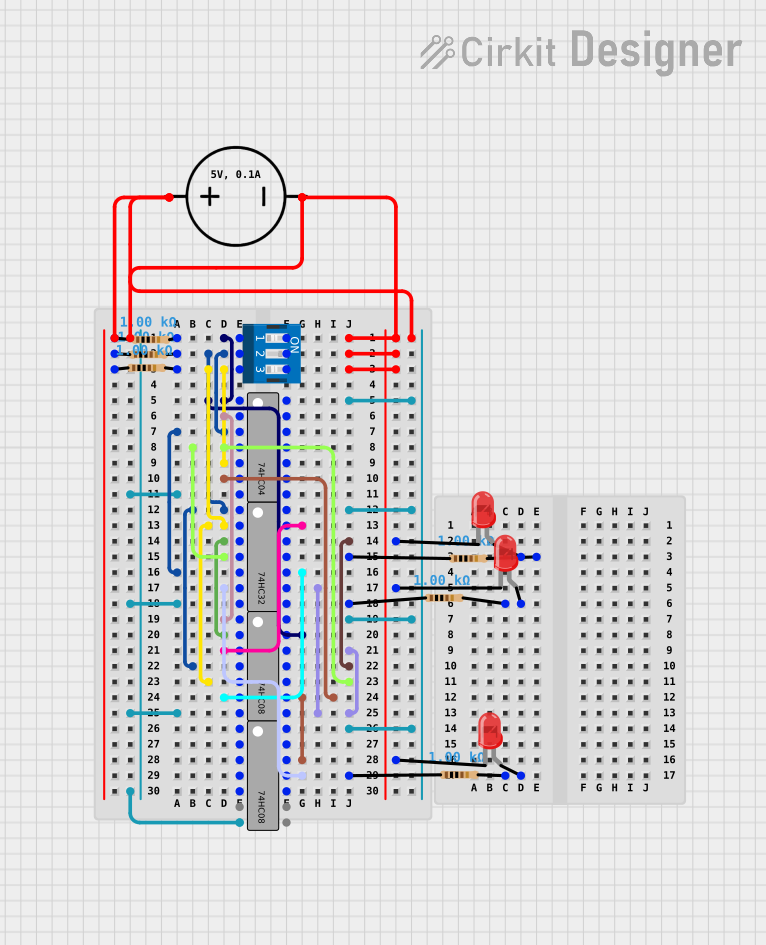
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer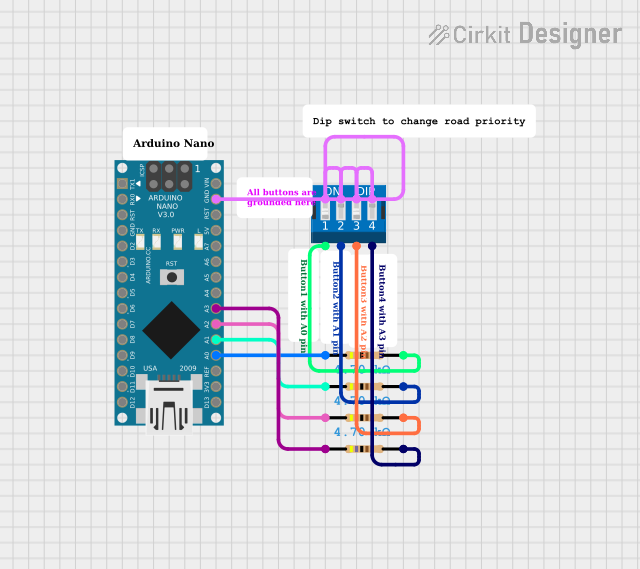
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DIP Switch (2 Position)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Device address setting for networked devices
- Configuration settings for computer peripherals
- Input selectors for electronic circuits
- Function mode selectors in consumer electronics
- Prototype and development boards for testing purposes
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Rating: Typically 5V to 24V
- Current Rating: Often rated at 25mA to 100mA
- Contact Resistance: Usually less than 50 milliohms
- Insulation Resistance: Typically greater than 1000 megohms
- Dielectric Strength: Commonly 500VAC for 1 minute
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Common terminal 1 |
| 2 | Switch 1 output |
| 3 | Common terminal 2 |
| 4 | Switch 2 output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Powering the Switch: Connect the common terminals (pins 1 and 3) to the power supply (e.g., VCC) or ground, depending on the logic level desired when the switch is in the ON position.
- Output Connection: Connect the output pins (2 and 4) to the input pins of the device you wish to control or configure with the DIP switch.
- Setting the Switch: Use a small tool like a screwdriver to set the switch positions to ON or OFF as required for your application.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: Although DIP switches do not typically bounce like push buttons, it is good practice to consider debouncing in software if the switch state is read frequently.
- Mounting: Ensure the DIP switch is properly seated on the PCB with all pins soldered to prevent intermittent connections.
- Switch Handling: Use appropriate force when changing switch positions to avoid damaging the switch mechanism.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Intermittent Connections: This can be due to poor soldering or debris in the switch. Check solder joints and clean the switch if necessary.
- Incorrect Logic Levels: Ensure that the common terminals are connected to the correct power supply level for your logic circuit.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Continuity: Use a multimeter to check for continuity between the common terminal and the output when the switch is in the ON position.
- Visual Inspection: Look for any signs of damage or improper soldering on the DIP switch and surrounding PCB area.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a DIP switch with higher voltage ratings in a 5V circuit? A: Yes, DIP switches with higher voltage ratings can be used safely in lower voltage applications.
Q: How do I know if the DIP switch is in the ON position? A: The ON position is typically when the switch actuator is pushed towards the numbered side of the switch body.
Q: Is it possible to change the position of a DIP switch while the power is on? A: Yes, but it is generally recommended to power down the system before changing switch positions to avoid potential issues.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the DIP switch pins
const int dipSwitch1 = 2; // Connect to pin 2 of the Arduino
const int dipSwitch2 = 3; // Connect to pin 3 of the Arduino
void setup() {
// Set the DIP switch pins as input
pinMode(dipSwitch1, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(dipSwitch2, INPUT_PULLUP);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the state of the DIP switches
bool switchState1 = digitalRead(dipSwitch1);
bool switchState2 = digitalRead(dipSwitch2);
// Print the state of the switches to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Switch 1 is ");
Serial.print(switchState1 ? "ON" : "OFF");
Serial.print(", Switch 2 is ");
Serial.println(switchState2 ? "ON" : "OFF");
// Add a delay to reduce the frequency of Serial prints
delay(500);
}
Note: The INPUT_PULLUP mode is used to enable the internal pull-up resistors. When the switch is in the OFF position, the pin is pulled high. When the switch is ON, the pin is connected to ground and reads low.