
How to Use SD CARD MODULE: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
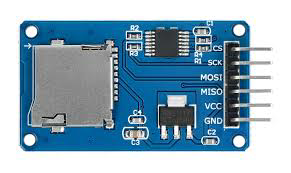
 Design with SD CARD MODULE in Cirkit Designer
Design with SD CARD MODULE in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SD Card Module is a versatile component used to interface with SD cards, enabling data storage and retrieval in various electronic projects. This module is particularly useful in applications where large amounts of data need to be logged, such as in data logging systems, multimedia projects, and portable devices. It is commonly used with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO to expand their storage capabilities.
Explore Projects Built with SD CARD MODULE
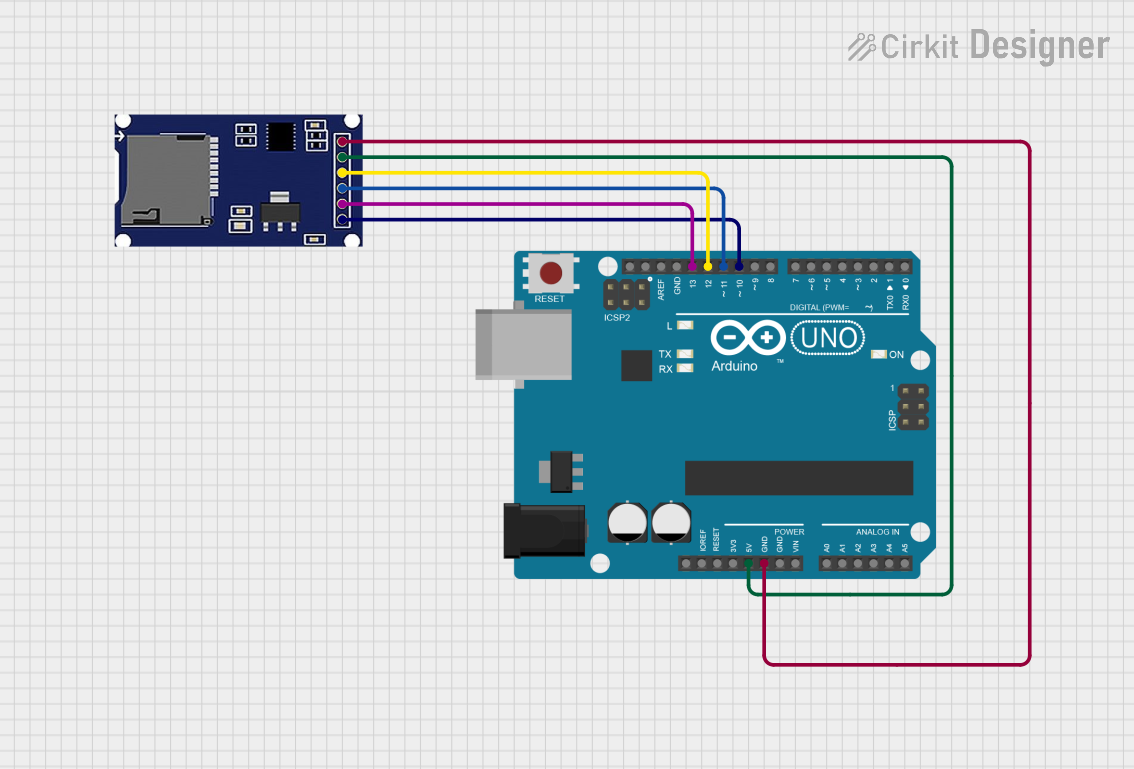
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer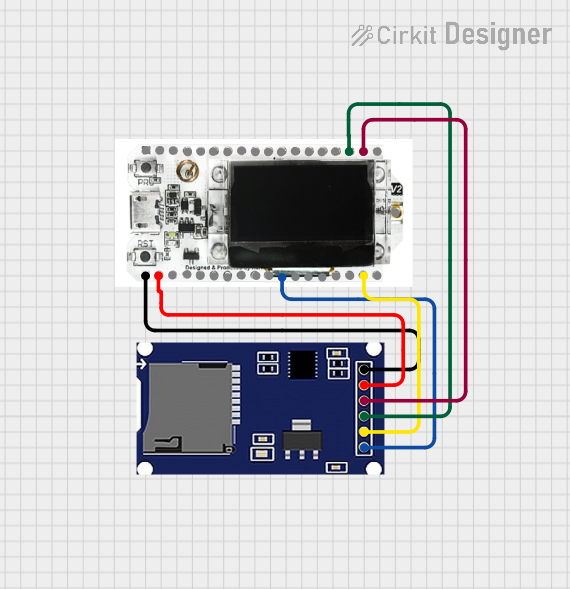
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer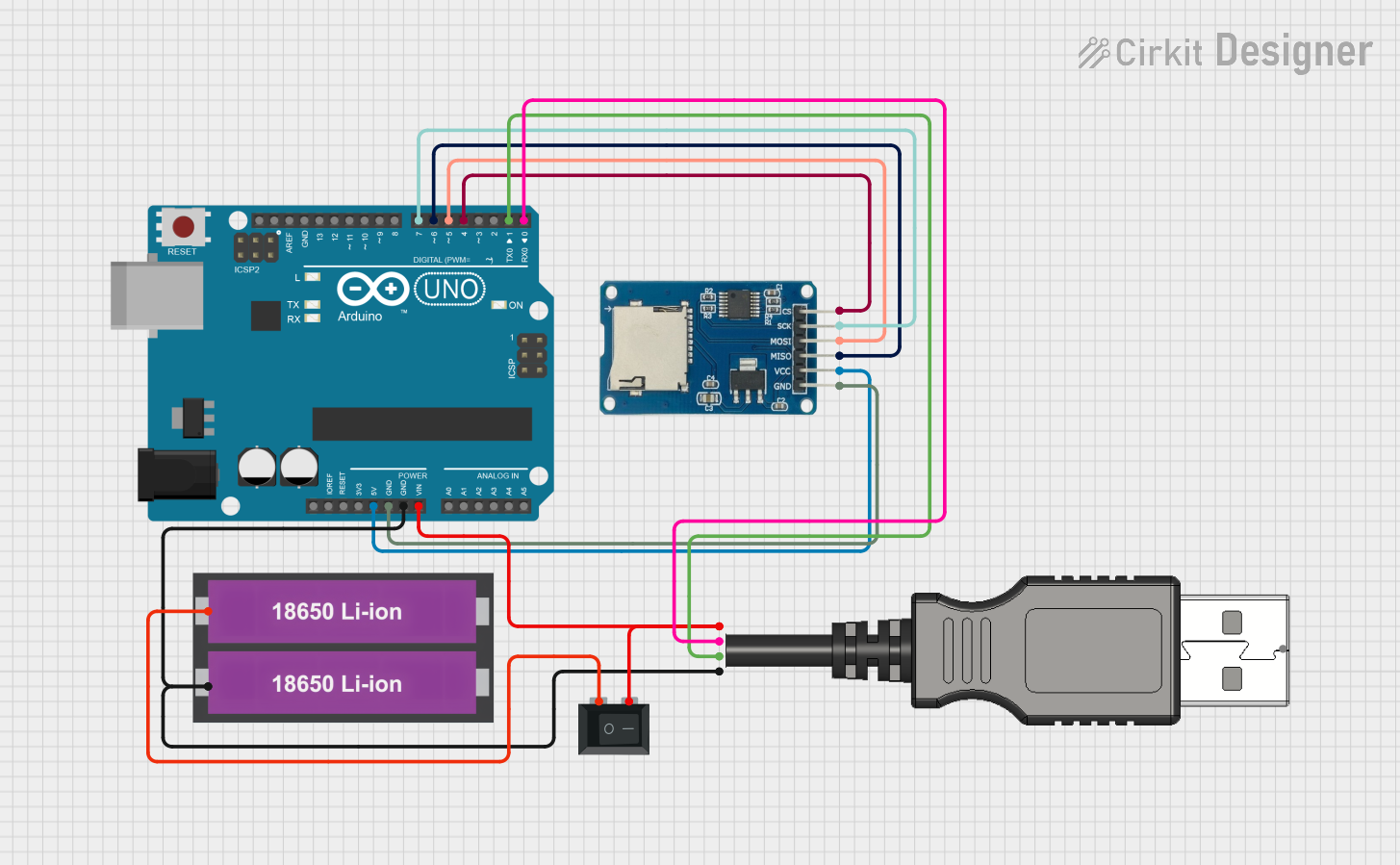
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SD CARD MODULE

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Interface | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) |
| Supported Cards | SD, SDHC |
| Storage Capacity | Up to 32GB (depending on the card) |
| Current Consumption | 100mA (typical) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | VCC | Power Supply (3.3V - 5V) |
| 3 | MISO | Master In Slave Out (SPI Data Output) |
| 4 | MOSI | Master Out Slave In (SPI Data Input) |
| 5 | SCK | Serial Clock (SPI Clock) |
| 6 | CS | Chip Select (SPI Enable) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Wiring the SD Card Module to Arduino UNO:
- Connect the
GNDpin of the SD Card Module to theGNDpin on the Arduino. - Connect the
VCCpin of the SD Card Module to the5Vpin on the Arduino. - Connect the
MISOpin of the SD Card Module to the12pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
MOSIpin of the SD Card Module to the11pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
SCKpin of the SD Card Module to the13pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
CSpin of the SD Card Module to the10pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the
Arduino Code Example:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the SD card
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("Initialization failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("Initialization done.");
// Open a file for writing
File dataFile = SD.open("datalog.txt", FILE_WRITE);
if (dataFile) {
dataFile.println("Hello, SD card!");
dataFile.close();
Serial.println("Data written to file.");
} else {
Serial.println("Error opening file.");
}
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the module is powered with a stable voltage between 3.3V and 5V.
- Card Formatting: Format the SD card to FAT16 or FAT32 before use.
- File Handling: Always close files after reading or writing to prevent data corruption.
- SPI Speed: Adjust the SPI speed if you encounter communication issues.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Initialization Failed:
- Solution: Check the wiring connections and ensure the SD card is properly inserted. Verify that the SD card is formatted correctly.
Error Opening File:
- Solution: Ensure the file name is valid and the SD card is not write-protected. Check if the SD card has sufficient free space.
Data Corruption:
- Solution: Always close files after operations. Avoid removing the SD card while the module is powered.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correctly mapped.
- Use Quality SD Cards: Use high-quality SD cards from reputable brands to avoid compatibility issues.
- Monitor Power Supply: Ensure the power supply is stable and within the specified range.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the SD Card Module into their projects, enabling reliable data storage and retrieval. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this guide provides the necessary information to get started and troubleshoot common issues.