
How to Use Analog Joystick: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Analog Joystick in Cirkit Designer
Design with Analog Joystick in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Analog Joystick is an input device that allows for two-dimensional control by detecting the position of a stick that pivots on a base. It is commonly used in gaming controllers, robotics, and other applications requiring precise navigation or control. The joystick typically provides two analog outputs corresponding to the X and Y axes, and often includes a push-button feature for additional functionality.
Explore Projects Built with Analog Joystick
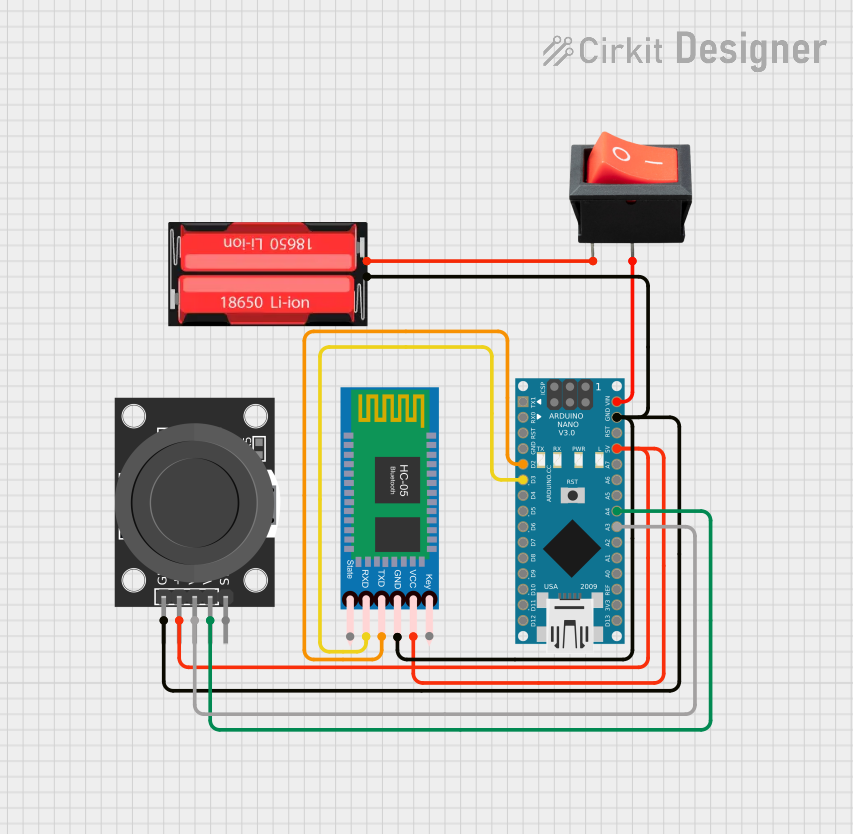
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer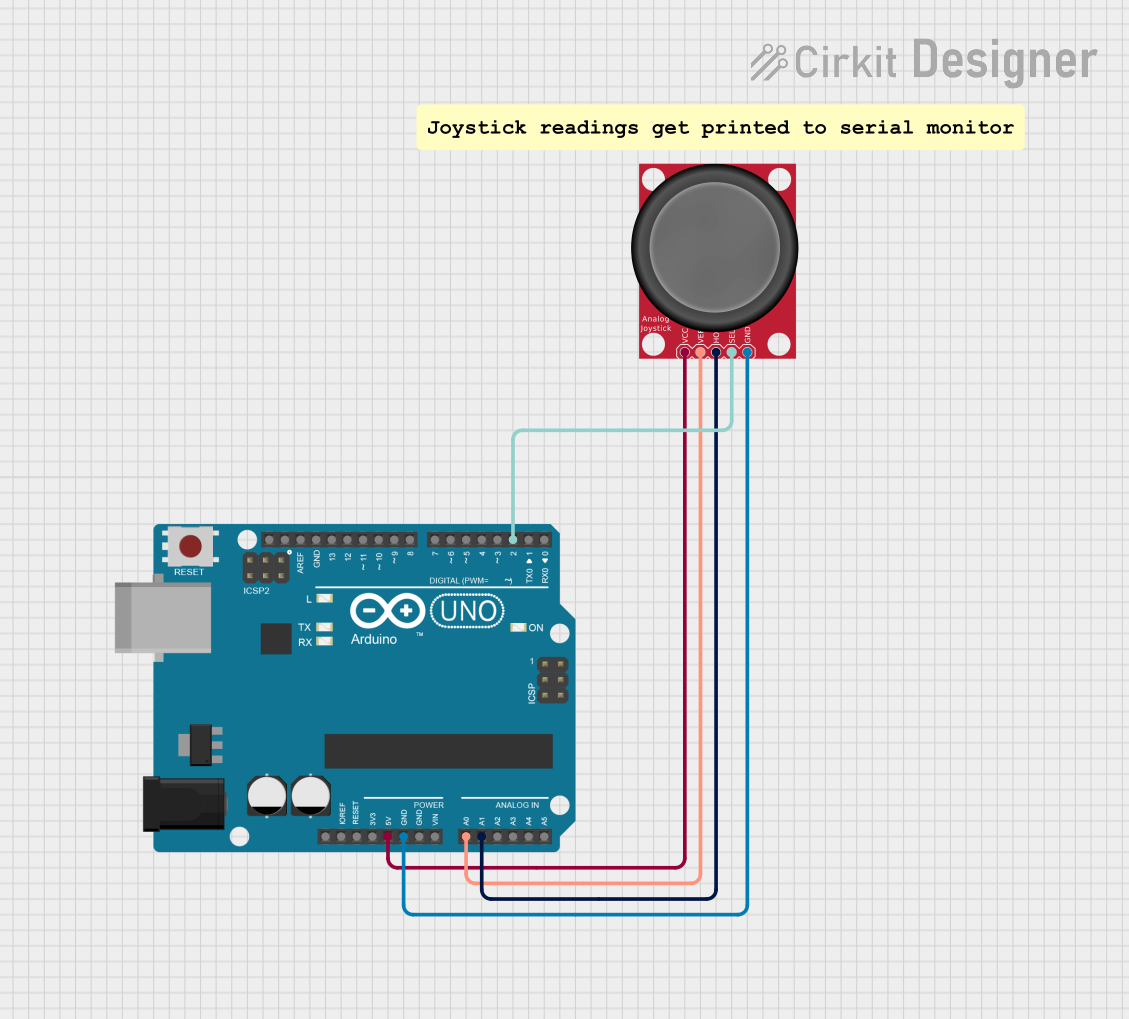
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer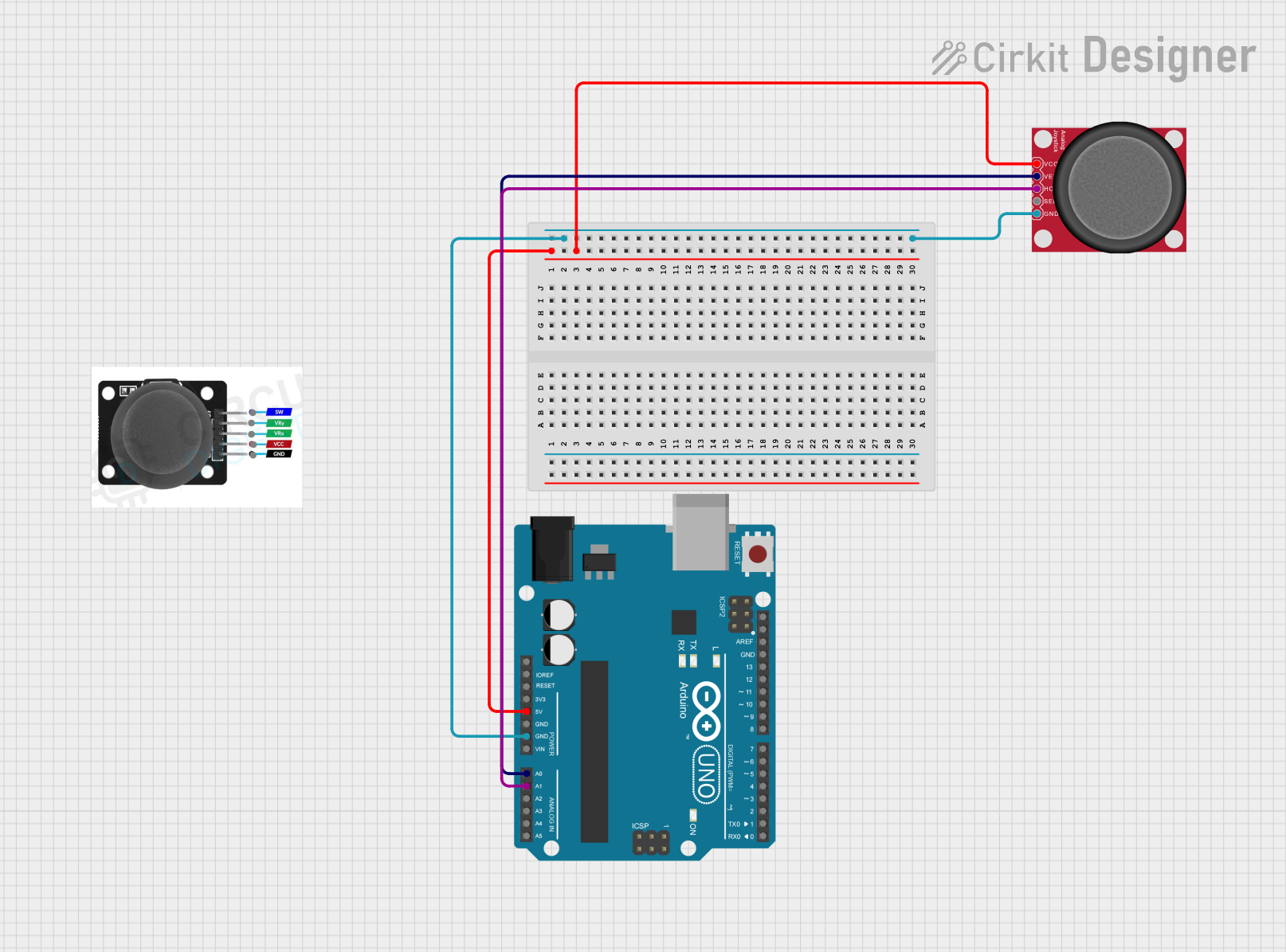
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer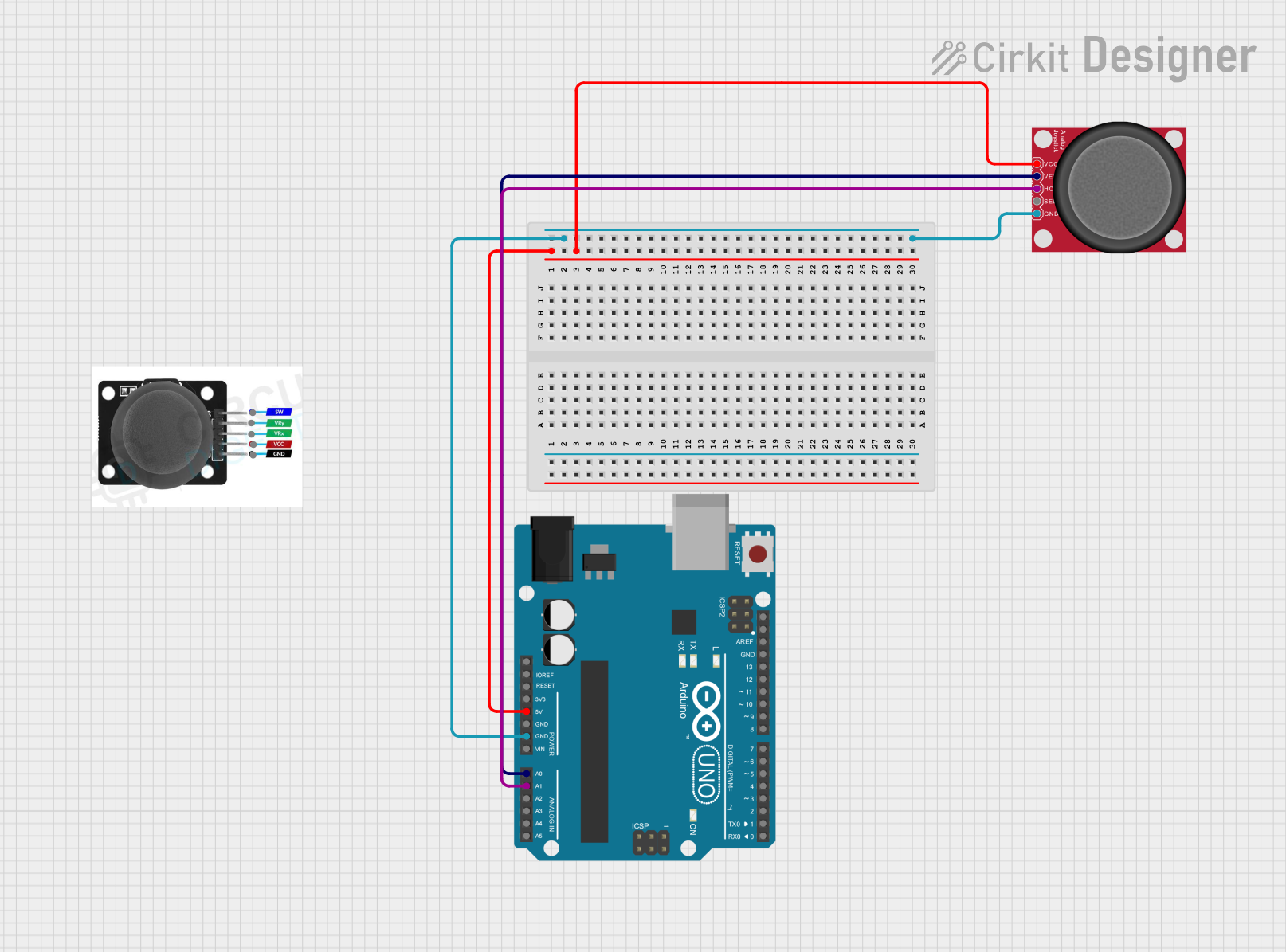
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Analog Joystick

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Gaming controllers for directional input
- Robotic navigation and control
- Camera gimbal control
- Remote-controlled vehicles and drones
- User interface navigation in embedded systems
Technical Specifications
The Analog Joystick is a simple yet versatile component. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Output Type | Analog (X and Y axes), Digital (button) |
| X-Axis Output Range | 0V to Vcc (centered at ~Vcc/2) |
| Y-Axis Output Range | 0V to Vcc (centered at ~Vcc/2) |
| Button Output | Digital (active low) |
| Dimensions | ~34mm x 34mm x 32mm |
Pin Configuration
The Analog Joystick typically has 5 pins. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| 3 | VRx | Analog output for X-axis position |
| 4 | VRy | Analog output for Y-axis position |
| 5 | SW | Digital output for the push-button (active low) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the Joystick
- Power Supply: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to ground. - Analog Outputs: Connect the
VRxandVRypins to the analog input pins of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino). - Button Output: Connect the
SWpin to a digital input pin of your microcontroller. Use a pull-up resistor if necessary.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the Analog Joystick to an Arduino UNO:
VCC→ 5VGND→ GNDVRx→ A0VRy→ A1SW→ D2
Sample Arduino Code
The following code reads the X and Y positions of the joystick and detects button presses:
// Define pin connections
const int VRxPin = A0; // X-axis analog pin
const int VRyPin = A1; // Y-axis analog pin
const int SWPin = 2; // Button digital pin
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
// Configure the button pin as input with pull-up resistor
pinMode(SWPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
// Read the X and Y axis values
int xValue = analogRead(VRxPin);
int yValue = analogRead(VRyPin);
// Read the button state (active low)
bool buttonPressed = (digitalRead(SWPin) == LOW);
// Print the joystick values to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(xValue);
Serial.print(" | Y: ");
Serial.print(yValue);
Serial.print(" | Button: ");
Serial.println(buttonPressed ? "Pressed" : "Released");
// Add a small delay for stability
delay(100);
}
Important Considerations
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the joystick's operating voltage matches your microcontroller's input voltage (e.g., 3.3V or 5V).
- Center Calibration: The joystick's center position typically outputs a voltage of approximately Vcc/2. Use this as a reference for neutral positioning.
- Debouncing: If the button is used, consider implementing software debouncing to avoid false triggers.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Output or Incorrect Readings
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, ensuring proper pin mapping and secure connections.
Button Not Responding
- Cause: Missing pull-up resistor or incorrect pin configuration.
- Solution: Use the
INPUT_PULLUPmode in your microcontroller or add an external pull-up resistor.
Inconsistent Axis Readings
- Cause: Electrical noise or faulty joystick.
- Solution: Add capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) between the analog output pins and ground to filter noise.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the joystick with a 3.3V microcontroller like ESP32?
A: Yes, the joystick operates at 3.3V and 5V. Ensure the VCC pin is connected to 3.3V for compatibility.
Q: How do I detect diagonal movement?
A: Diagonal movement occurs when both X and Y axis values deviate significantly from their center positions. You can write logic to detect this condition.
Q: Can I use the joystick for PWM motor control?
A: Yes, you can map the joystick's analog output values to PWM signals for motor speed and direction control.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Analog Joystick into your projects for precise and intuitive control.