
How to Use MCP41010: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with MCP41010 in Cirkit Designer
Design with MCP41010 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MCP41010 is a single-channel digital potentiometer with a 256-position wiper, offering precise resistance adjustments in electronic circuits. It features an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) for digital control, making it ideal for applications requiring variable resistance without mechanical potentiometers. The MCP41010 is commonly used in audio equipment, sensor calibration, programmable gain amplifiers, and other circuits where fine-tuned resistance is essential.
Explore Projects Built with MCP41010
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MCP41010

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Audio volume control
- Sensor calibration and trimming
- Programmable gain amplifiers
- Adjustable voltage dividers
- LED dimming and brightness control
- Resistance-based signal conditioning
Technical Specifications
The MCP41010 is designed for ease of use and integration into a variety of circuits. Below are its key technical details:
Key Features
- Resistance Range: 10 kΩ (nominal)
- Resolution: 256 steps (8-bit)
- Interface: SPI (up to 10 MHz clock speed)
- Supply Voltage: 2.7V to 5.5V
- Wiper Current: ±1 mA (maximum)
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
- Package Types: PDIP, SOIC, TSSOP
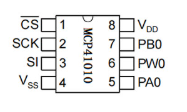
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MCP41010 has an 8-pin configuration. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CS | Chip Select (Active Low). Enables communication with the device. |
| 2 | SCK | Serial Clock Input. Used to synchronize data transfer over SPI. |
| 3 | SI | Serial Data Input. Receives data from the microcontroller. |
| 4 | VSS | Ground. Connect to the system ground. |
| 5 | PW0 | Terminal 0 of the potentiometer. Connect to one end of the resistive track. |
| 6 | PW1 | Terminal 1 of the potentiometer. Connect to the other end of the track. |
| 7 | VW | Wiper Terminal. Provides the adjustable resistance output. |
| 8 | VDD | Positive Supply Voltage. Connect to 2.7V to 5.5V. |
Usage Instructions
The MCP41010 is controlled via SPI, allowing for precise adjustment of the wiper position. Below are the steps to use the component in a circuit:
Basic Circuit Setup
- Power Supply: Connect
VDDto a 3.3V or 5V power source andVSSto ground. - SPI Connections:
- Connect
CSto a GPIO pin on the microcontroller (active low). - Connect
SCKto the SPI clock pin. - Connect
SIto the SPI data output pin (MOSI) of the microcontroller.
- Connect
- Potentiometer Terminals:
- Connect
PW0andPW1to the desired circuit points (e.g., voltage divider). - Use
VWas the adjustable output terminal.
- Connect
SPI Communication
To set the wiper position, send an 8-bit command followed by an 8-bit data byte over SPI:
- Command Byte:
00010000(Write to potentiometer 0) - Data Byte: Wiper position (0 to 255)
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to control the MCP41010 using an Arduino UNO:
#include <SPI.h>
// Define MCP41010 pins
const int CS_PIN = 10; // Chip Select pin connected to Arduino pin 10
void setup() {
pinMode(CS_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set CS pin as output
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Set CS pin high (inactive)
SPI.begin(); // Initialize SPI communication
}
void loop() {
setPotentiometer(128); // Set wiper to mid-position (128 out of 255)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
setPotentiometer(64); // Set wiper to 1/4 position
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
// Function to set the wiper position
void setPotentiometer(byte value) {
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, LOW); // Activate the MCP41010
SPI.transfer(0x10); // Send command byte (write to potentiometer 0)
SPI.transfer(value); // Send data byte (wiper position)
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Deactivate the MCP41010
}
Important Considerations
- Ensure the SPI clock speed does not exceed 10 MHz.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum wiper current of ±1 mA to prevent damage.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) near the
VDDpin for stable operation. - The wiper position resets to 0 (minimum resistance) on power-up.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Response from MCP41010:
- Ensure the
CSpin is correctly toggled (active low during communication). - Verify SPI connections and ensure the clock speed is within the specified range.
- Ensure the
Incorrect Wiper Position:
- Check the data byte sent over SPI. Ensure it is within the range of 0 to 255.
- Verify the SPI mode is set to Mode 0 (CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0).
Overheating or Damage:
- Ensure the wiper current does not exceed ±1 mA.
- Verify the supply voltage is within the 2.7V to 5.5V range.
FAQs
Q: Can the MCP41010 be used with 3.3V systems?
A: Yes, the MCP41010 operates with supply voltages as low as 2.7V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
Q: What happens to the wiper position on power loss?
A: The wiper position resets to 0 (minimum resistance) when power is lost or the device is reset.
Q: Can I use multiple MCP41010 devices on the same SPI bus?
A: Yes, you can connect multiple devices by assigning each a unique CS pin.
Q: Is the MCP41010 suitable for high-power applications?
A: No, the MCP41010 is designed for low-power applications with a maximum wiper current of ±1 mA.