
How to Use Modbus 4CH I/O: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Modbus 4CH I/O in Cirkit Designer
Design with Modbus 4CH I/O in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Modbus 4CH I/O module (Manufacturer: Somewhere, Part ID: modbus) is a versatile 4-channel input/output device designed for seamless communication and control over a Modbus network. This module enables the integration of multiple sensors and actuators, making it ideal for industrial automation, home automation, and other applications requiring reliable and efficient data exchange.
Explore Projects Built with Modbus 4CH I/O
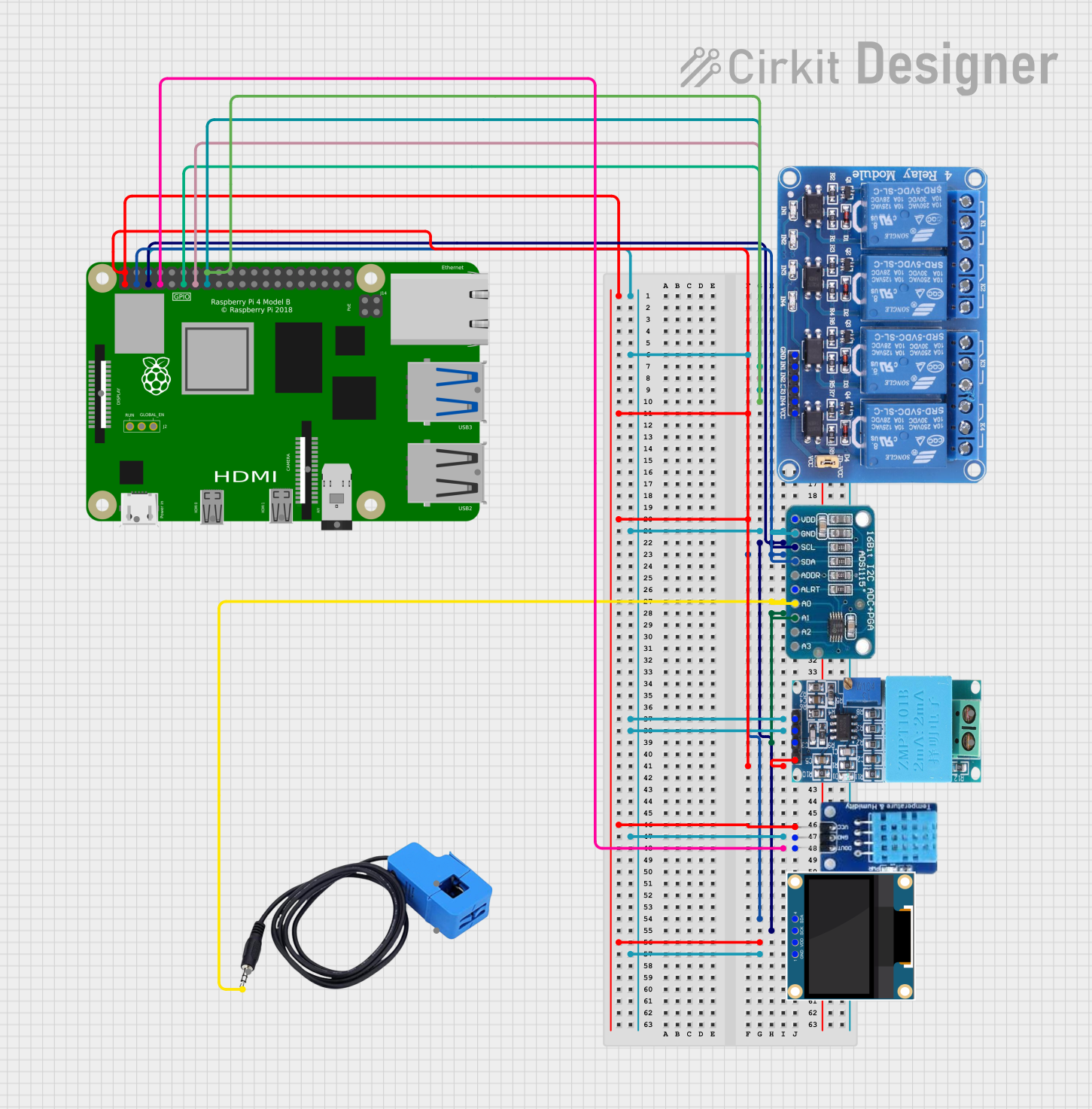
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer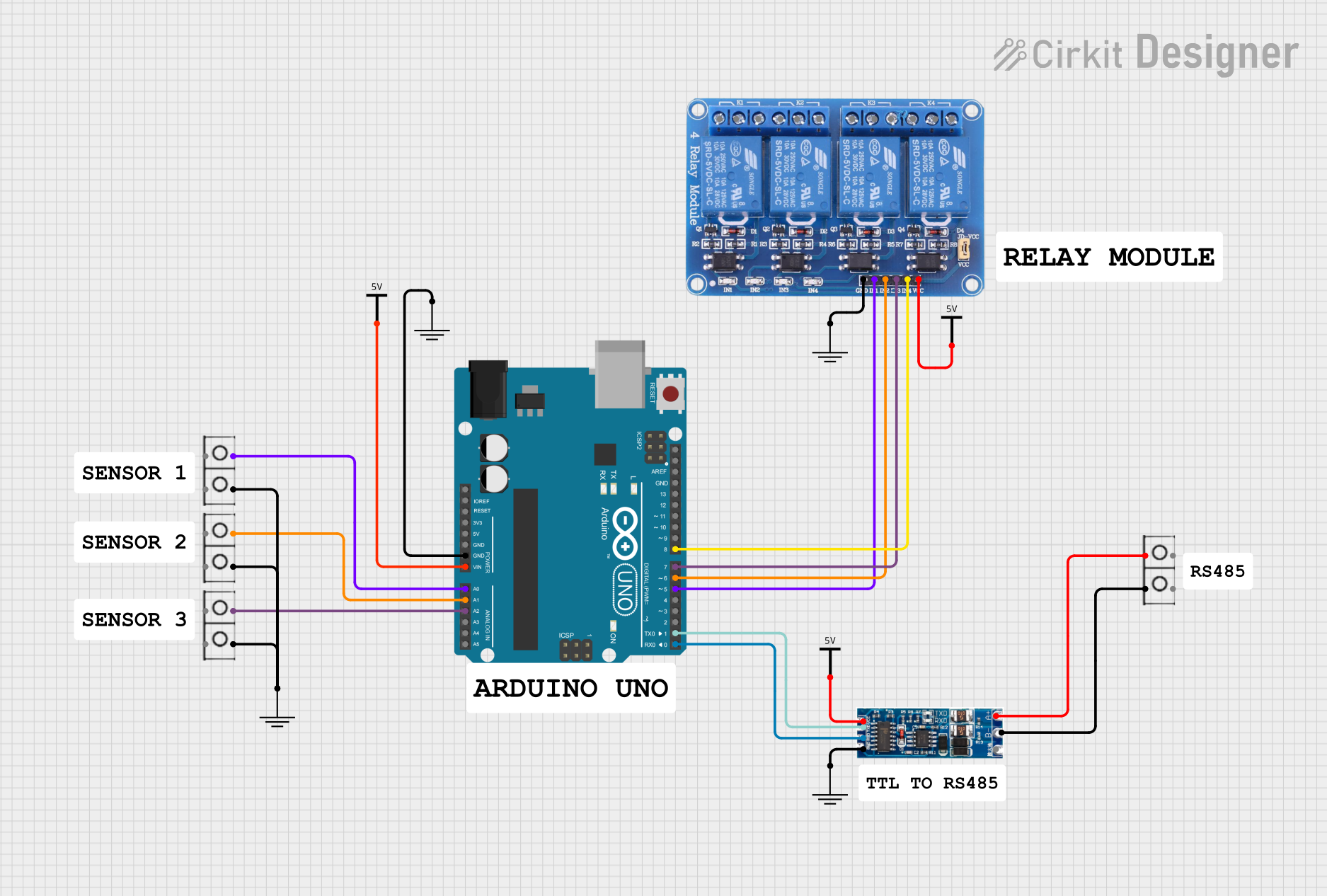
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer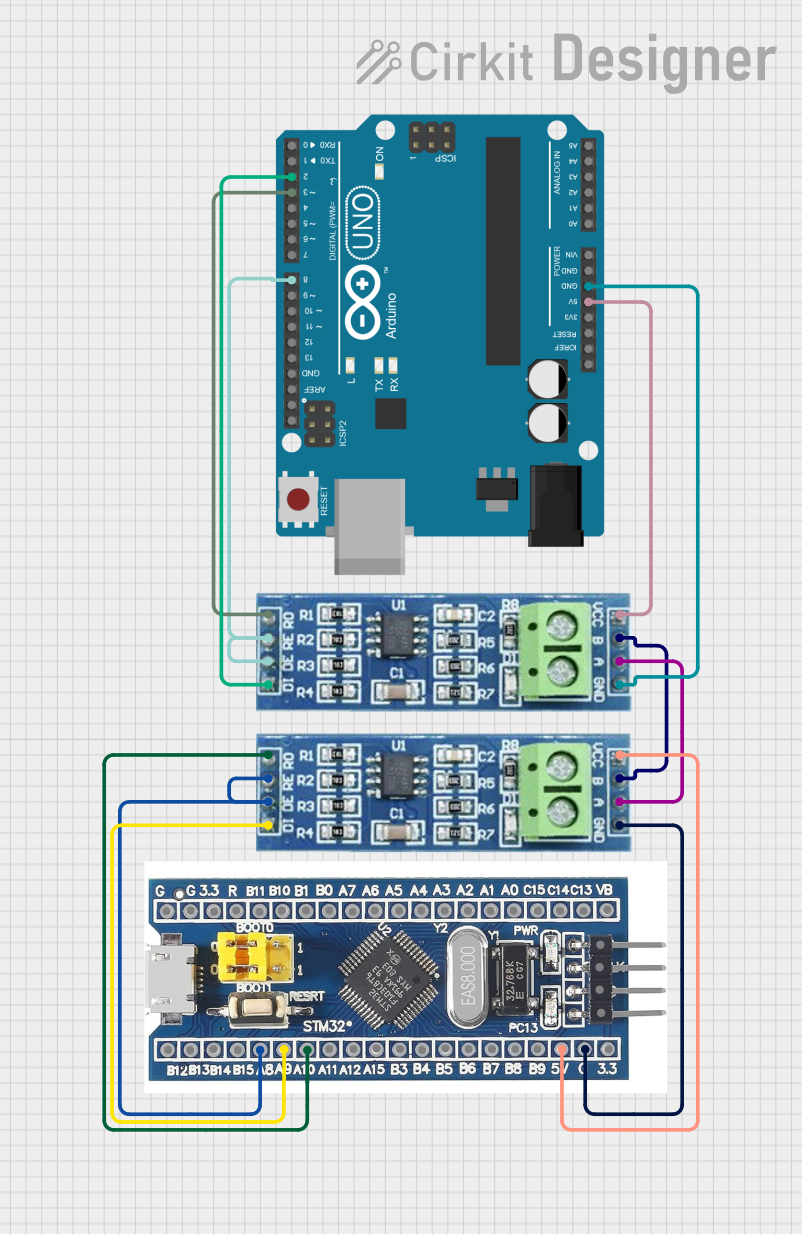
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Modbus 4CH I/O

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial automation systems for monitoring and controlling machinery.
- Home automation for managing lighting, HVAC, and security systems.
- Data acquisition systems for collecting sensor data.
- Remote control of actuators such as relays, motors, and solenoids.
- Integration of legacy devices into modern Modbus-based networks.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Communication Protocol: Modbus RTU (RS-485)
- Input Channels: 4 digital inputs (optically isolated)
- Output Channels: 4 digital outputs (relay or transistor-based, depending on model)
- Operating Voltage: 12V to 24V DC
- Input Voltage Range: 0V to 24V DC
- Output Current Rating: Up to 2A per channel
- Baud Rate: Configurable (default: 9600 bps)
- Parity: None, Even, or Odd (configurable)
- Stop Bits: 1 or 2 (configurable)
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
- Dimensions: 100mm x 80mm x 25mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Power and Communication Terminals
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| V+ | Positive power supply (12V-24V DC) |
| GND | Ground (0V) |
| A | RS-485 communication line A |
| B | RS-485 communication line B |
Input Terminals
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| IN1 | Digital input channel 1 |
| IN2 | Digital input channel 2 |
| IN3 | Digital input channel 3 |
| IN4 | Digital input channel 4 |
| GND | Common ground for input signals |
Output Terminals
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OUT1 | Digital output channel 1 |
| OUT2 | Digital output channel 2 |
| OUT3 | Digital output channel 3 |
| OUT4 | Digital output channel 4 |
| COM | Common terminal for output signals |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Connection: Connect the V+ and GND terminals to a 12V-24V DC power supply.
- Communication Setup: Connect the A and B terminals to the RS-485 bus of your Modbus master device (e.g., PLC, PC, or microcontroller).
- Input Connections: Connect sensors or switches to the IN1-IN4 terminals, ensuring the common ground (GND) is shared.
- Output Connections: Connect actuators (e.g., relays, motors) to the OUT1-OUT4 terminals, using the COM terminal as the common connection.
- Configuration: Set the Modbus address, baud rate, parity, and stop bits using the DIP switches or configuration software (refer to the manufacturer's manual for details).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure proper termination resistors are used on the RS-485 bus to prevent signal reflections.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating (2A) for each output channel.
- Use optically isolated inputs to protect the module from voltage spikes or noise.
- Verify the Modbus address and communication settings to avoid conflicts on the network.
- Use shielded twisted-pair cables for RS-485 communication to minimize interference.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the Modbus 4CH I/O module using an Arduino UNO and the ModbusMaster library.
Arduino Code Example
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
// Instantiate ModbusMaster object
ModbusMaster node;
// Define the Modbus slave ID of the 4CH I/O module
#define SLAVE_ID 1
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize RS-485 communication (using pins 0 and 1 for Arduino UNO)
Serial1.begin(9600); // Adjust baud rate as per module configuration
// Assign the RS-485 serial port to the ModbusMaster object
node.begin(SLAVE_ID, Serial1);
}
void loop() {
uint8_t result;
// Example: Turn ON output channel 1
result = node.writeSingleCoil(0x0000, 1); // Address 0x0000 corresponds to OUT1
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
Serial.println("Output 1 turned ON successfully.");
} else {
Serial.print("Error: ");
Serial.println(result, HEX);
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Example: Turn OFF output channel 1
result = node.writeSingleCoil(0x0000, 0); // Address 0x0000 corresponds to OUT1
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
Serial.println("Output 1 turned OFF successfully.");
} else {
Serial.print("Error: ");
Serial.println(result, HEX);
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication with the Module
- Verify the RS-485 connections (A and B lines) and ensure they are not swapped.
- Check the Modbus address and communication settings (baud rate, parity, stop bits).
- Ensure the master device is configured to communicate with the correct slave ID.
Inputs Not Responding
- Confirm that the input voltage levels are within the specified range (0V-24V DC).
- Check the wiring and ensure the common ground (GND) is properly connected.
Outputs Not Activating
- Verify that the connected actuators are within the output current rating (2A per channel).
- Check the COM terminal connection and ensure it is properly wired.
Intermittent Communication Errors
- Use shielded twisted-pair cables for RS-485 communication.
- Add termination resistors (120Ω) at both ends of the RS-485 bus.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this module with a Modbus TCP network?
A: No, this module is designed for Modbus RTU (RS-485) communication. You would need a Modbus RTU-to-TCP gateway for integration with a Modbus TCP network.
Q: How do I change the Modbus address of the module?
A: The Modbus address can be configured using the DIP switches or configuration software provided by the manufacturer. Refer to the manufacturer's manual for detailed instructions.
Q: What happens if I exceed the output current rating?
A: Exceeding the 2A current rating may damage the output channels. Use external relays or drivers for high-current loads.
Q: Can I use this module in outdoor environments?
A: The module is not weatherproof. Use an appropriate enclosure to protect it from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures.