
How to Use TTP-223: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TTP-223 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TTP-223 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TTP-223 is a touch-sensitive switch IC designed to detect touch inputs. It is a capacitive touch sensor that can replace traditional mechanical switches, offering a more modern and reliable solution for user interfaces. The TTP-223 is compact, easy to use, and highly versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Explore Projects Built with TTP-223

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer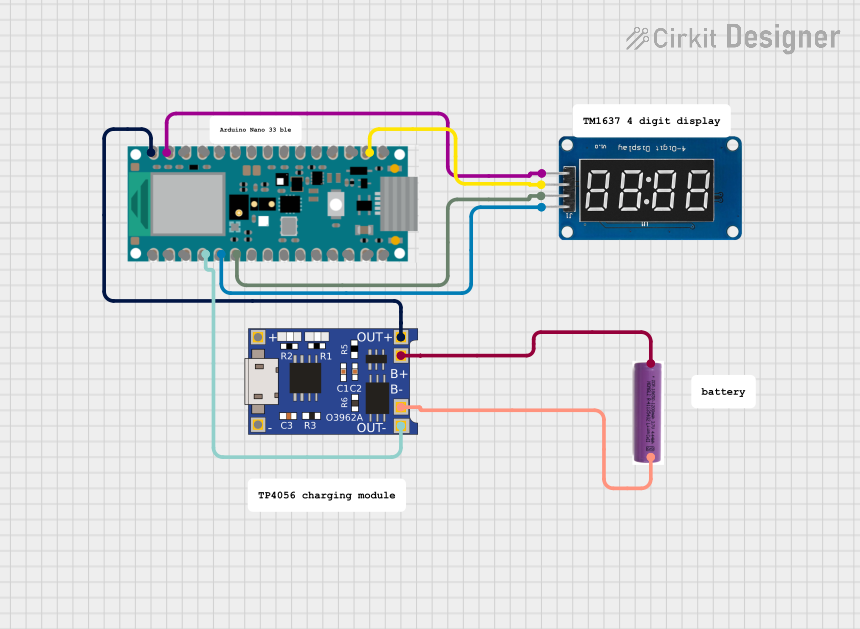
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TTP-223

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Touch-sensitive buttons for home appliances
- Capacitive touch panels for consumer electronics
- Interactive kiosks and displays
- Prototyping touch-based user interfaces
- Replacement for mechanical switches in embedded systems
Technical Specifications
The TTP-223 is a single-channel capacitive touch sensor IC with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 2.0V to 5.5V |
| Operating Current | 1.5µA (typical at 3V) |
| Response Time | ~60ms (fast mode), ~220ms (low power mode) |
| Output Type | Digital (active high or low) |
| Touch Sensitivity | Adjustable via external capacitor |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | SOT-23-6 or DIP-8 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TTP-223 is available in a 6-pin SOT-23 package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power supply input (2.0V to 5.5V). |
| 2 | OUT | Digital output pin. Outputs HIGH or LOW based on touch detection. |
| 3 | AHLB | Active HIGH/LOW selection pin. Connect to GND for active HIGH, VDD for active LOW. |
| 4 | MODE | Mode selection pin. Connect to GND for toggle mode, VDD for momentary mode. |
| 5 | TPAD | Touch pad input. Connect to a conductive touch surface. |
| 6 | GND | Ground connection. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TTP-223 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a 2.0V–5.5V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Touch Pad: Attach a conductive material (e.g., copper foil) to the TPAD pin to act as the touch-sensitive surface.
- Output Configuration:
- Use the AHLB pin to set the output type:
- Connect to GND for active HIGH output.
- Connect to VDD for active LOW output.
- Use the MODE pin to set the operating mode:
- Connect to GND for toggle mode (output state changes with each touch).
- Connect to VDD for momentary mode (output is active only while touch is detected).
- Use the AHLB pin to set the output type:
- Output Pin: Connect the OUT pin to the input of a microcontroller or other digital logic circuit to read the touch state.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Sensitivity Adjustment: The sensitivity of the TTP-223 can be adjusted by connecting an external capacitor between the TPAD pin and ground. A larger capacitor increases sensitivity.
- Debouncing: If the TTP-223 is used in toggle mode, ensure proper software debouncing in your microcontroller to avoid false triggers.
- PCB Design: For optimal performance, minimize noise and interference by keeping the touch pad trace short and away from high-frequency signals.
- Power Supply Decoupling: Add a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor close to the VDD pin to stabilize the power supply.
Example: Using the TTP-223 with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use the TTP-223 with an Arduino UNO in momentary mode:
Circuit Connections
- TTP-223 VDD → Arduino 5V
- TTP-223 GND → Arduino GND
- TTP-223 OUT → Arduino digital pin 2
- TTP-223 MODE → Arduino 5V (momentary mode)
- TTP-223 AHLB → Arduino GND (active HIGH output)
Arduino Code
// TTP-223 Touch Sensor Example
// This code reads the touch state from the TTP-223 and toggles an LED.
const int touchPin = 2; // TTP-223 OUT pin connected to digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Onboard LED pin
void setup() {
pinMode(touchPin, INPUT); // Set touchPin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set ledPin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int touchState = digitalRead(touchPin); // Read the touch sensor state
if (touchState == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on the LED if touch is detected
Serial.println("Touch detected!");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off the LED if no touch is detected
}
delay(100); // Small delay to stabilize readings
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Response from the Sensor
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify that the VDD and GND pins are properly connected and the supply voltage is within the specified range.
False Triggers or Unstable Output
- Cause: Electrical noise or improper grounding.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor (0.1µF) near the VDD pin and ensure a solid ground connection.
Low Sensitivity
- Cause: Touch pad size or external capacitor value is too small.
- Solution: Increase the size of the touch pad or use a larger capacitor on the TPAD pin.
Output Always HIGH or LOW
- Cause: Incorrect mode or AHLB pin configuration.
- Solution: Double-check the connections for the MODE and AHLB pins.
FAQs
Q: Can the TTP-223 detect multiple touches simultaneously?
A: No, the TTP-223 is a single-channel sensor and can only detect one touch at a time.
Q: What materials can be used for the touch pad?
A: Any conductive material, such as copper foil, aluminum foil, or conductive ink, can be used as a touch pad.
Q: Can the TTP-223 work with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the TTP-223 operates within a voltage range of 2.0V to 5.5V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
Q: How do I increase the detection range?
A: Increase the size of the touch pad or use a larger external capacitor to enhance sensitivity.