
How to Use 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery is a widely used energy storage device that provides a nominal voltage of 12 volts. It is designed for reliable performance in various applications, including automotive systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), solar energy storage, and emergency backup power. This battery operates using lead dioxide and sponge lead plates immersed in an electrolyte solution, enabling efficient energy storage and discharge cycles.
Explore Projects Built with 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery
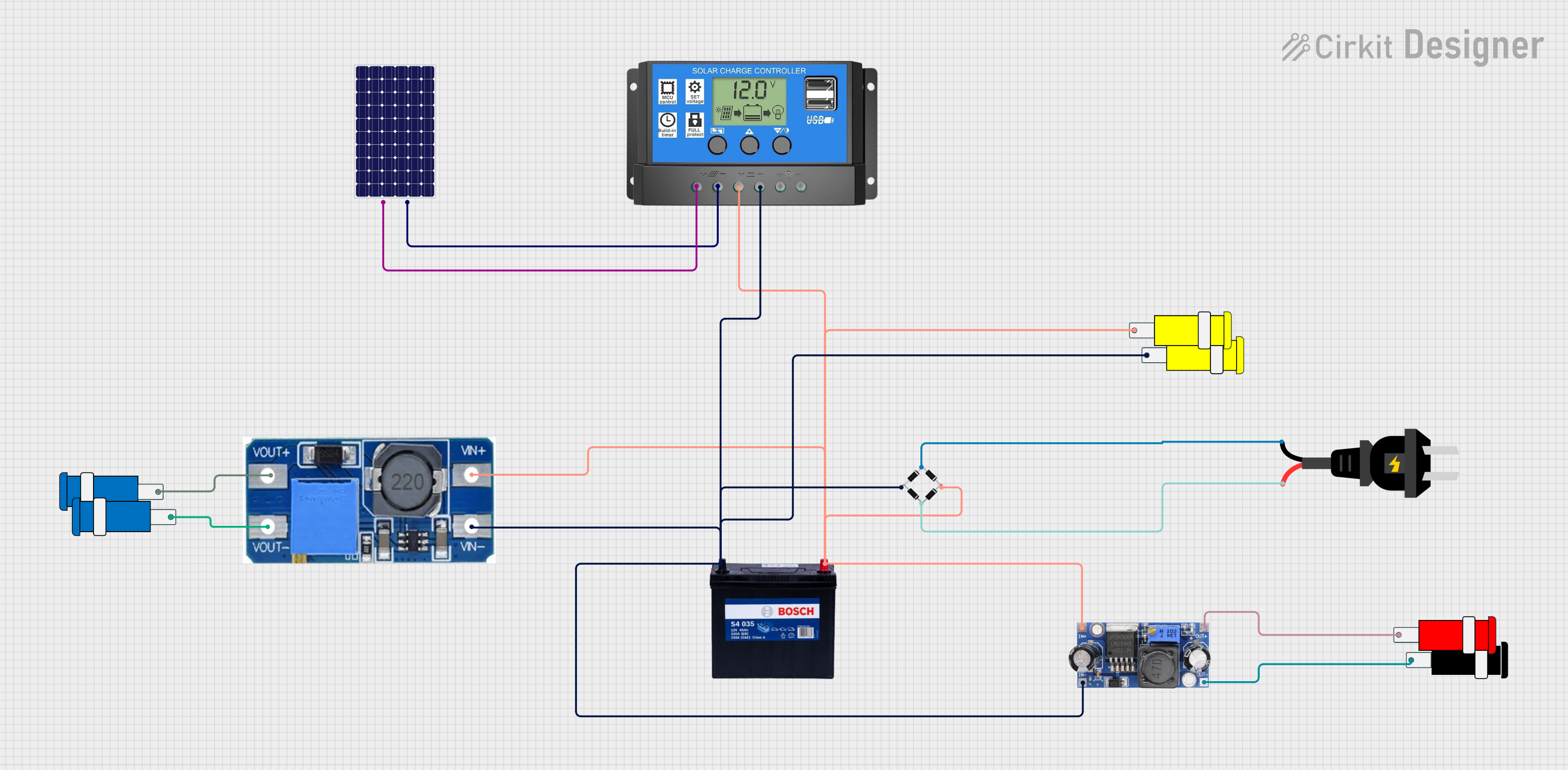
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer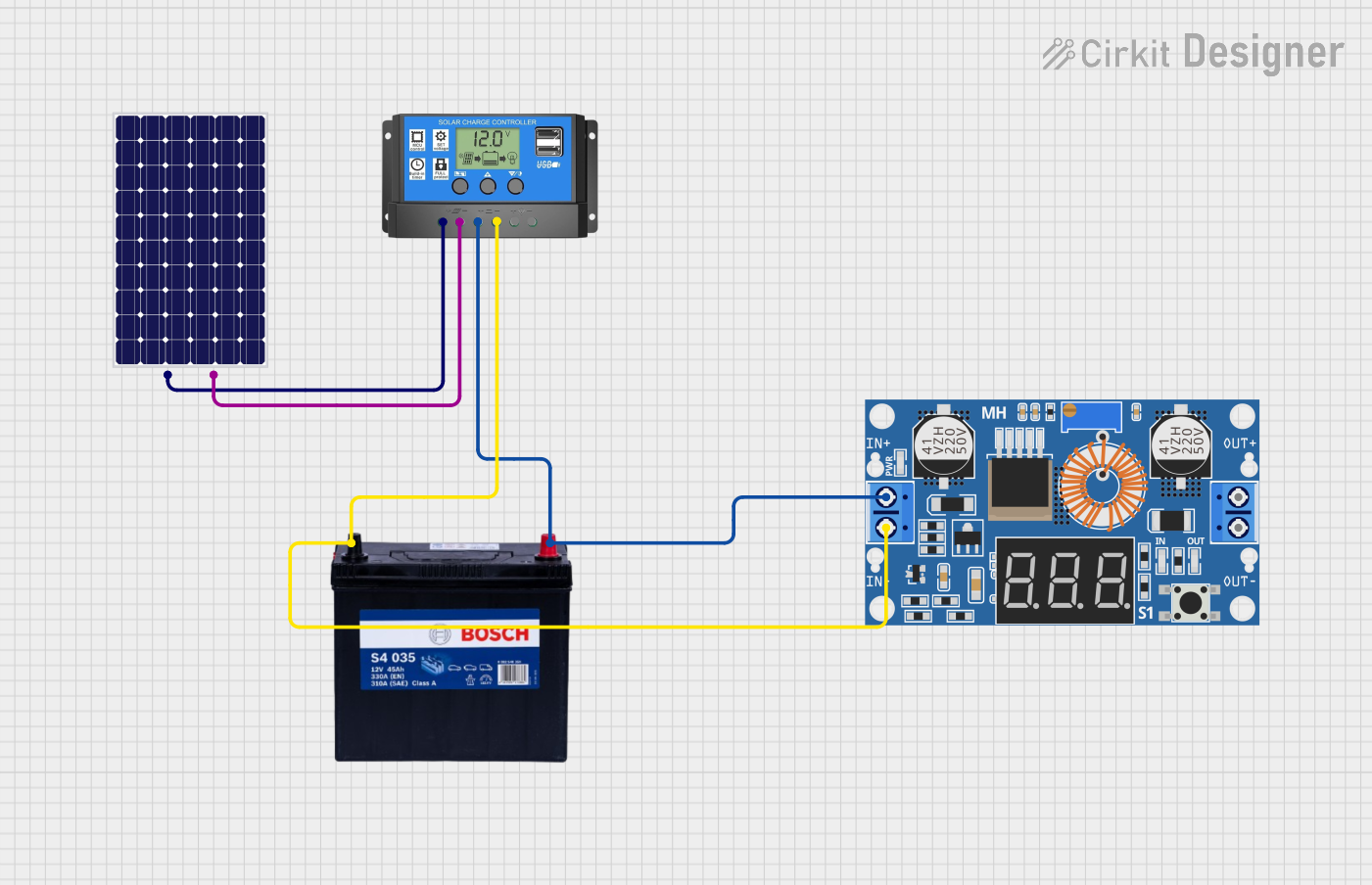
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer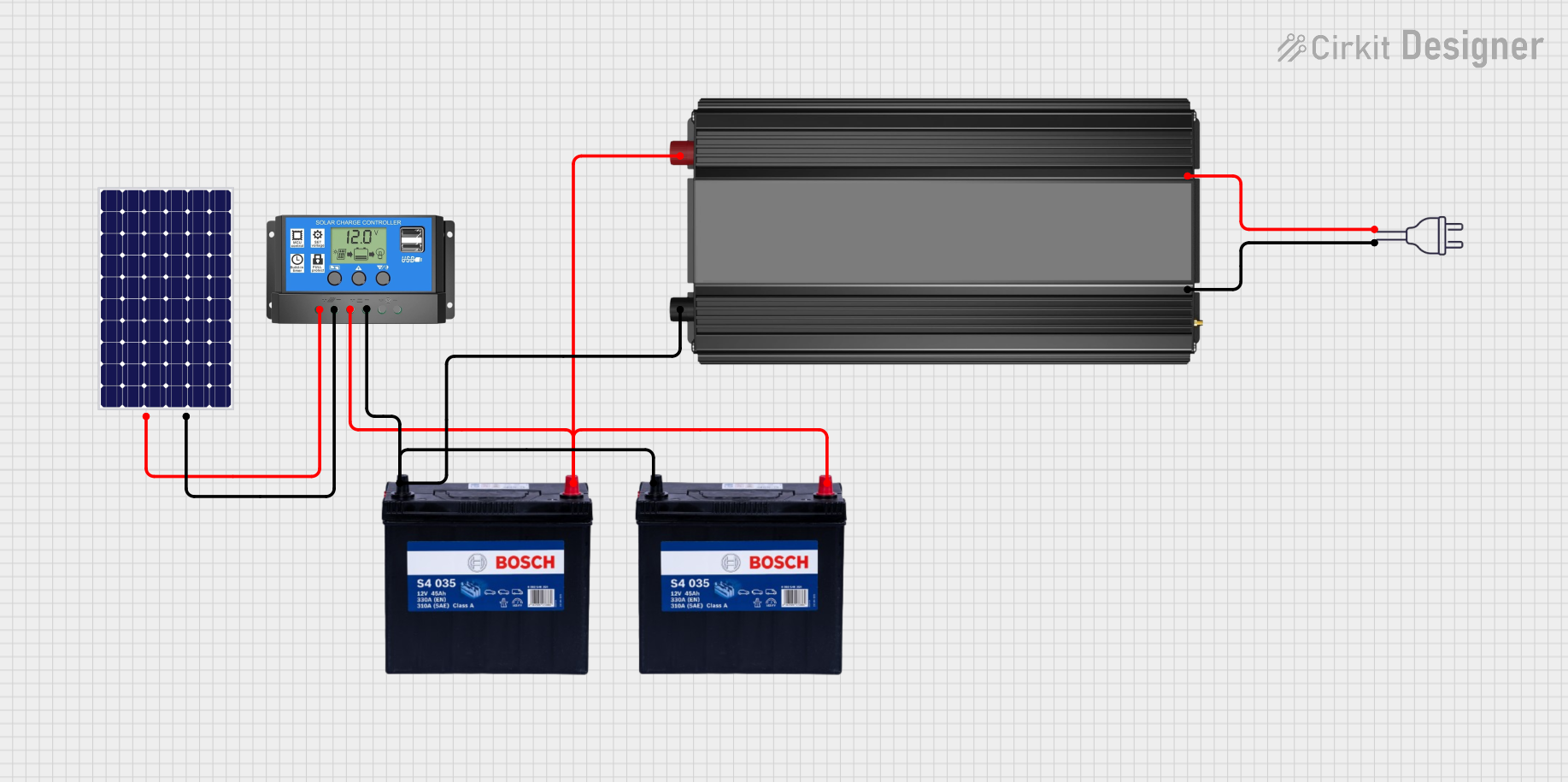
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer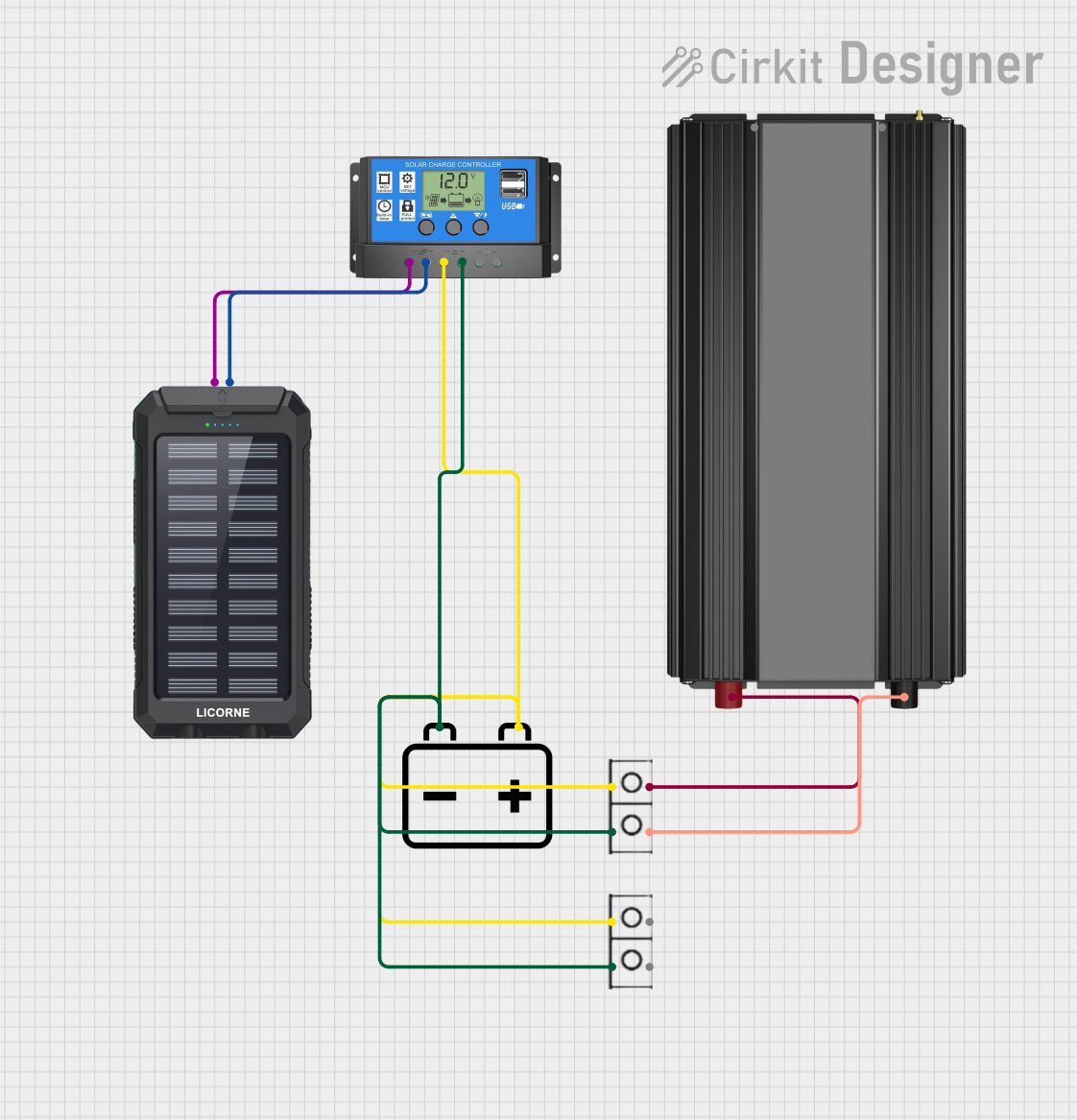
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) systems
- Backup power for uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar and wind energy storage)
- Emergency lighting and alarm systems
- Electric scooters, wheelchairs, and small vehicles
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for the 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 12V |
| Capacity Range | 1.2Ah to 200Ah (varies by model) |
| Chemistry | Lead-acid |
| Charging Voltage | 13.8V to 14.4V |
| Float Voltage | 13.2V to 13.8V |
| Discharge Cutoff Voltage | 10.5V |
| Maximum Discharge Current | Varies by model (e.g., 10A to 100A) |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 50°C |
| Cycle Life | 200 to 1000 cycles (depending on usage) |
| Weight | Varies by capacity (e.g., 2kg to 30kg) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Connects to the positive terminal of the load or circuit. |
| Negative (-) | Connects to the negative terminal of the load or circuit. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery.
- Use appropriate gauge wires to connect the battery to your circuit or load.
- Ensure the polarity is correct to avoid damage to the battery or connected devices.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a compatible lead-acid battery charger with a charging voltage of 13.8V to 14.4V.
- Avoid overcharging by using a charger with automatic cutoff or float charging capability.
- Monitor the charging process to ensure the battery does not overheat.
Discharging the Battery:
- Ensure the load does not draw more current than the battery's maximum discharge current.
- Avoid deep discharges below the cutoff voltage (10.5V) to prolong battery life.
Safety Precautions:
- Always handle the battery with care to avoid short circuits.
- Keep the battery away from open flames or sparks, as it may emit hydrogen gas during charging.
- Use the battery in a well-ventilated area to prevent gas buildup.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Temperature Management: Operate the battery within the recommended temperature range (-20°C to 50°C) to maintain performance and longevity.
- Storage: Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use. Recharge the battery every 3-6 months to prevent sulfation.
- Maintenance: Periodically check the terminals for corrosion and clean them as needed. For flooded lead-acid batteries, check the electrolyte levels and top up with distilled water if necessary.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The 12V DC lead-acid battery can be used to power an Arduino UNO through a voltage regulator or DC-DC converter to step down the voltage to 5V. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the input of a 5V DC-DC converter.
- Connect the output of the converter to the Arduino UNO's 5V and GND pins.
- Ensure proper polarity and secure connections.
Example Code
// Example code to blink an LED using Arduino UNO powered by a 12V lead-acid battery
// Ensure the battery is connected to a 5V DC-DC converter before powering the Arduino
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Battery not charging | Faulty charger or loose connections | Check charger and connections |
| Battery discharges too quickly | Overloading or aging battery | Reduce load or replace the battery |
| Corroded terminals | Exposure to moisture or acid leakage | Clean terminals and apply anti-corrosion grease |
| Low voltage output | Deep discharge or sulfation | Recharge fully or replace the battery |
FAQs
Can I use this battery indoors?
- Yes, but ensure proper ventilation to prevent hydrogen gas buildup during charging.
How do I know when the battery is fully charged?
- A fully charged lead-acid battery typically reaches a voltage of 13.8V to 14.4V. Use a charger with an automatic cutoff for convenience.
Can I connect multiple batteries together?
- Yes, you can connect batteries in series to increase voltage or in parallel to increase capacity. Ensure all batteries are of the same type and capacity.
What happens if I overcharge the battery?
- Overcharging can cause overheating, gas release, and reduced battery life. Always use a charger with overcharge protection.
By following these guidelines, you can safely and effectively use the 12V DC lead-acid rechargeable battery in your projects and applications.