
How to Use Bidirectional battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Bidirectional battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with Bidirectional battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A bidirectional battery is a versatile energy storage device capable of both charging and discharging in two directions. This functionality allows it to store energy from a source and supply energy back to a load or grid when needed. Bidirectional batteries are commonly used in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power setups, as well as in electric vehicles (EVs) to enable regenerative braking and efficient energy management.
Explore Projects Built with Bidirectional battery
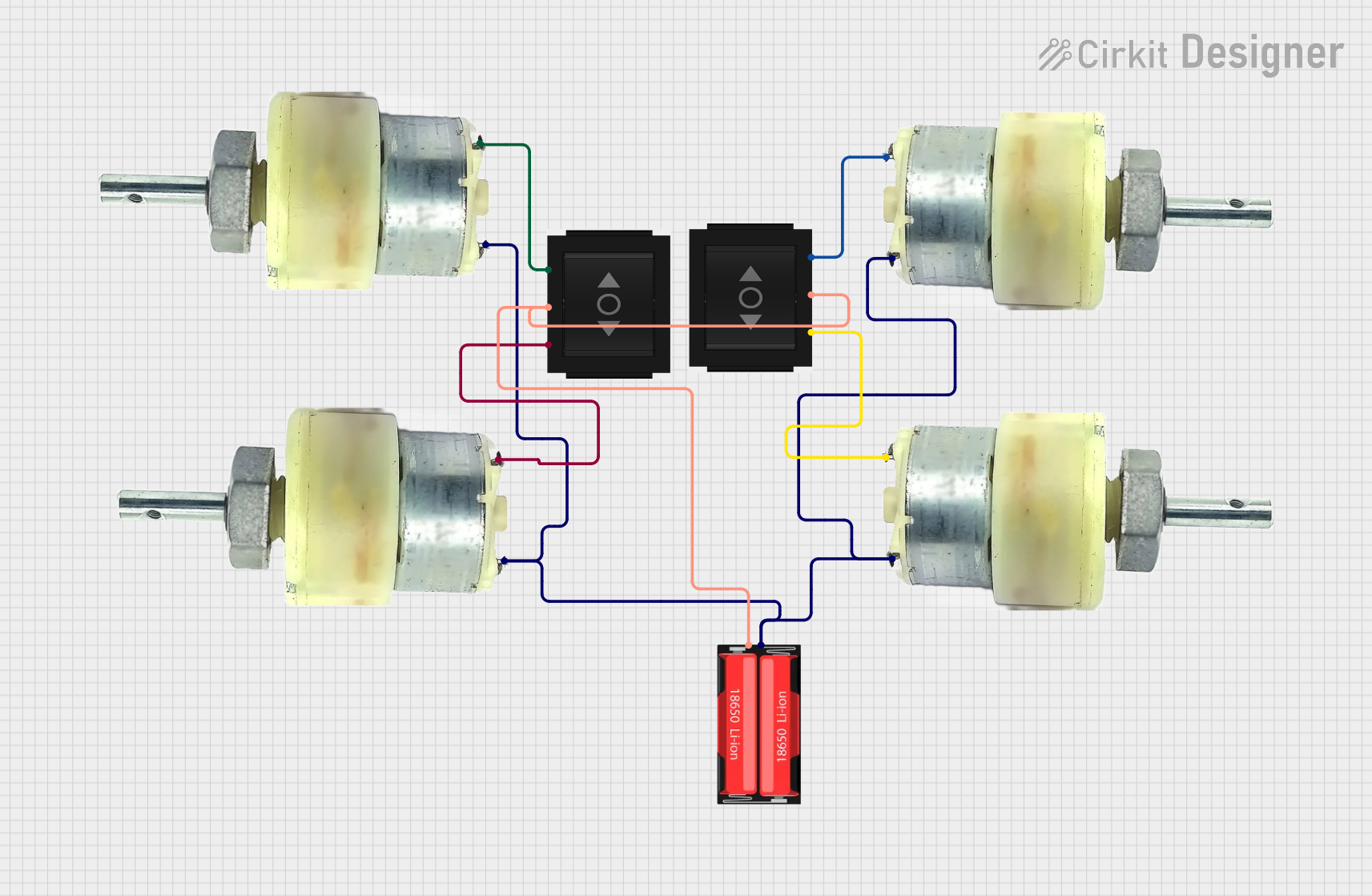
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer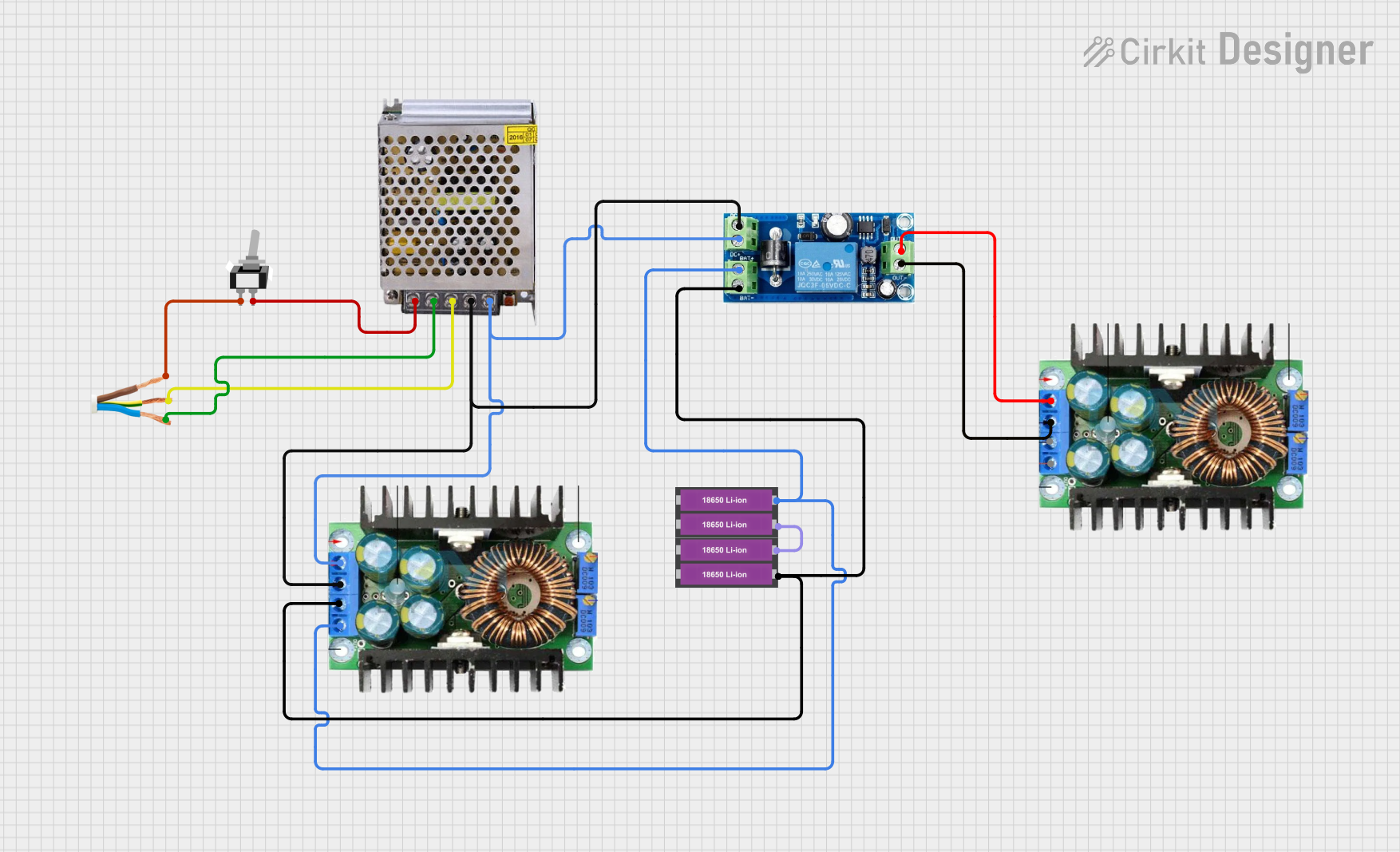
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer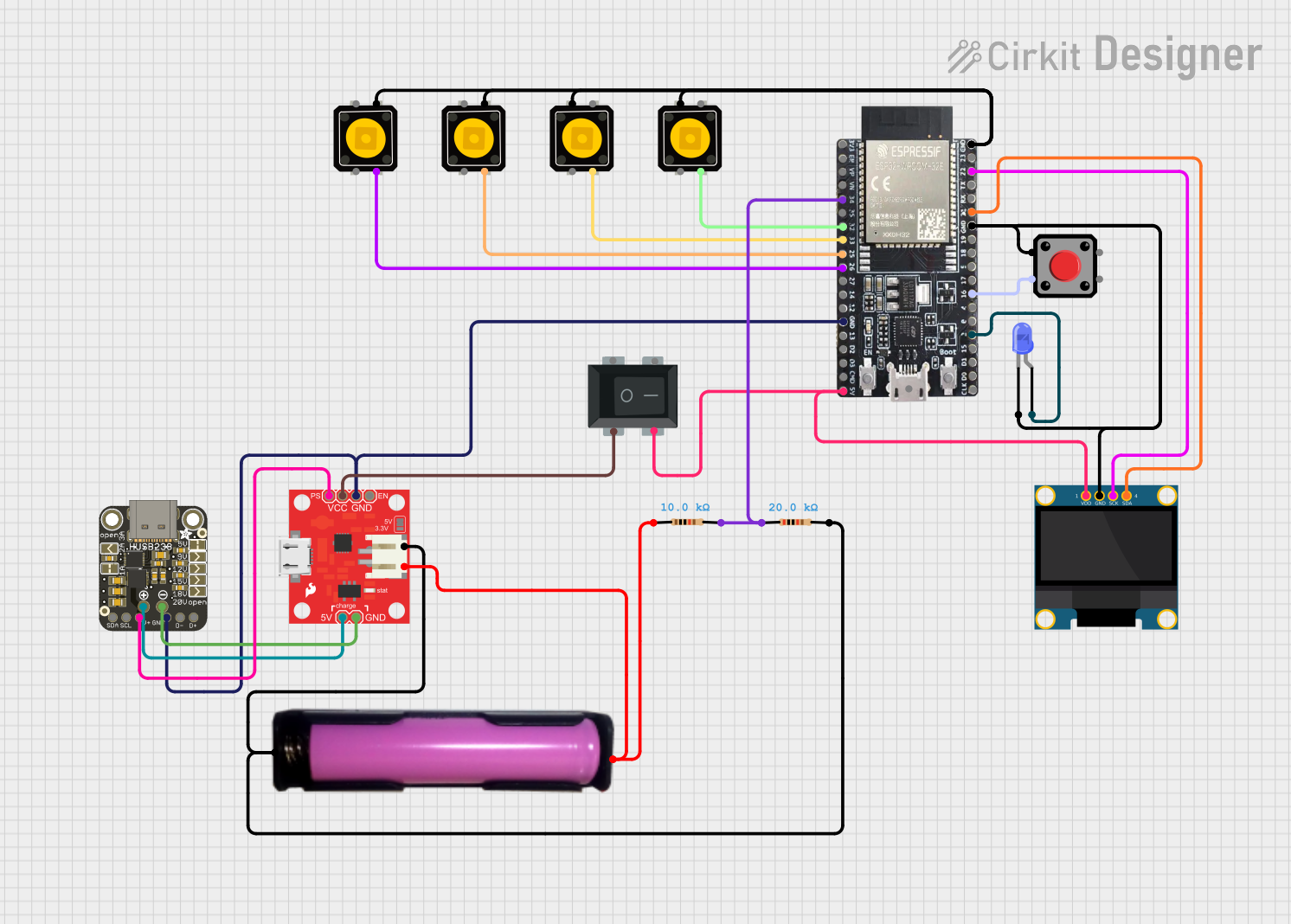
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Bidirectional battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar and wind energy storage)
- Electric vehicles (EVs) for energy recovery and propulsion
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for backup power
- Smart grids for energy balancing and peak shaving
- Industrial energy storage systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Nominal Voltage: 12V, 24V, or 48V (varies by model)
- Capacity: 50Ah to 500Ah (depending on application)
- Charge/Discharge Efficiency: Up to 95%
- Maximum Charge Current: 50A to 200A
- Maximum Discharge Current: 50A to 200A
- Cycle Life: 2000 to 5000 cycles (at 80% Depth of Discharge)
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 60°C
- Communication Interface: CAN, RS485, or Bluetooth (optional, for monitoring)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The bidirectional battery typically has the following terminals and communication ports:
| Pin/Port | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive Terminal (+) | Connects to the positive side of the load or charging source. |
| Negative Terminal (-) | Connects to the negative side of the load or charging source. |
| CAN/RS485 Port | Communication interface for monitoring and control (optional, model-dependent). |
| Temperature Sensor | Monitors the battery's internal temperature to prevent overheating. |
| State of Charge (SOC) Indicator | Provides a visual or digital indication of the battery's charge level. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the positive terminal of the load or charging source.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the negative terminal of the load or charging source.
- Ensure proper polarity to avoid damage to the battery or connected devices.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a compatible bidirectional charger or inverter that supports the battery's voltage and current ratings.
- Monitor the charging process to ensure the battery does not exceed its maximum charge voltage or current.
Discharging the Battery:
- Connect the battery to the load, ensuring the load's power requirements are within the battery's discharge capacity.
- Use a battery management system (BMS) to prevent over-discharge and protect the battery.
Communication and Monitoring:
- If the battery includes a communication interface (e.g., CAN or RS485), connect it to a compatible monitoring system.
- Use the monitoring system to track parameters such as state of charge (SOC), voltage, current, and temperature.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a battery management system (BMS) to protect the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating.
- Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures, as this can reduce its lifespan and performance.
- Use appropriate fuses or circuit breakers to protect the battery and connected devices from short circuits.
- Regularly inspect the battery terminals and connections for corrosion or damage.
- Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for charging and discharging cycles to maximize the battery's lifespan.
Example: Connecting a Bidirectional Battery to an Arduino UNO
If you want to monitor the battery's voltage and state of charge using an Arduino UNO, you can use an analog voltage divider circuit and the Arduino's analog input pins. Below is an example code snippet:
// Arduino code to monitor bidirectional battery voltage
// Ensure the voltage divider output does not exceed 5V for Arduino's analog input
const int voltagePin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 5.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
const float maxBatteryVoltage = 48.0; // Maximum battery voltage (adjust as needed)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(voltagePin, INPUT); // Set the voltage pin as input
}
void loop() {
int analogValue = analogRead(voltagePin); // Read the analog input
float batteryVoltage = (analogValue / 1023.0) * 5.0 * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
// Add a delay to avoid flooding the Serial Monitor
delay(1000);
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to scale down the battery voltage to a safe level for the Arduino's analog input (0-5V). Select resistor values carefully to match the battery's maximum voltage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect charger settings or faulty charger.
- Solution: Verify the charger's voltage and current settings. Ensure compatibility with the battery.
Battery Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive charge/discharge current or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the current and ensure proper airflow around the battery.
Low Cycle Life:
- Cause: Frequent deep discharges or exposure to high temperatures.
- Solution: Limit the depth of discharge to 80% and avoid extreme temperatures.
Communication Interface Not Working:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or incompatible monitoring system.
- Solution: Check the wiring and ensure the monitoring system supports the battery's communication protocol.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a bidirectional battery without a BMS?
- A: It is not recommended. A BMS is essential for protecting the battery and ensuring safe operation.
Q: How do I calculate the battery's state of charge (SOC)?
- A: SOC can be estimated using voltage measurements or by integrating current over time. Many bidirectional batteries include built-in SOC indicators.
Q: Can I connect multiple bidirectional batteries in series or parallel?
- A: Yes, but ensure the batteries are of the same type, capacity, and state of charge. Use a BMS designed for series or parallel configurations.
Q: What is the typical lifespan of a bidirectional battery?
- A: The lifespan depends on the battery type and usage. Lithium-ion bidirectional batteries typically last 2000-5000 cycles at 80% depth of discharge.