
How to Use Soil Moisture Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
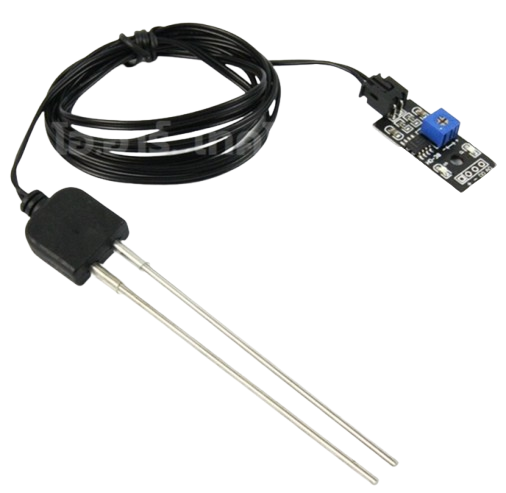

 Design with Soil Moisture Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Soil Moisture Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Soil Moisture Sensor is a device designed to measure the moisture content in soil. It provides real-time data that can be used to monitor and manage irrigation systems, ensuring plants receive the optimal amount of water. This sensor is widely used in agricultural automation, gardening, and environmental monitoring projects. Its simplicity and compatibility with microcontrollers make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with Soil Moisture Sensor
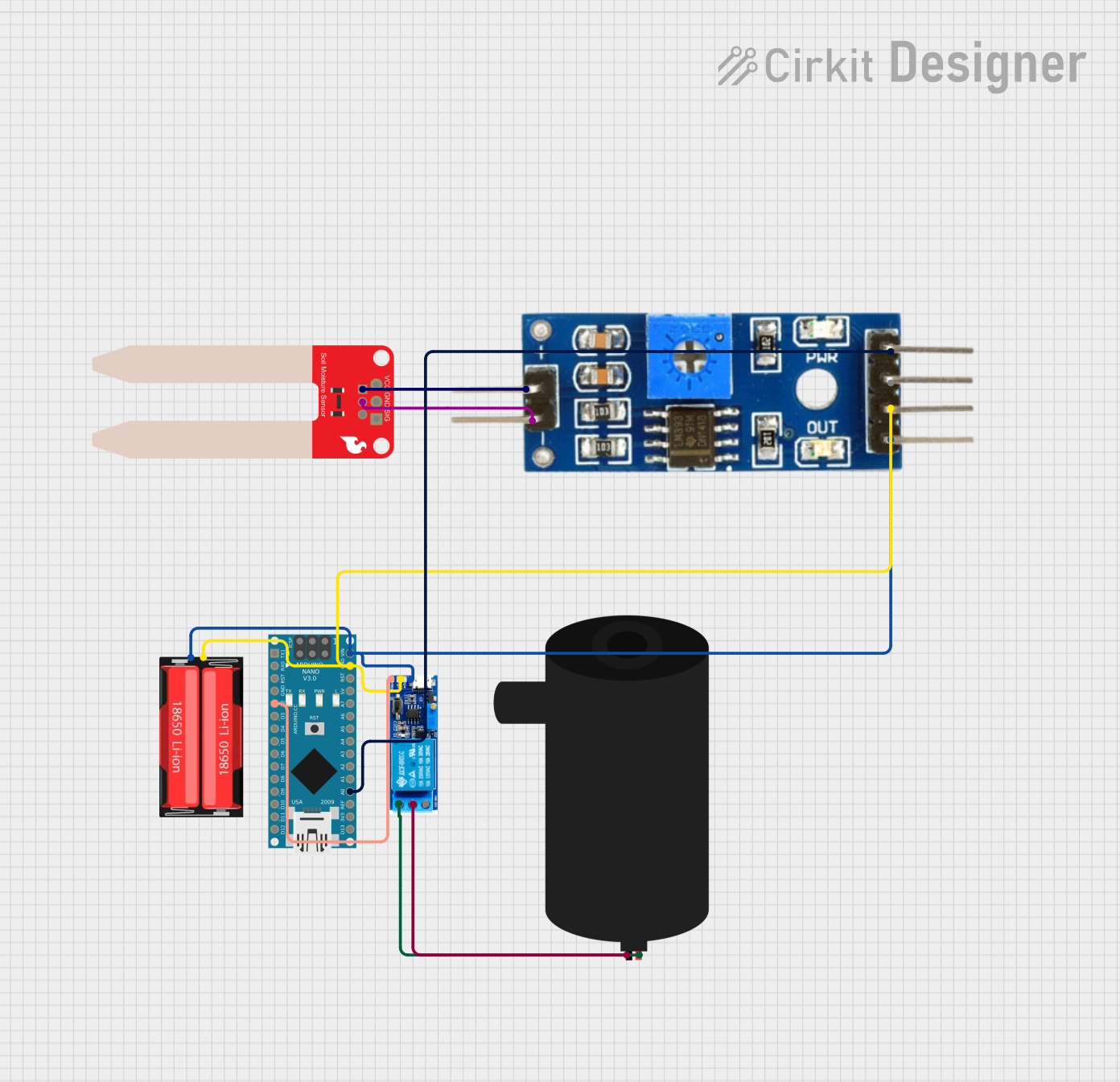
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer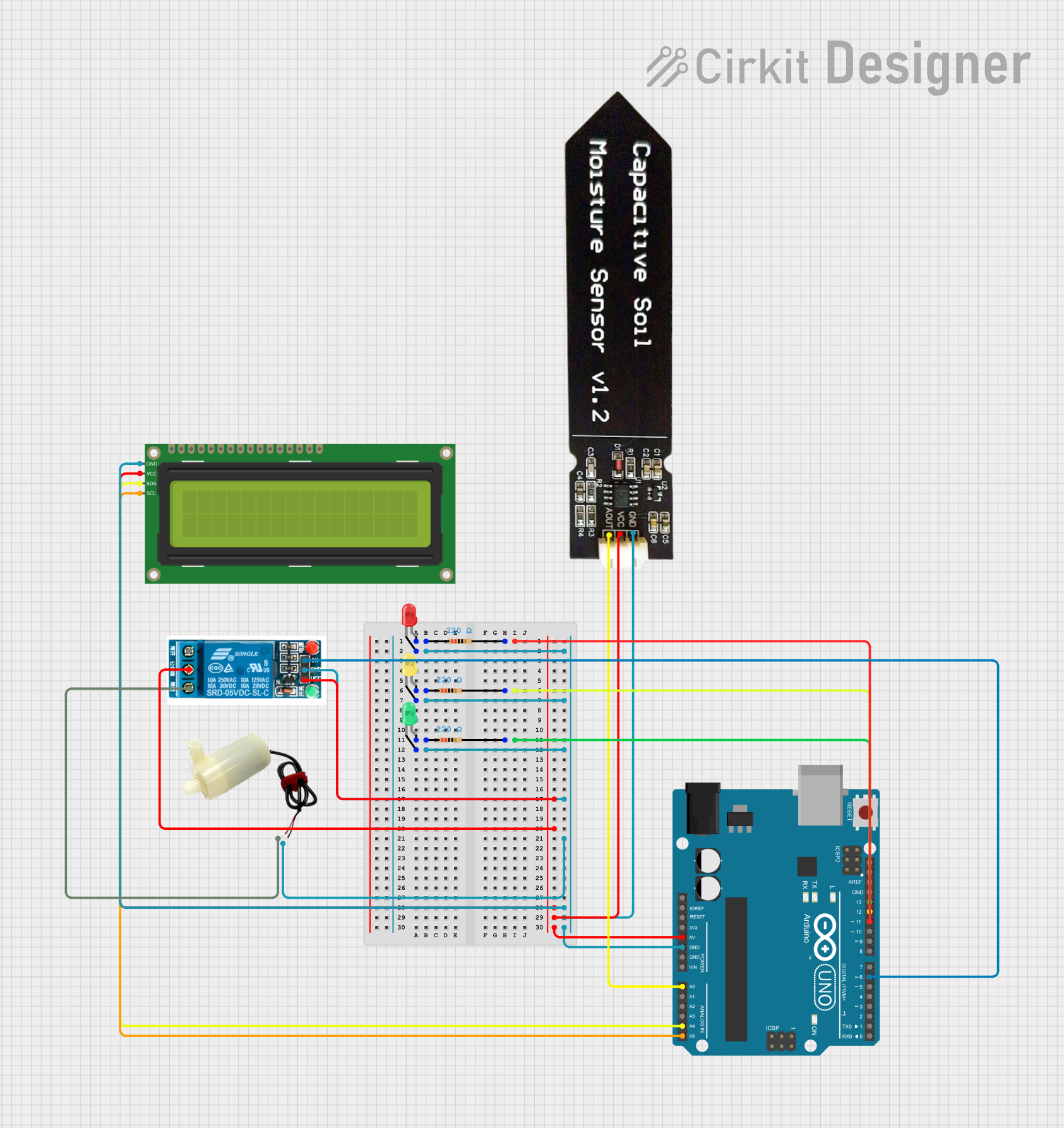
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer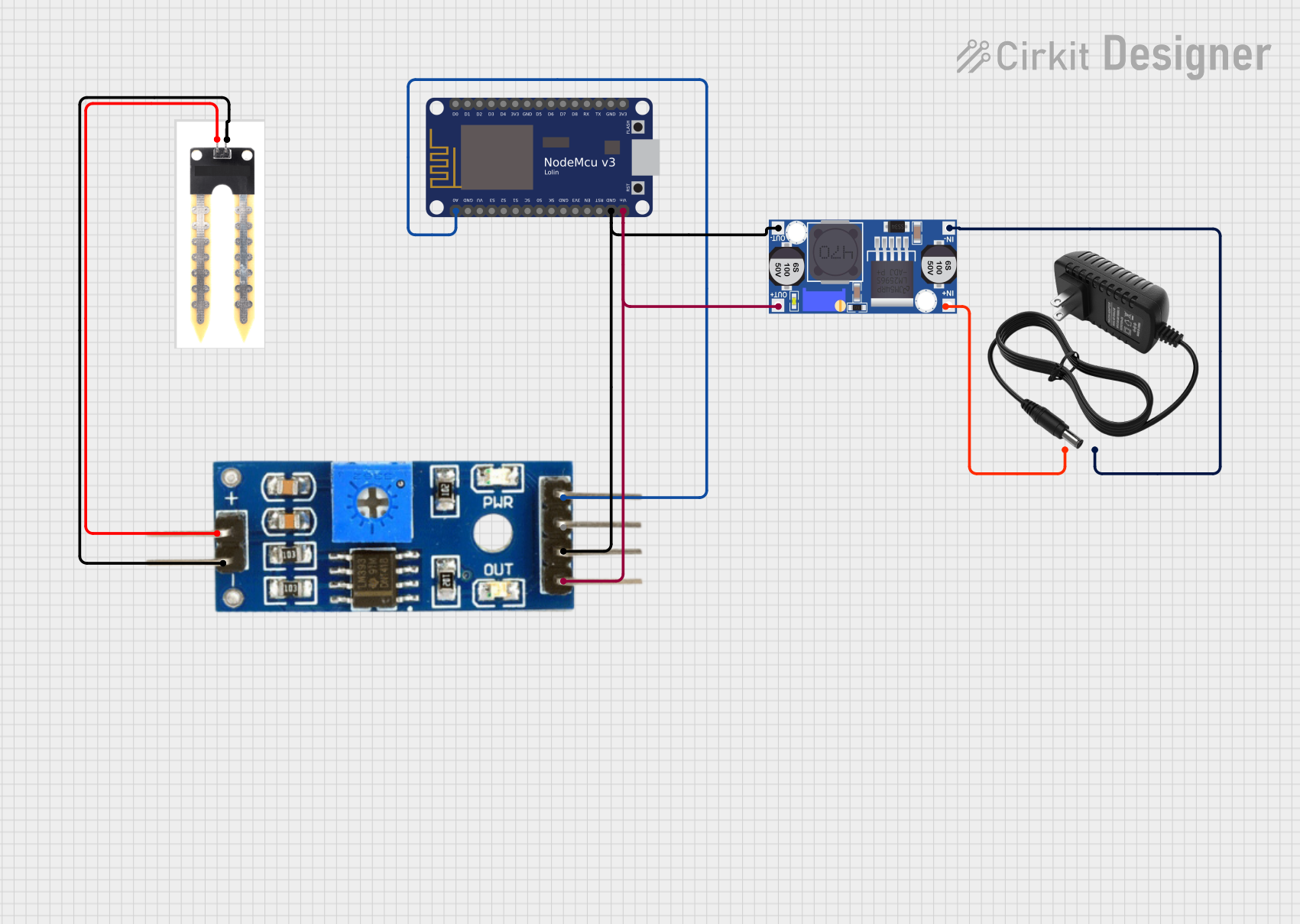
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer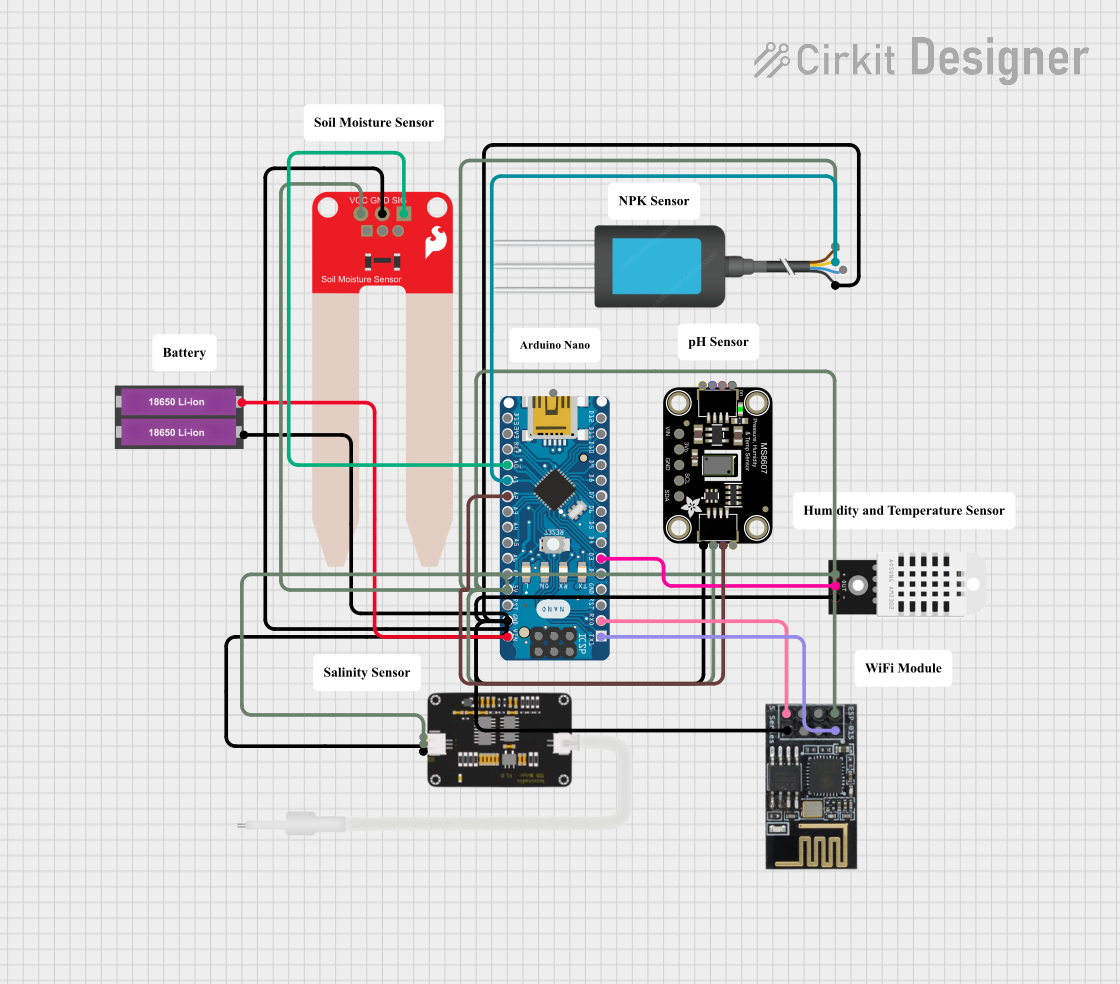
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Soil Moisture Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automated irrigation systems
- Smart gardening projects
- Agricultural monitoring
- Environmental research
- Soil analysis in educational projects
Technical Specifications
The Soil Moisture Sensor typically consists of two main parts: the probe (which detects soil moisture) and the control board (which processes the signal). Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V - 5V
- Output Types: Analog and Digital
- Current Consumption: < 20mA
- Moisture Detection Range: 0% (dry) to 100% (wet)
- Dimensions: Varies by model, typically 60mm x 20mm (probe)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The control board of the Soil Moisture Sensor usually has four pins. The table below describes each pin:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power | Connect to the 3.3V or 5V power supply of the microcontroller. |
| GND | Ground | Connect to the ground (GND) of the microcontroller. |
| A0 | Analog Out | Outputs an analog voltage proportional to the soil moisture level. |
| D0 | Digital Out | Outputs a HIGH or LOW signal based on the moisture threshold set via a potentiometer. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Soil Moisture Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor to a Microcontroller:
- Connect the VCC pin to the 5V (or 3.3V) pin of the microcontroller.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground (GND) of the microcontroller.
- Connect the A0 pin to an analog input pin (e.g., A0 on an Arduino UNO).
- Optionally, connect the D0 pin to a digital input pin if you want to use the threshold feature.
Insert the Probe into the Soil:
- Place the probe into the soil you want to measure. Ensure the probe is fully inserted for accurate readings.
Read the Output:
- Use the analog output (A0) to get a continuous moisture level reading.
- Use the digital output (D0) to detect whether the soil moisture is above or below the set threshold.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Corrosion: The probe may corrode over time if left in the soil for extended periods. Consider using corrosion-resistant probes for long-term projects.
- Power Supply: Ensure the sensor operates within its voltage range (3.3V - 5V) to avoid damage.
- Calibration: Adjust the potentiometer on the control board to set the desired moisture threshold for the digital output.
- Placement: Avoid placing the probe in waterlogged soil, as this may damage the sensor or give inaccurate readings.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the Soil Moisture Sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pins for the sensor
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog output pin connected to A0
const int digitalPin = 7; // Digital output pin connected to D7
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED for indication
void setup() {
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT); // Set digital pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
int moistureLevel = analogRead(analogPin);
// Read the digital value from the sensor
int digitalState = digitalRead(digitalPin);
// Print the analog moisture level to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Moisture Level (Analog): ");
Serial.println(moistureLevel);
// Check the digital output and control the LED
if (digitalState == LOW) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on LED if soil is dry
Serial.println("Soil is dry!");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED if soil is wet
Serial.println("Soil is wet!");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Solution: Check all connections and ensure the sensor is powered correctly. Verify that the probe is properly inserted into the soil.
Corroded Probe:
- Solution: Replace the probe or use a corrosion-resistant version. Avoid leaving the sensor in the soil for long periods without maintenance.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Solution: Ensure the soil is not overly compacted or waterlogged. Check for loose connections.
Digital Output Not Triggering:
- Solution: Adjust the potentiometer on the control board to set the correct moisture threshold.
FAQs
Q: Can the sensor be used in water?
A: No, the sensor is designed for soil moisture measurement. Submerging it in water may damage the probe or control board.
Q: How do I extend the lifespan of the sensor?
A: Use corrosion-resistant probes and avoid leaving the sensor in the soil for extended periods without cleaning.
Q: Can I use multiple sensors in one project?
A: Yes, you can connect multiple sensors to different analog or digital pins on your microcontroller.
Q: What is the difference between analog and digital output?
A: The analog output provides a continuous voltage proportional to the soil moisture level, while the digital output gives a HIGH or LOW signal based on the set threshold.