
How to Use Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V in Cirkit Designer
Design with Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V by LiTech is a high-current fuse designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. With a current rating of 60 amps and a voltage rating of 48 volts, this fuse is ideal for use in high-power applications such as automotive systems, renewable energy setups, and industrial equipment. Its robust design ensures reliable performance in demanding environments.
Explore Projects Built with Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V
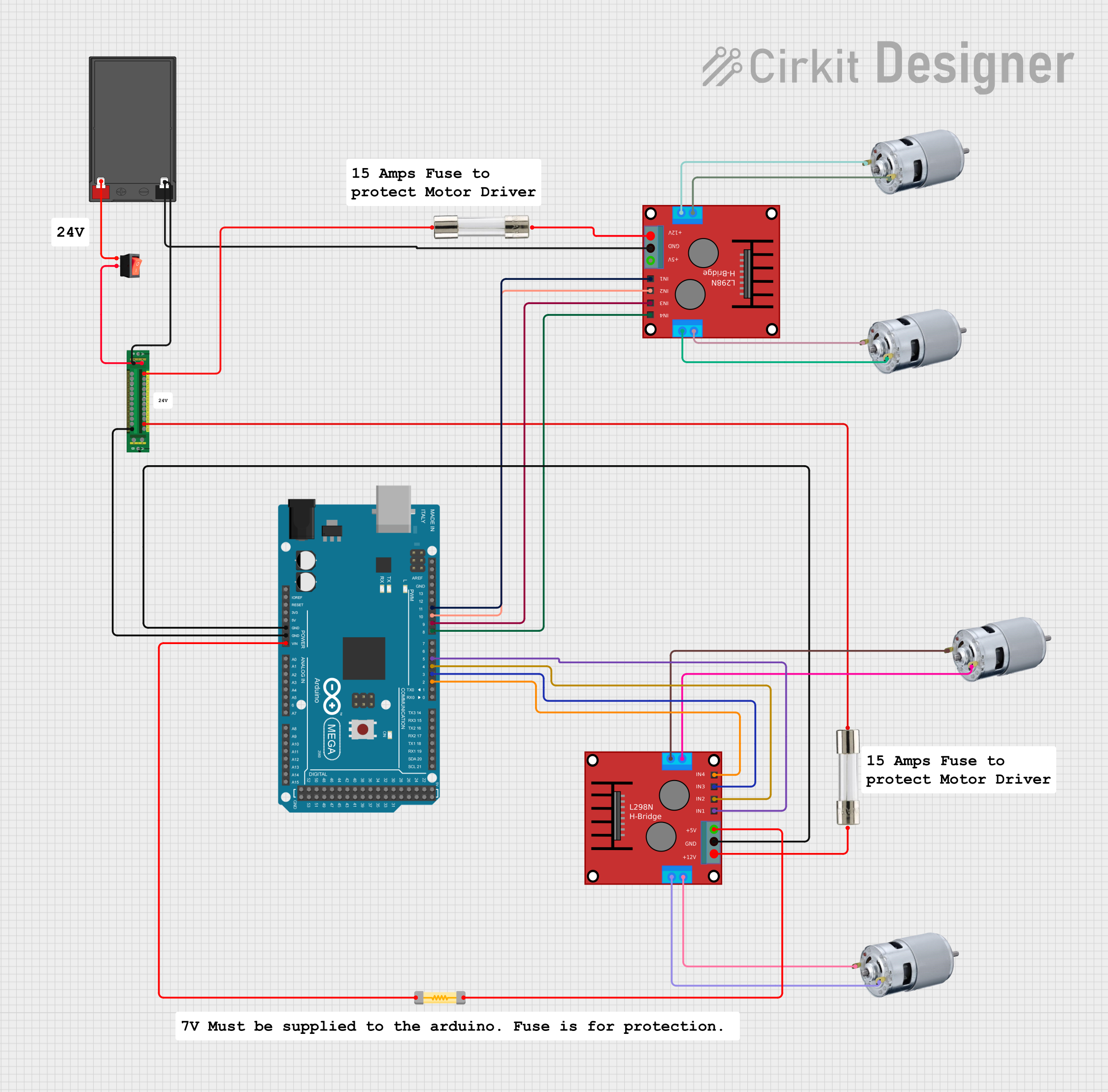
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer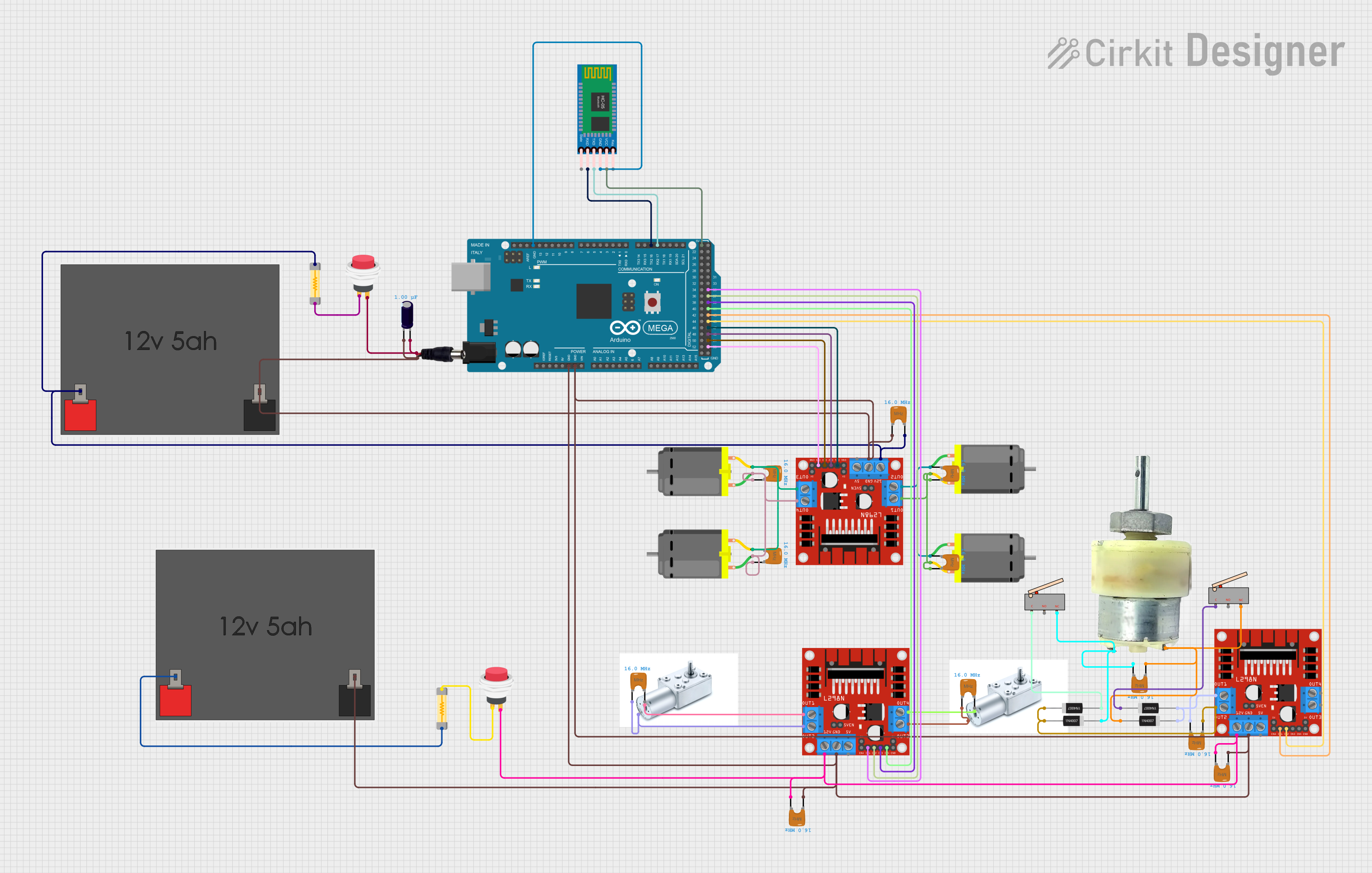
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer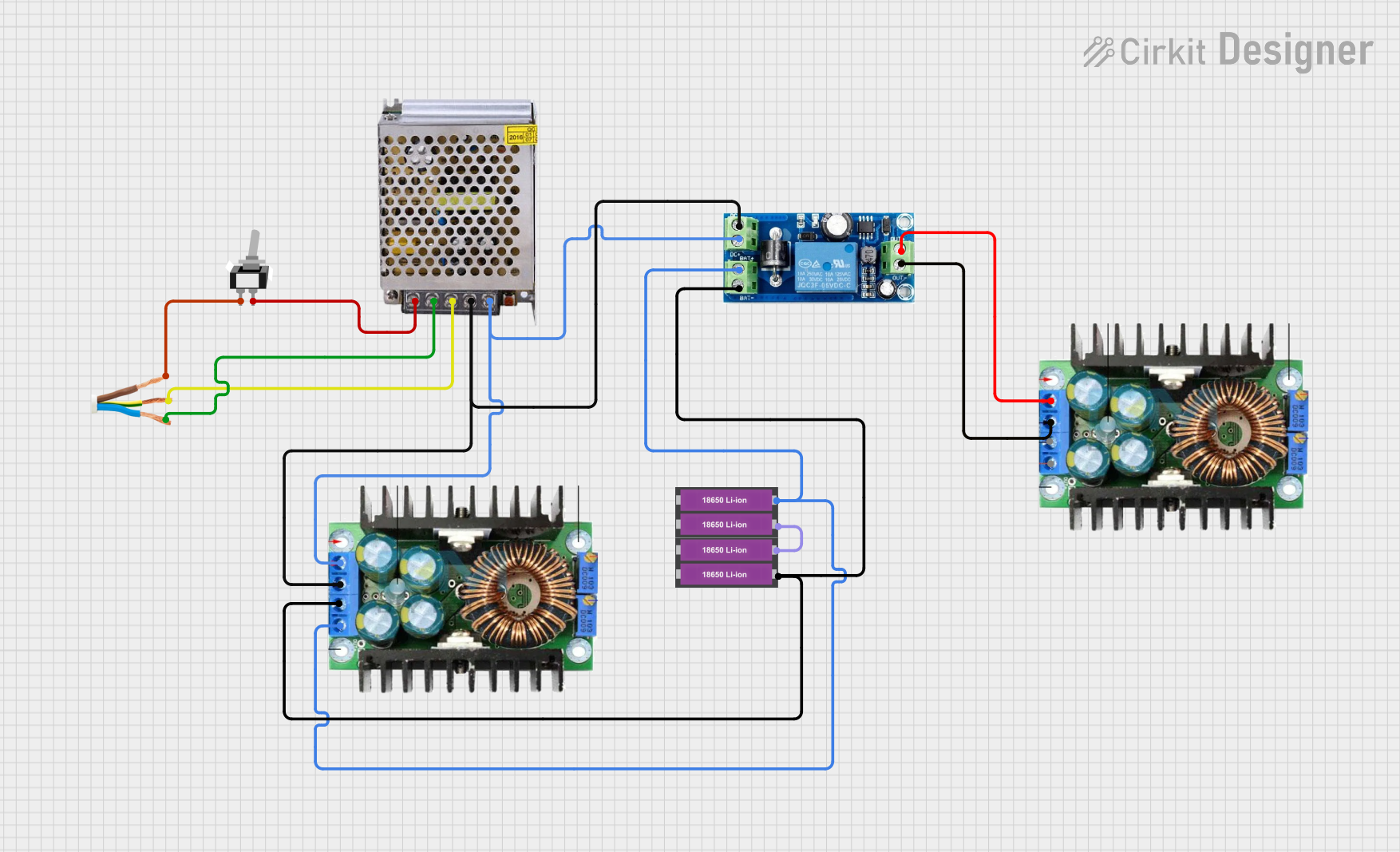
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive electrical systems (e.g., battery protection, alternator circuits)
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panel arrays, inverters)
- Industrial machinery and equipment
- Marine and RV power systems
- High-current DC circuits requiring overcurrent protection
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | LiTech |
| Part ID | Fusible |
| Current Rating | 60A |
| Voltage Rating | 48V DC |
| Fuse Type | MEGA-Fuse |
| Interrupting Capacity | 2000A @ 48V DC |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Mounting Style | Bolt-on |
| Material | Tin-plated copper terminals |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 68mm x 19mm x 8mm |
| Weight | 15g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V has two bolt-on terminals for electrical connections. The table below describes the terminals:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Input terminal: Connects to the power source |
| Terminal 2 | Output terminal: Connects to the protected circuit |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Determine the Fuse Rating: Ensure the 60A / 48V rating is appropriate for your circuit. The fuse should be rated slightly higher than the normal operating current of the circuit but lower than the maximum current the wiring or components can handle.
- Select a Fuse Holder: Use a compatible MEGA-fuse holder or mounting block that supports bolt-on connections.
- Install the Fuse:
- Secure the fuse in the holder using the bolt-on terminals.
- Ensure tight and secure connections to minimize resistance and heat generation.
- Connect the Circuit:
- Attach the input terminal to the power source (e.g., battery positive terminal).
- Attach the output terminal to the load or protected circuit.
- Test the Circuit: Power on the system and verify that the fuse is functioning correctly. If the circuit exceeds 60A, the fuse will blow to protect the system.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Do not use the fuse in systems exceeding 48V DC.
- Current Rating: Avoid using the fuse in circuits with a continuous current close to or exceeding 60A.
- Mounting: Ensure the fuse is securely mounted to prevent vibration or movement, especially in automotive or industrial applications.
- Replacement: Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same rating (60A / 48V) to maintain proper protection.
- Safety: Disconnect power before installing or replacing the fuse to avoid electric shock or short circuits.
Example: Using the Fuse with an Arduino UNO
While the Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V is not directly used with low-power devices like the Arduino UNO, it can be part of a larger system that powers the Arduino. For example, in a solar power system, the fuse can protect the battery and inverter, which in turn powers the Arduino.
// Example: Monitoring a 48V battery system with Arduino
// Note: This code assumes the Arduino is powered by a step-down converter
// from the 48V system. The fuse protects the battery and connected devices.
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin to read battery voltage
float voltageDividerRatio = 11.0; // Adjust based on your resistor divider
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(batteryPin, INPUT); // Set the battery pin as input
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue * 5.0 / 1023.0) * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Ensure the Arduino is isolated from the high-current circuit. Use appropriate voltage dividers and optoisolators for safe monitoring.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Fuse Blows Frequently:
- Cause: Circuit current exceeds 60A due to overload or short circuit.
- Solution: Check the circuit for faults or reduce the load to stay within the fuse's rating.
Fuse Overheats Without Blowing:
- Cause: Loose connections at the terminals causing high resistance.
- Solution: Tighten the terminal connections and ensure proper contact.
Fuse Does Not Blow During Overload:
- Cause: Incorrect fuse rating or faulty fuse.
- Solution: Verify the fuse rating and replace it if necessary.
Difficulty Mounting the Fuse:
- Cause: Incompatible fuse holder or mounting block.
- Solution: Use a compatible MEGA-fuse holder designed for bolt-on connections.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Always use a multimeter to check for continuity across the fuse terminals.
- Inspect the fuse visually for signs of damage, such as melted or broken elements.
- Ensure the fuse is installed in the correct orientation and securely fastened.
- Replace the fuse with a genuine LiTech MEGA-Fuse to ensure reliability and performance.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the Fusible MEGA-Fuse 60A / 48V into their systems, ensuring reliable overcurrent protection and safe operation.