
How to Use HAfiHA JDM11-6H: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
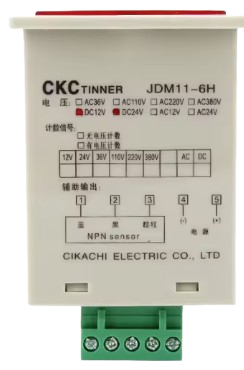
 Design with HAfiHA JDM11-6H in Cirkit Designer
Design with HAfiHA JDM11-6H in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The HAfiHA JDM11-6H, manufactured by Cikachi, is a high-performance relay designed for switching applications. It features low power consumption, high reliability, and a compact design, making it ideal for use in a wide range of electronic circuits and automation systems. This relay is particularly suited for applications requiring precise control and durability, such as industrial automation, home appliances, and control panels.
Explore Projects Built with HAfiHA JDM11-6H

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer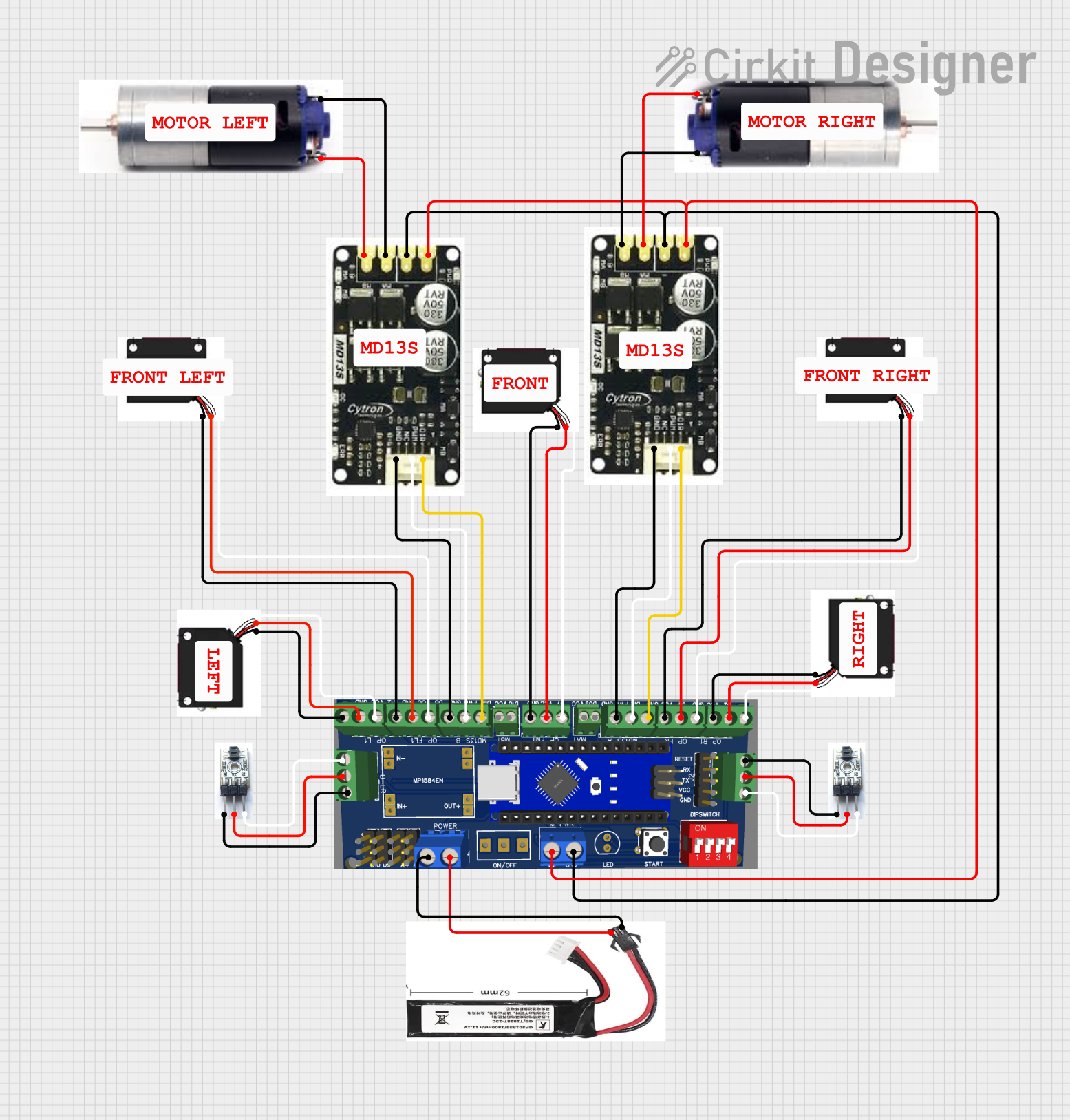
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer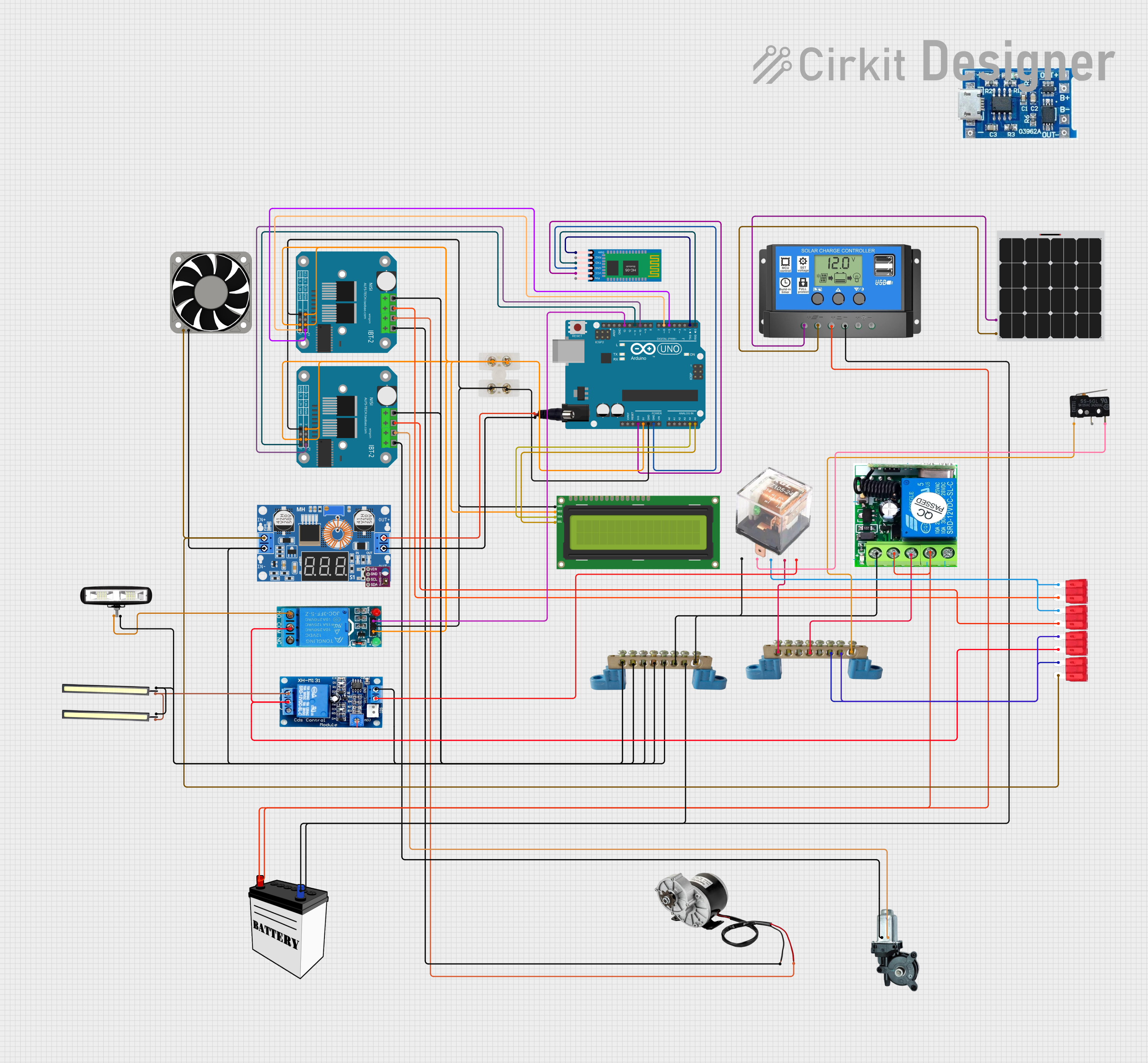
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer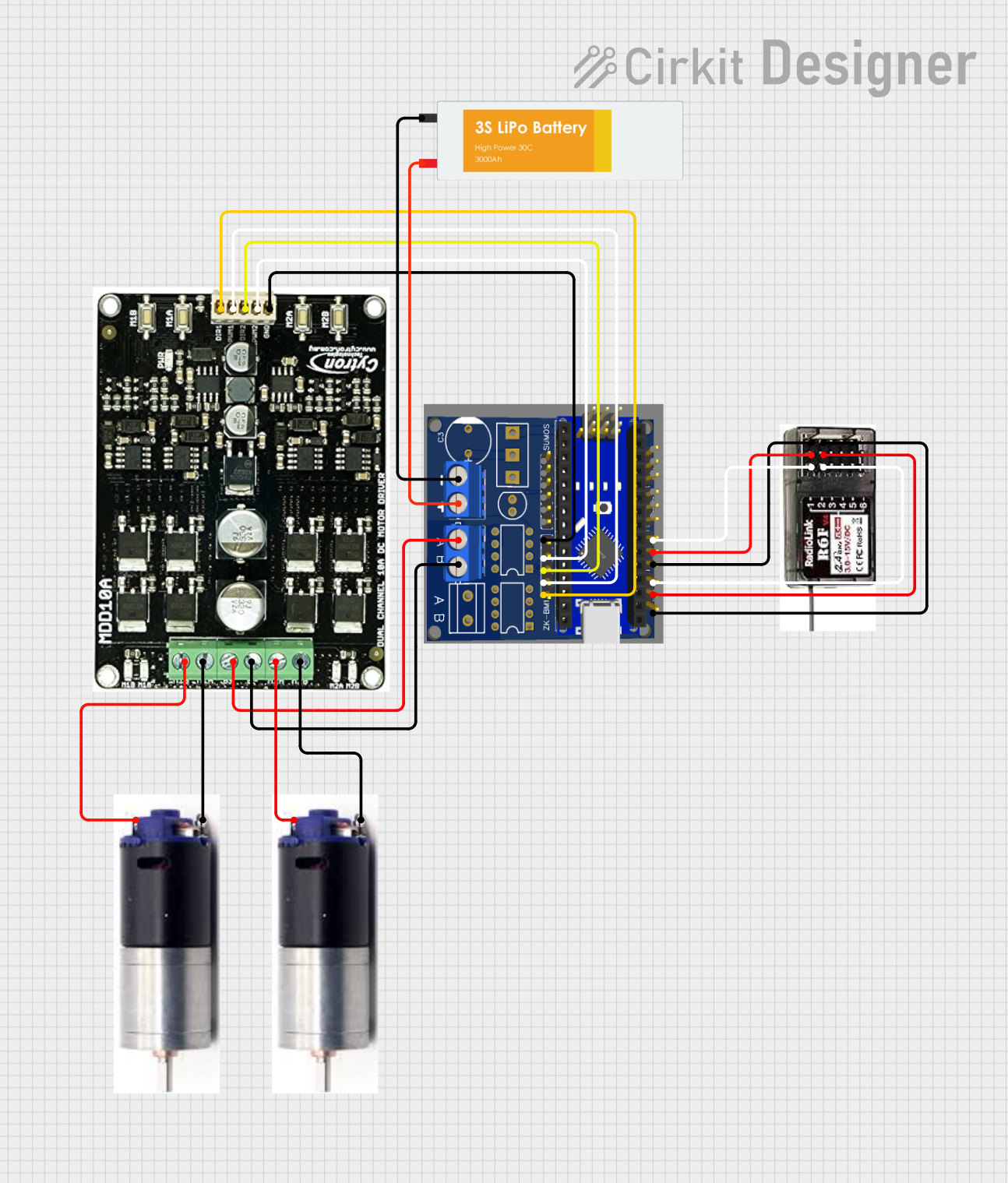
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with HAfiHA JDM11-6H

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Industrial automation systems
- Home appliances (e.g., washing machines, HVAC systems)
- Control panels and circuit switching
- Timing and sequencing circuits
- Motor control and protection systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Cikachi |
| Part Number | JDM11-6H |
| Operating Voltage | 12V DC / 24V DC / 220V AC |
| Contact Configuration | SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) |
| Contact Rating | 5A at 250V AC / 30V DC |
| Coil Power Consumption | 0.9W |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥ 100MΩ at 500V DC |
| Dielectric Strength | 1500V AC for 1 minute |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to +55°C |
| Dimensions | 28mm x 12mm x 15mm |
| Weight | 15g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
The HAfiHA JDM11-6H relay has a standard pinout for SPDT relays. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coil (+) | Positive terminal of the relay coil |
| 2 | Coil (-) | Negative terminal of the relay coil |
| 3 | Common (COM) | Common terminal for the switching contacts |
| 4 | Normally Open (NO) | Contact that is open when the relay is inactive |
| 5 | Normally Closed (NC) | Contact that is closed when the relay is inactive |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the HAfiHA JDM11-6H in a Circuit:
- Power the Relay Coil: Connect the coil terminals (Pin 1 and Pin 2) to the appropriate voltage source (e.g., 12V DC, 24V DC, or 220V AC, depending on the relay variant). Ensure the voltage matches the relay's rated operating voltage.
- Connect the Load:
- Connect the load to the Common (COM) terminal (Pin 3).
- Use the Normally Open (NO) terminal (Pin 4) if you want the load to be powered only when the relay is activated.
- Use the Normally Closed (NC) terminal (Pin 5) if you want the load to be powered when the relay is inactive.
- Control the Relay: Use a microcontroller, switch, or other control circuit to energize the relay coil. When the coil is energized, the relay switches from NC to NO.
Important Considerations and Best Practices:
- Voltage Matching: Ensure the relay's coil voltage matches the control circuit's output voltage.
- Current Rating: Do not exceed the relay's contact current rating (5A at 250V AC or 30V DC).
- Flyback Diode: When using the relay with a DC coil, add a flyback diode across the coil terminals to protect the control circuit from voltage spikes.
- Mounting: Secure the relay in a stable position to prevent mechanical stress or vibration.
Example: Connecting the HAfiHA JDM11-6H to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the relay using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pin connected to the relay's coil
const int relayPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the relay pin as an output
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Activate the relay (coil energized)
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay on for 1 second
// Deactivate the relay (coil de-energized)
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay off for 1 second
}
Note: Use a transistor or relay driver circuit to interface the Arduino with the relay, as the Arduino's GPIO pins cannot directly supply enough current to energize the relay coil.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
Relay Not Switching:
- Cause: Insufficient voltage or current to the coil.
- Solution: Verify the coil voltage and ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current.
Load Not Powered:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring of the load to the relay terminals.
- Solution: Double-check the connections to the COM, NO, and NC terminals.
Relay Buzzing Noise:
- Cause: Unstable or insufficient power supply to the coil.
- Solution: Use a stable power source and ensure the voltage matches the relay's rated voltage.
Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the relay's contact current rating.
- Solution: Ensure the load current does not exceed 5A.
FAQs:
Q: Can I use the HAfiHA JDM11-6H with an AC load?
- A: Yes, the relay supports AC loads up to 250V at 5A.
Q: Do I need a flyback diode for an AC coil?
- A: No, flyback diodes are only required for DC coils to suppress voltage spikes.
Q: Can I use this relay for high-frequency switching?
- A: The relay is not designed for high-frequency switching. For such applications, consider using a solid-state relay (SSR).
Q: How do I identify the coil voltage variant of my relay?
- A: The coil voltage is typically printed on the relay's casing. Ensure it matches your circuit's requirements.