
How to Use MCB: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
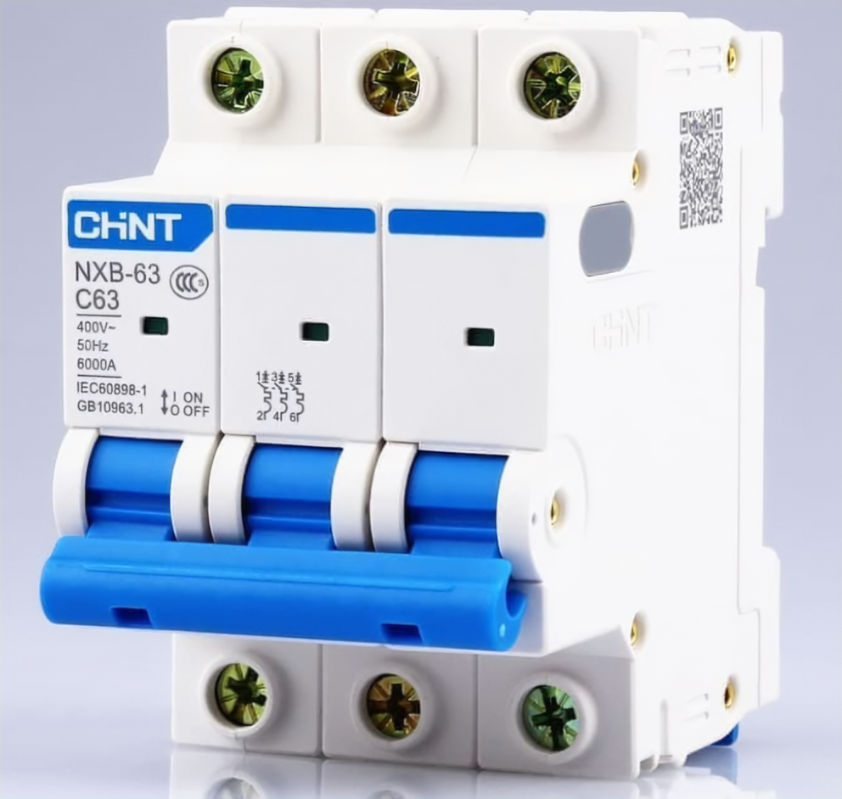

 Design with MCB in Cirkit Designer
Design with MCB in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an essential safety device in modern electrical installations. It is designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current resulting from an overload or a short circuit. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, an MCB can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. MCBs are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Explore Projects Built with MCB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer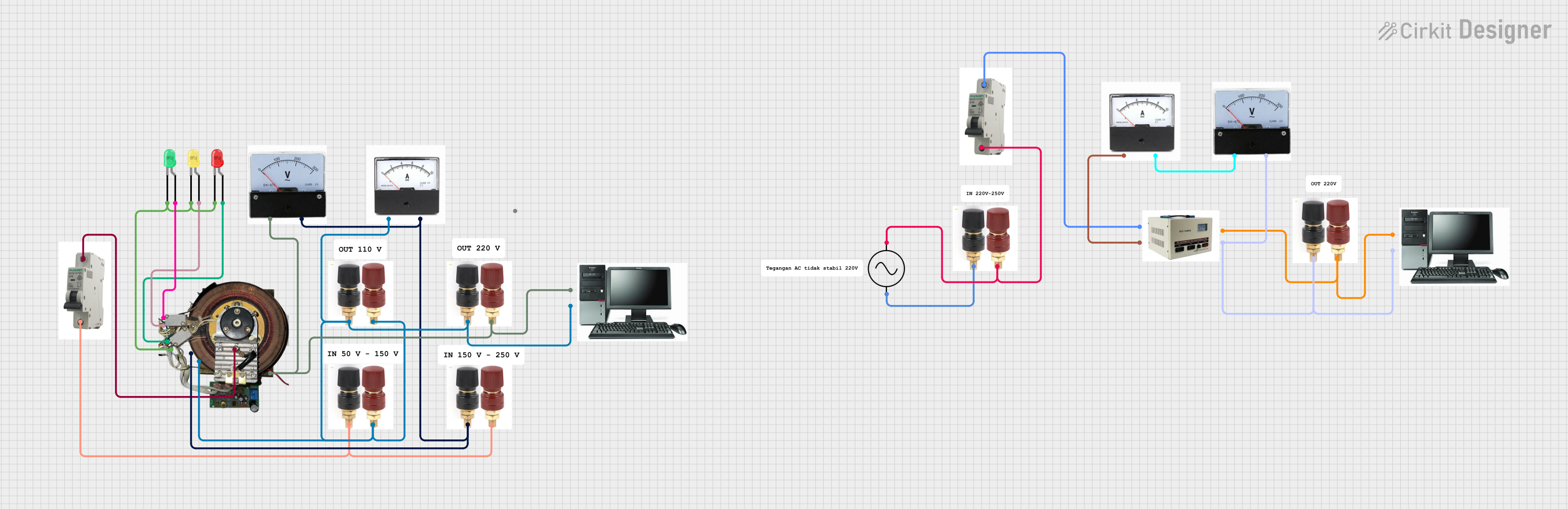
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer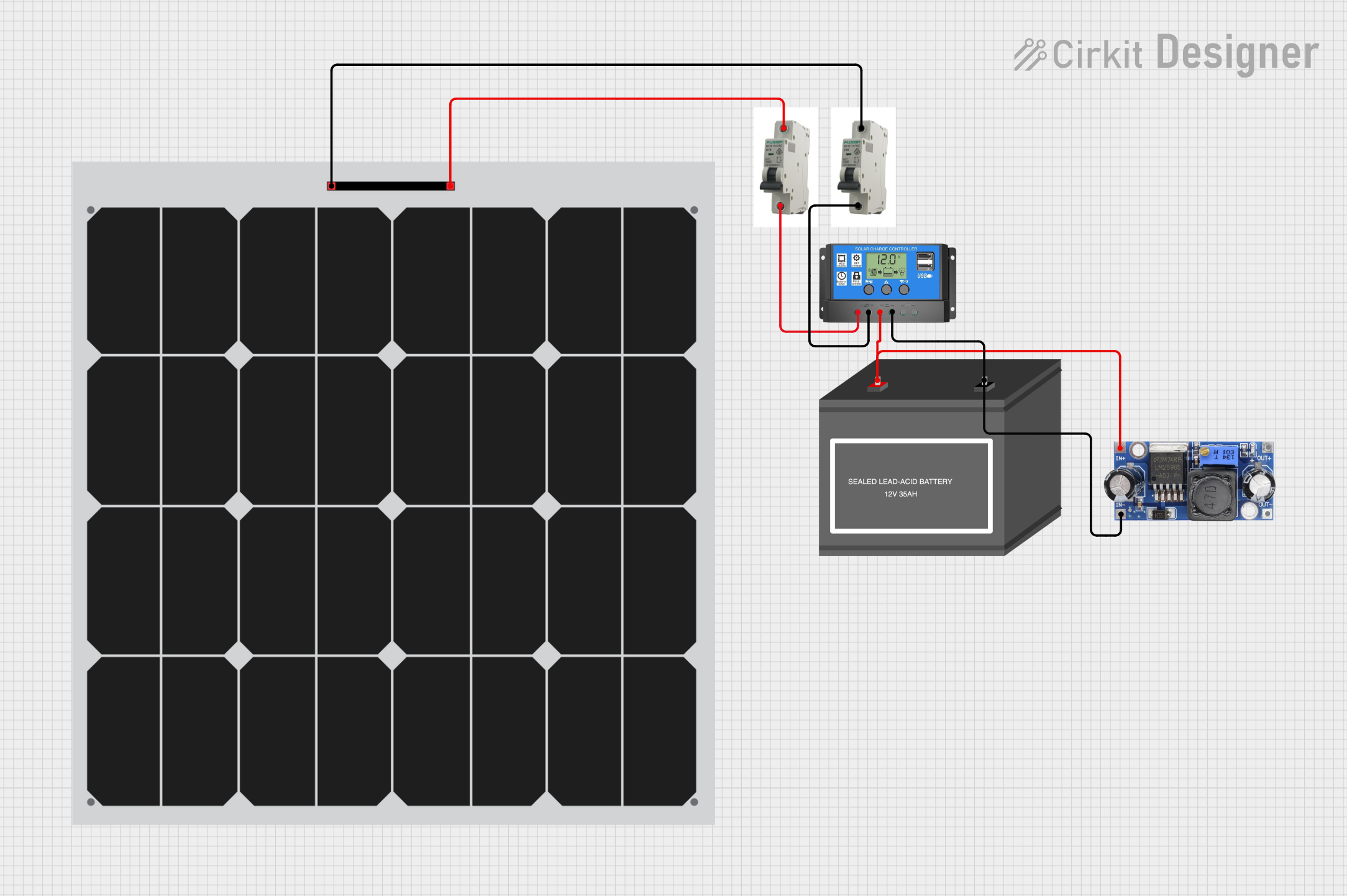
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MCB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential electrical circuits for lighting, heating, and power outlets
- Commercial building electrical systems
- Industrial control panels and machinery
- Protection for motors and transformers
- Overcurrent protection in consumer electronics
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Rated Current (In): The maximum continuous current that the MCB can carry without tripping.
- Rated Voltage (Ue): The operating voltage range of the MCB.
- Breaking Capacity (Icn): The maximum fault current that the MCB can interrupt without damage.
- Tripping Characteristics: The response curve of the MCB to various levels of overcurrent, typically labeled as B, C, or D curves.
- Number of Poles: Single-pole, double-pole, triple-pole, or four-pole configurations, depending on the application.
- Energy Limiting Class: The level of energy let-through by the MCB during fault conditions.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phase Input (Live) | Connect to the live supply line |
| 2 | Phase Output (Load) | Connect to the load |
| 3 | Neutral Input (if applicable) | Connect to the neutral line |
| 4 | Neutral Output (if applicable) | Connect to the load |
Note: The pin configuration may vary based on the number of poles in the MCB.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MCB in a Circuit
- Selection: Choose an MCB with the appropriate rated current and tripping characteristics for your application.
- Installation: Mount the MCB onto a DIN rail within a distribution board or consumer unit.
- Wiring: Connect the incoming live wire to the MCB's input terminal and the outgoing live wire to the load from the MCB's output terminal. For multi-pole MCBs, ensure that all phases and neutral (if applicable) are connected correctly.
- Testing: Once installed, switch on the MCB and test the circuit for proper operation. Use a test button if available to ensure the tripping mechanism functions correctly.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the MCB's rated current is slightly higher than the normal operating current of the circuit.
- Do not exceed the MCB's rated voltage.
- Regularly inspect the MCB for any signs of damage or wear.
- Test the MCB periodically using the built-in test function to ensure it trips as expected.
- Always follow local electrical codes and standards when installing an MCB.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- MCB Tripping Frequently: This could be due to an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, or a faulty MCB.
- MCB Not Tripping: The MCB may be undersized for the circuit, or there could be a mechanical failure within the MCB.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Frequent Tripping: Check the circuit for any signs of overload or short circuits. Reduce the load or repair the fault before resetting the MCB.
- MCB Not Tripping: Ensure the MCB is correctly sized for the circuit. If the MCB is of the correct rating and the problem persists, replace the MCB.
FAQs
Q: Can I replace a fuse with an MCB? A: Yes, an MCB can be used as a more convenient and reusable alternative to a fuse, provided it is correctly rated for the circuit.
Q: How do I know if my MCB is faulty? A: If an MCB trips frequently without an apparent overload or short circuit, or if it fails to trip when a fault is present, it may be faulty and should be tested or replaced.
Q: What does the 'B', 'C', or 'D' rating on an MCB mean? A: These letters indicate the tripping characteristics of the MCB. 'B' type trips at 3-5 times the rated current, 'C' type at 5-10 times, and 'D' type at 10-20 times, catering to different levels of inrush currents.
Note: This documentation is for informational purposes only. Always consult a professional electrician for electrical work and adhere to local regulations and safety standards.