
How to Use AC Wire: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
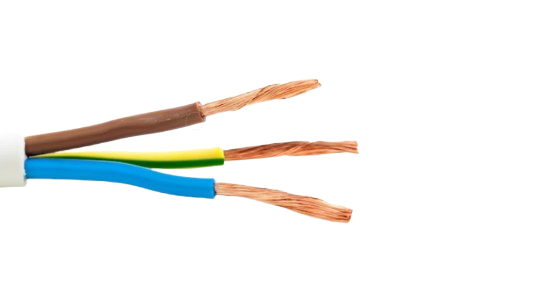
 Design with AC Wire in Cirkit Designer
Design with AC Wire in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An AC Wire is a fundamental component in electrical circuits, designed to carry alternating current (AC) from one point to another. It is essential in residential, commercial, and industrial power systems. AC wires are used in a variety of applications, including power transmission, home wiring, and in connecting electrical appliances.
Explore Projects Built with AC Wire
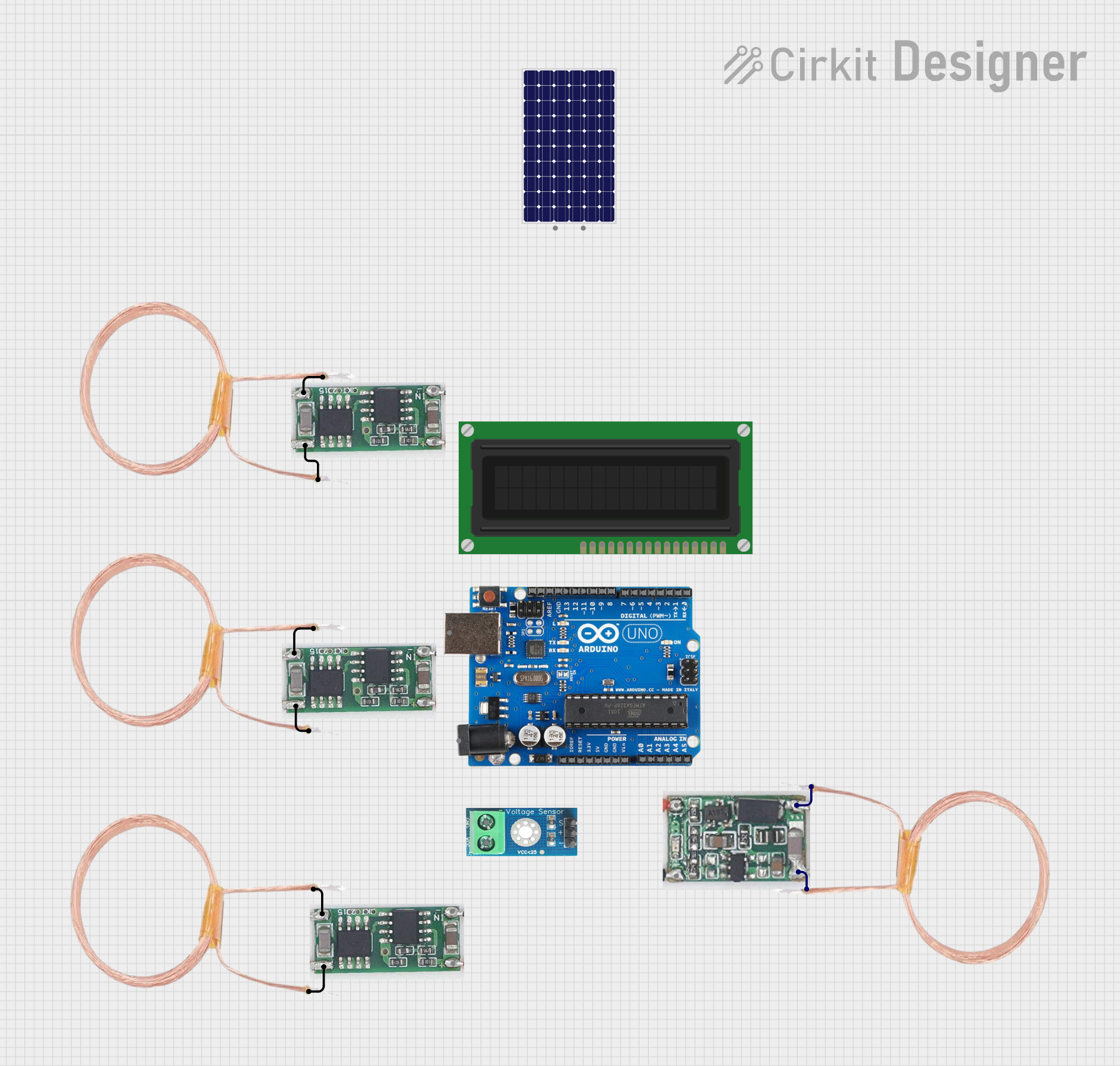
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer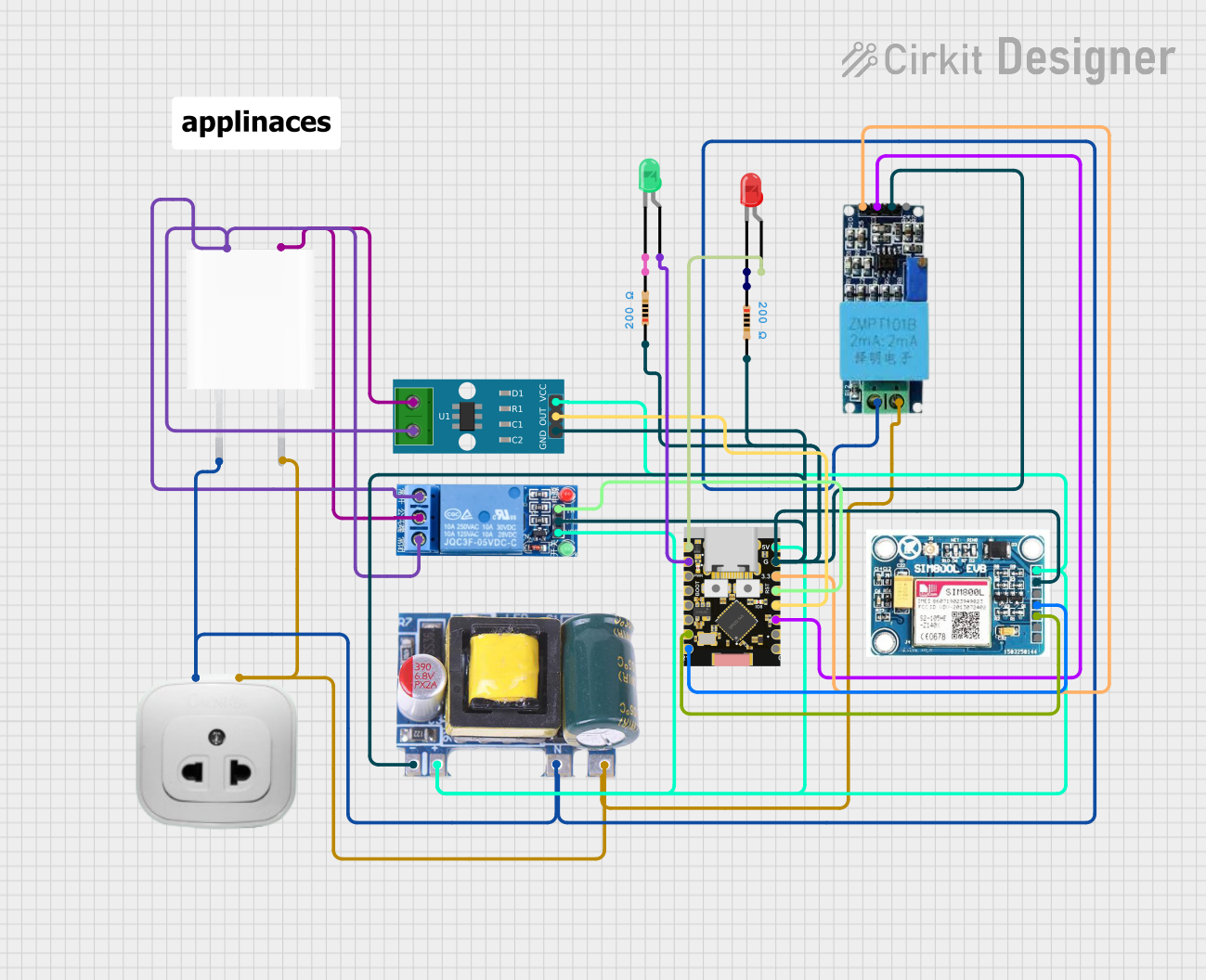
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer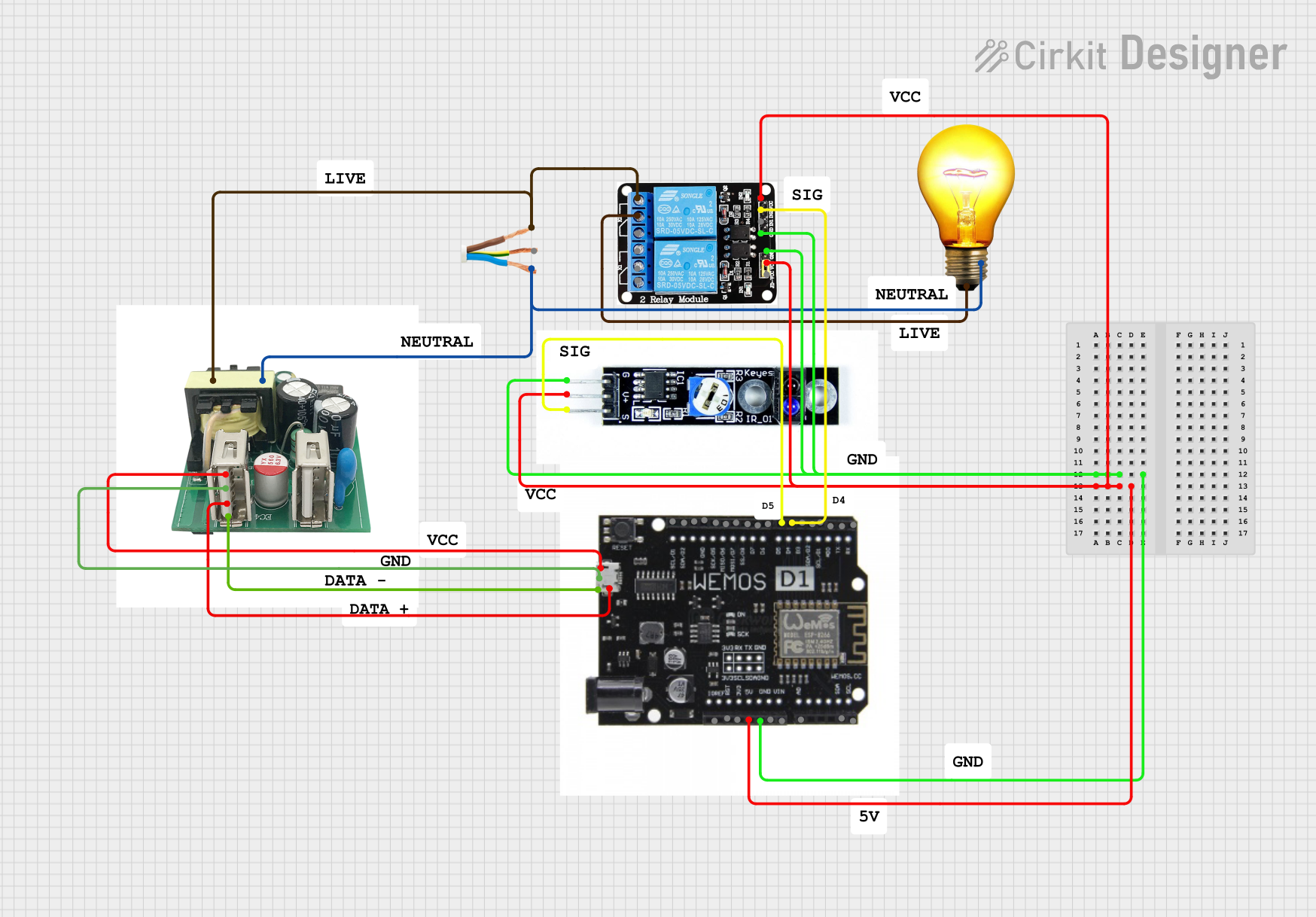
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with AC Wire

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Conductor Material: Copper or aluminum, typically stranded or solid.
- Insulation Material: PVC, rubber, Teflon, or other dielectrics.
- Voltage Rating: Varies by application, commonly from 110/120V to 220/240V in residential wiring, and up to several kilovolts for transmission lines.
- Current Rating: Depends on the wire gauge and material, but must be chosen according to the expected load to prevent overheating.
- Temperature Rating: The maximum operating temperature before the insulation material degrades.
- Wire Gauge: Measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG) or square millimeters (mm²), indicating the cross-sectional area of the wire.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
AC wires do not have a "pin" configuration as they are not components with pins but rather conductive paths. However, the wire gauge and current capacity are critical specifications that can be tabulated as follows:
| AWG Size | Diameter (mm) | Current Capacity (Amps) |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | 1.628 | 15 |
| 12 | 2.053 | 20 |
| 10 | 2.588 | 30 |
| 8 | 3.264 | 40 |
| 6 | 4.115 | 55 |
| 4 | 5.189 | 70 |
| 2 | 6.544 | 95 |
Note: The current capacity values are approximate and can vary based on the insulation material, ambient temperature, and installation conditions.
Usage Instructions
How to Use AC Wire in a Circuit
- Selecting the Wire: Choose an AC wire with the appropriate gauge for the current load and voltage rating for the application.
- Stripping Insulation: Use a wire stripper to remove the insulation at the ends of the wire where connections will be made.
- Making Connections: Twist the stripped wire ends and connect them to terminals or other wires using wire nuts, terminal blocks, or soldering, depending on the application.
- Securing the Wire: Use cable clips or conduits to secure the wire in place, ensuring it is protected from physical damage and not subject to tension.
- Testing: After installation, test the circuit with a multimeter to ensure proper voltage and that there are no short circuits.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always turn off the power before working on electrical circuits.
- Use wires with insulation suitable for the environment (e.g., moisture-resistant for outdoor use).
- Ensure that the wire gauge is appropriate for the current to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Follow local electrical codes and standards for installation and safety.
- Label wiring appropriately for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Overheating: If a wire is too hot to touch, it may be undersized for the current it is carrying.
- Voltage Drop: Long wire runs can result in a significant voltage drop, affecting the performance of electrical devices.
- Intermittent Power: Loose connections can cause flickering lights or intermittent power to outlets.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Overheating: Replace the wire with one of a larger gauge that can handle the current load.
- Voltage Drop: Minimize the length of the wire run or use a wire with a larger cross-sectional area to reduce resistance.
- Intermittent Power: Check all connections for tightness and security. Re-terminate any loose connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I use any wire for AC applications? A: No, you must use a wire that is rated for the voltage and current of your specific application and complies with electrical codes.
Q: How do I know which wire gauge to use? A: Use a wire gauge that matches or exceeds the current capacity required for your circuit. Refer to the National Electrical Code (NEC) or consult a professional electrician.
Q: Is it safe to join different metals, like copper and aluminum? A: Joining dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion and is not recommended without proper connectors designed for that purpose.
Q: Can AC wires be run alongside data cables? A: AC wires can induce noise in data cables. It's best to run them separately or use shielded data cables if they must be run together.
Note: This documentation is for informational purposes only. Always consult a professional electrician for electrical work to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.