
How to Use Power Supply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Power Supply in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Supply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A power supply is a device that provides electrical energy to a circuit, converting AC or DC voltage from a source into a usable form for electronic components. It is an essential component in virtually all electronic systems, ensuring that devices receive the correct voltage and current for proper operation. Power supplies come in various types, including linear, switching, and unregulated, each suited for specific applications.
Explore Projects Built with Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer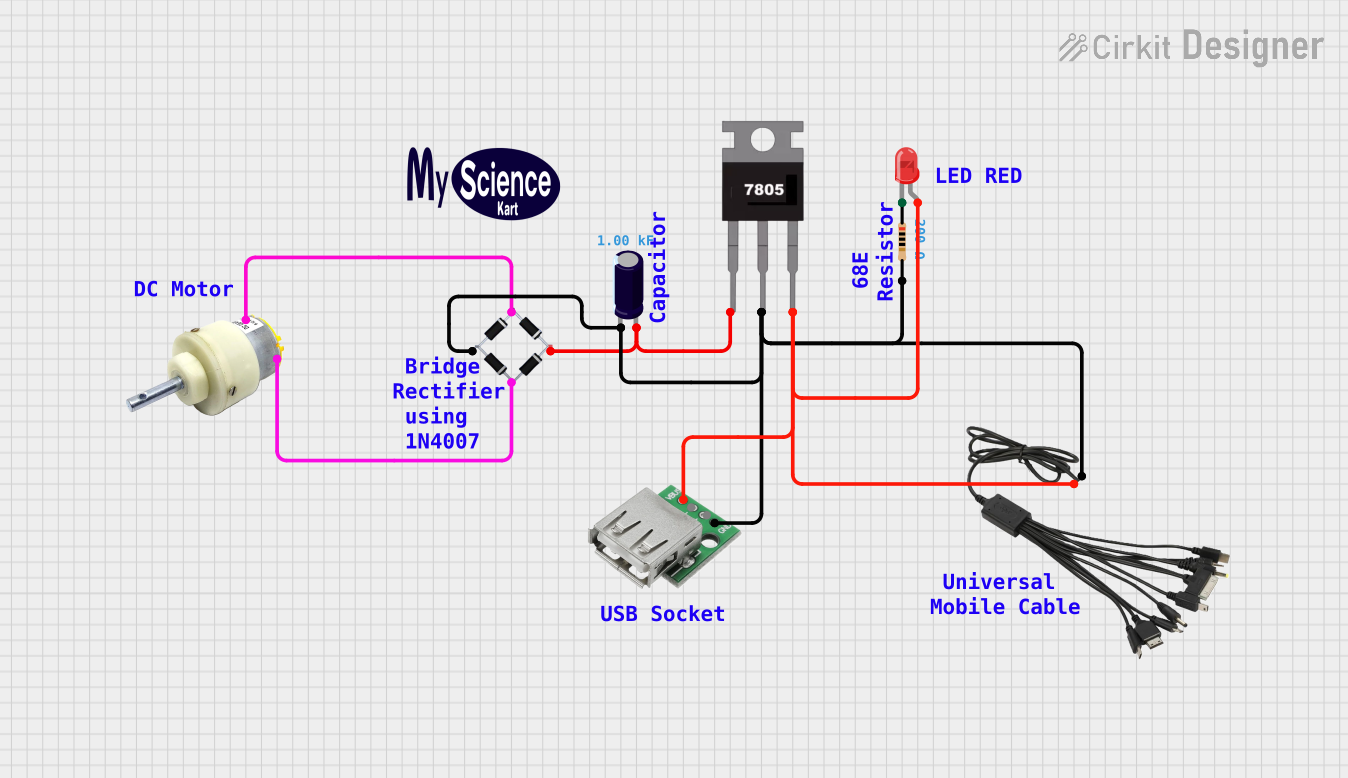
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer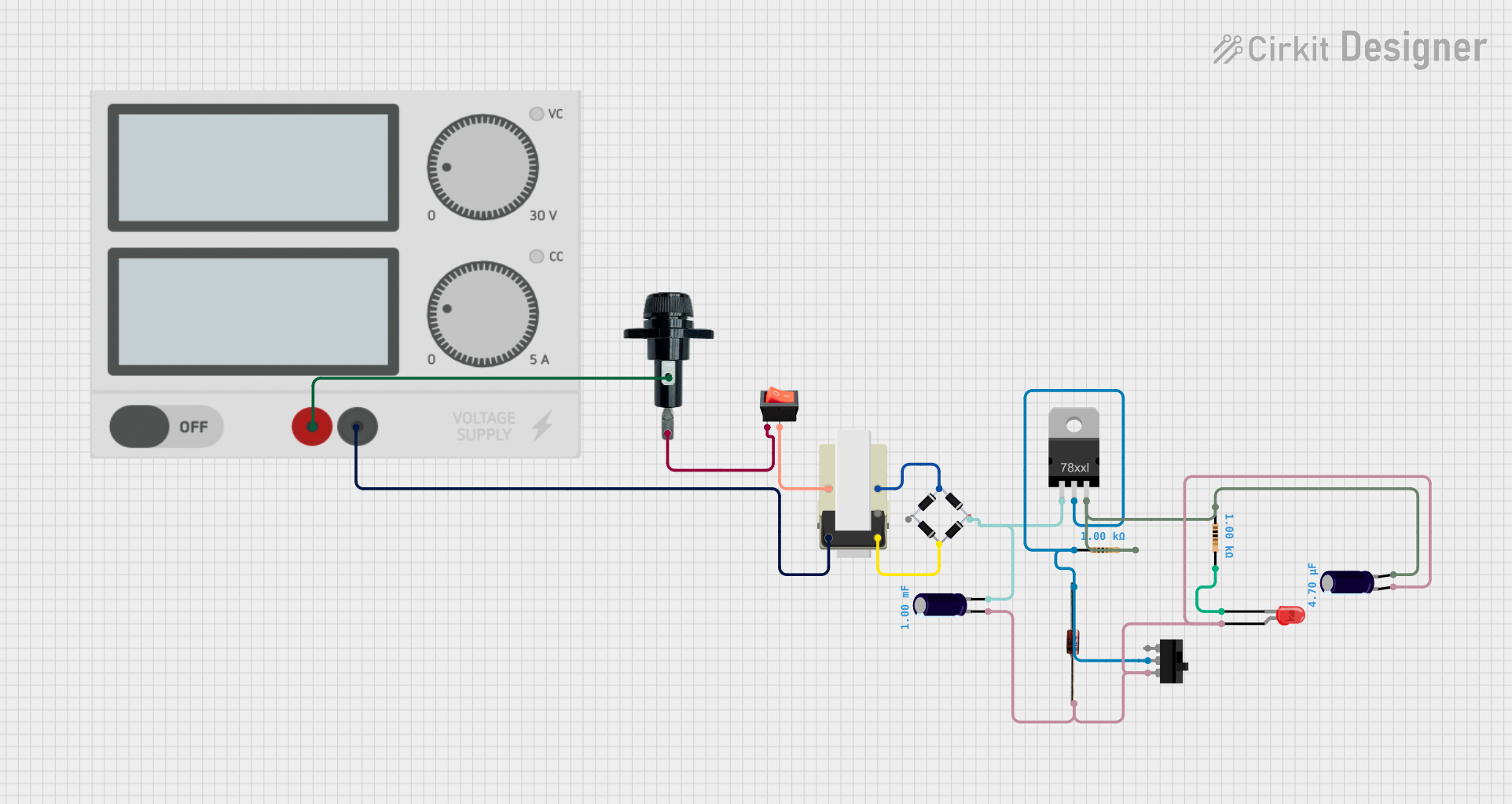
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators in embedded systems
- Supplying energy to consumer electronics such as laptops, smartphones, and TVs
- Providing stable voltage for industrial equipment and machinery
- Charging batteries in portable devices
- Laboratory testing and prototyping of electronic circuits
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical power supply. Note that specific models may vary in their ratings and features.
General Specifications
- Input Voltage: 100-240V AC (typical for wall-powered supplies)
- Output Voltage: 3.3V, 5V, 12V, 24V DC (common fixed outputs)
- Output Current: 0.5A to 10A (depending on the model)
- Power Rating: 5W to 500W (varies by application)
- Efficiency: 70% to 95% (higher for switching power supplies)
- Ripple and Noise: <50mV (for regulated supplies)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
For a DC power supply with a barrel jack connector, the pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Supplies the positive DC voltage output. |
| Negative (-) | Ground connection for the circuit. |
For a power supply with screw terminals:
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| V+ | Supplies the positive DC voltage output. |
| V- | Ground connection for the circuit. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Power Supply in a Circuit
- Determine Voltage and Current Requirements: Identify the voltage and current requirements of your circuit or device. Ensure the power supply can meet these specifications.
- Connect the Power Supply:
- For barrel jack connectors, plug the jack into the corresponding socket on your device.
- For screw terminals, connect the V+ terminal to the positive input of your circuit and the V- terminal to the ground.
- Power On the Supply: Turn on the power supply and verify the output voltage using a multimeter before connecting it to sensitive components.
- Monitor the Circuit: Ensure the circuit operates as expected and that the power supply does not overheat or exceed its rated capacity.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Matching: Always match the output voltage of the power supply to the voltage rating of your circuit.
- Current Capacity: Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current without exceeding its maximum rating.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of the connections to avoid damaging components.
- Heat Dissipation: Allow adequate ventilation for the power supply to prevent overheating.
- Short Circuit Protection: Use a power supply with built-in protection features or add external fuses to safeguard your circuit.
Example: Using a Power Supply with an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO using a 9V DC power supply:
- Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to the Arduino's barrel jack center pin.
- Connect the negative terminal to the outer sleeve of the barrel jack.
- Ensure the power supply is set to 9V and can provide at least 500mA of current.
Here is an example Arduino sketch to blink an LED while powered by the external supply:
// Blink an LED connected to pin 13
// Ensure the Arduino is powered by a 9V DC power supply
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Check if the power supply is properly connected to the input source.
- Verify that the power switch is turned on (if applicable).
- Inspect for blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers.
Overheating:
- Ensure the power supply is not overloaded. Reduce the load if necessary.
- Provide adequate ventilation or cooling to the power supply.
Voltage Fluctuations:
- Use a regulated power supply to maintain a stable output voltage.
- Check for loose connections or damaged cables.
Device Not Powering On:
- Verify the polarity of the connections.
- Ensure the output voltage matches the device's requirements.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a power supply with a higher current rating than my device requires?
A: Yes, as long as the voltage matches, the device will only draw the current it needs.
Q: What happens if I reverse the polarity of the connections?
A: Reversing polarity can damage your circuit. Always double-check connections before powering on.
Q: How do I know if my power supply is regulated?
A: Regulated power supplies maintain a constant output voltage regardless of load changes. Check the product specifications or test the output with varying loads.
Q: Can I use a single power supply for multiple devices?
A: Yes, provided the total current draw of all devices does not exceed the power supply's maximum current rating.