
How to Use SW420: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with SW420 in Cirkit Designer
Design with SW420 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
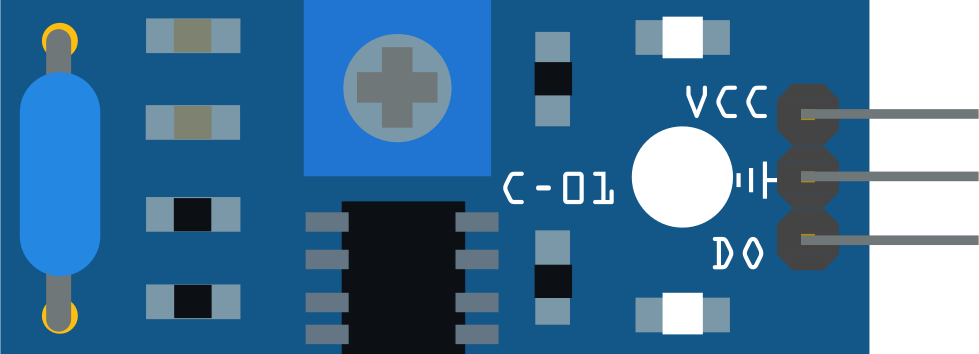
The SW420 is a tilt switch designed to detect changes in orientation or position. It operates by closing or opening its internal contacts when tilted beyond a specific angle. This component is widely used in applications such as motion detection, anti-theft systems, orientation sensing, and robotics. Its simplicity and reliability make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
The SW420 is manufactured by ARDUINO, with the part ID "UNO," and is compatible with a variety of microcontrollers, including the Arduino UNO.
Explore Projects Built with SW420
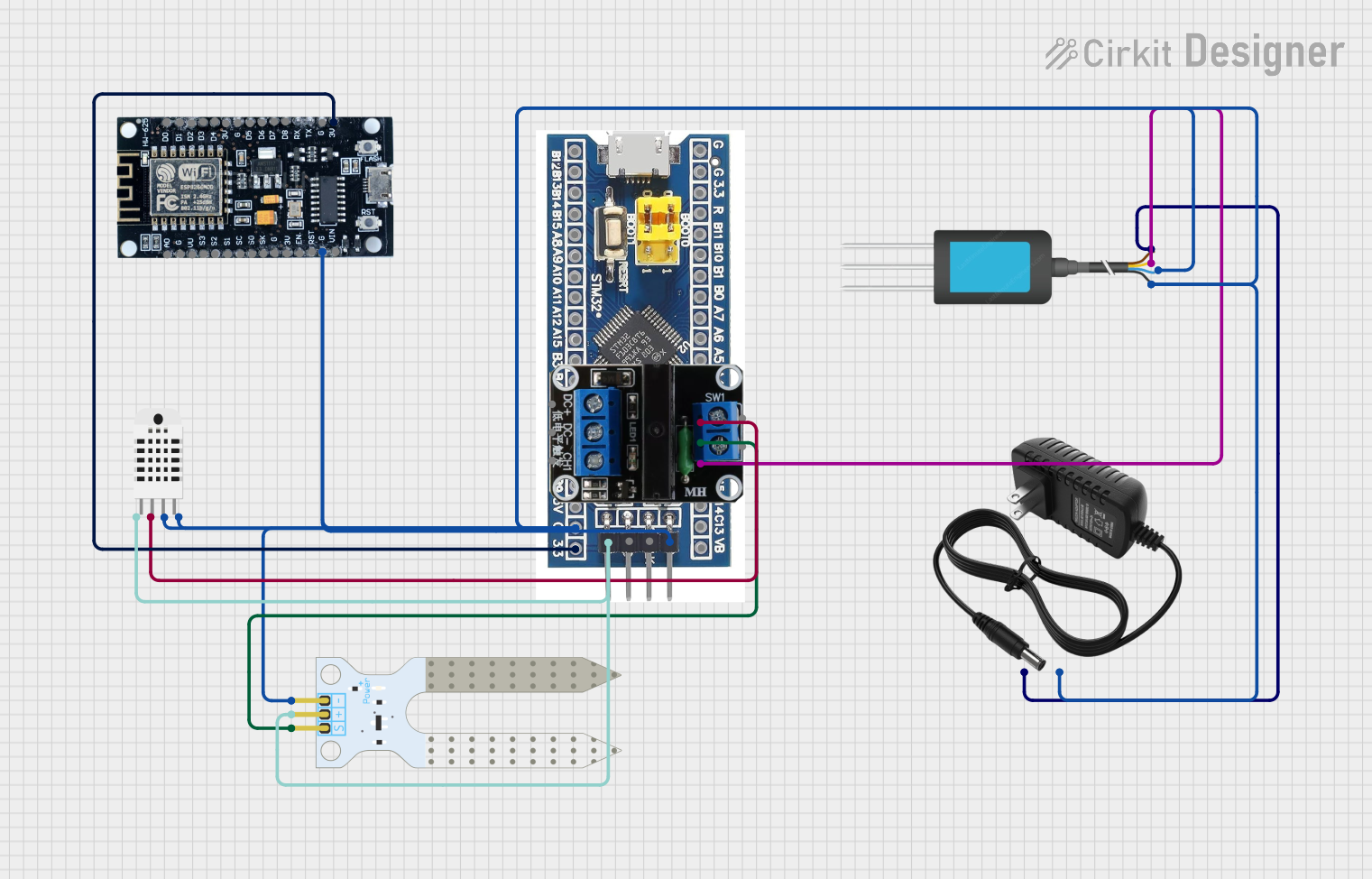
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer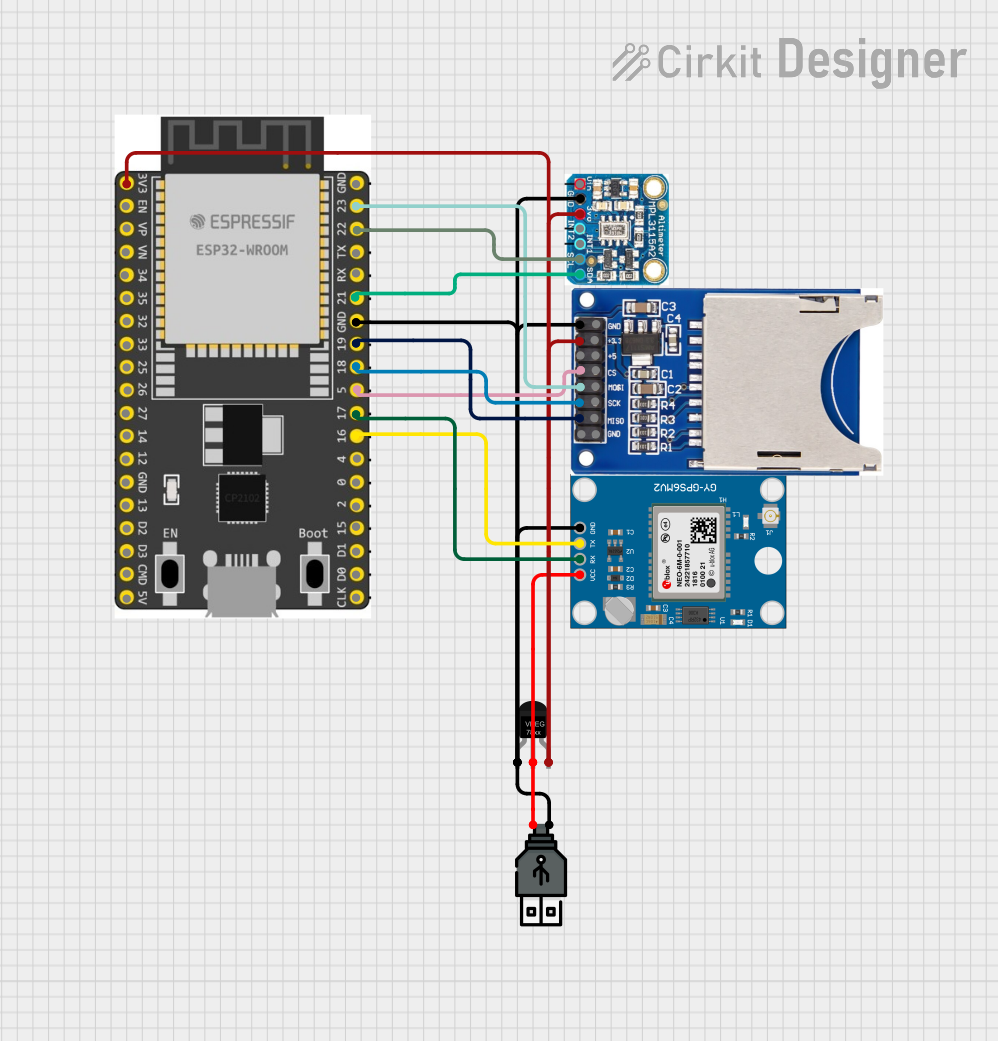
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer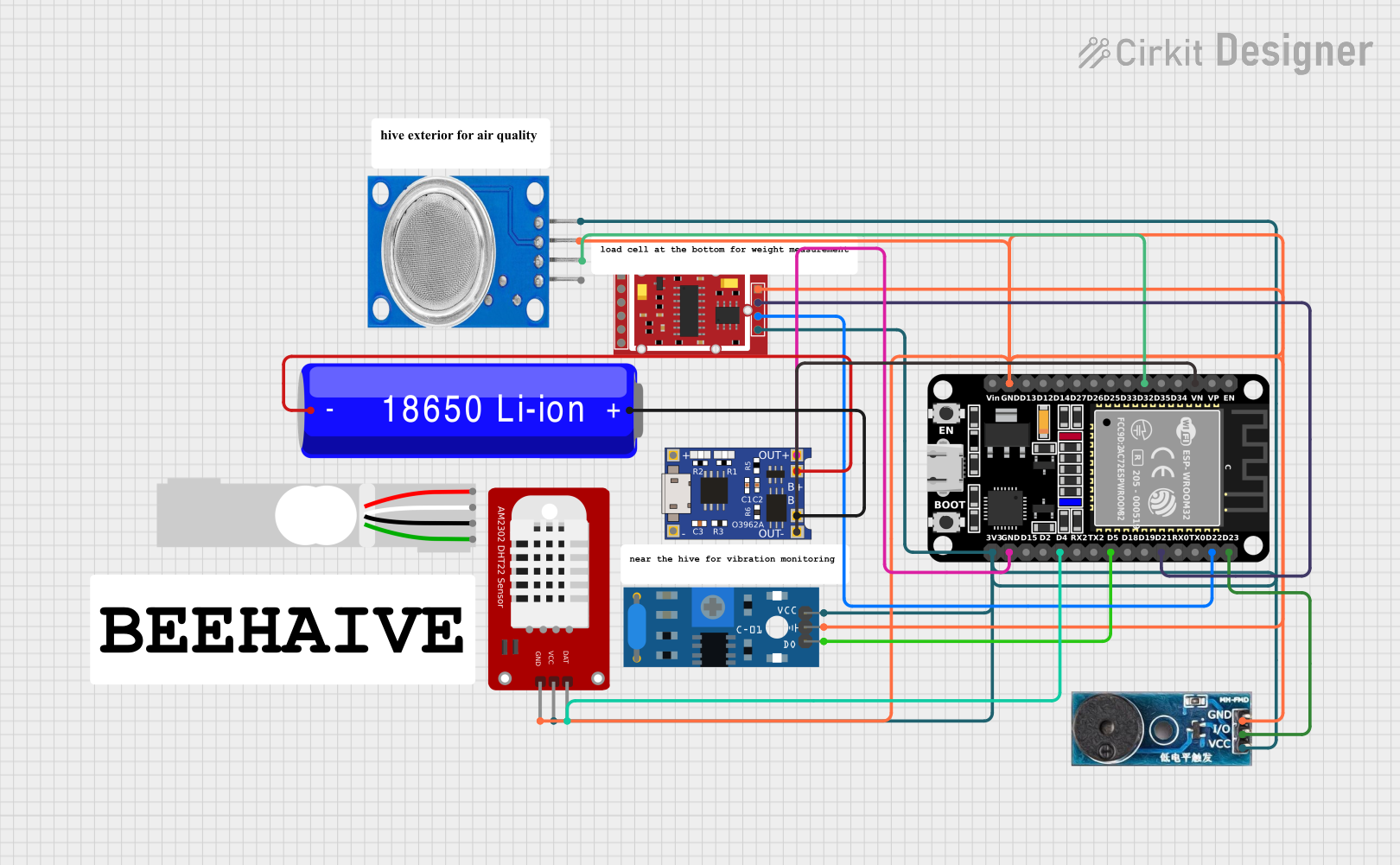
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SW420

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The SW420 tilt switch is a passive component with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | ≤ 20mA |
| Output Type | Digital (High/Low) |
| Tilt Angle Threshold | Typically 15° to 45° |
| Dimensions | 14mm x 5mm x 5mm (approx.) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The SW420 module typically comes with three pins:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V to 5V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| DO | Digital output pin (HIGH when stable, LOW when tilted) |
Usage Instructions
The SW420 tilt switch is straightforward to use in a circuit. Below are the steps and best practices for integrating it into your project:
Wiring the Component:
- Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the
DO(Digital Output) pin to a digital input pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- Connect the
Circuit Example:
- Use a pull-up resistor (typically 10kΩ) on the
DOpin to ensure stable readings. - Optionally, add a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) between
VCCandGNDto reduce noise.
- Use a pull-up resistor (typically 10kΩ) on the
Arduino UNO Example Code: Below is an example code snippet to interface the SW420 with an Arduino UNO:
// SW420 Tilt Switch Example Code // Connect SW420 DO pin to Arduino digital pin 2 const int tiltPin = 2; // Digital pin connected to SW420 DO pin const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED pin for status indication void setup() { pinMode(tiltPin, INPUT); // Set tiltPin as input pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set ledPin as output Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication } void loop() { int tiltState = digitalRead(tiltPin); // Read the state of the tilt switch if (tiltState == LOW) { // If the switch is tilted, turn on the LED digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); Serial.println("Tilt detected!"); } else { // If the switch is stable, turn off the LED digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); Serial.println("No tilt detected."); } delay(100); // Small delay for stability }Important Considerations:
- Ensure the SW420 is mounted securely in your project to avoid false triggers due to vibrations.
- Avoid exposing the component to excessive moisture or extreme temperatures beyond its operating range.
- Use debounce logic in your code if the tilt switch is prone to rapid state changes.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: The SW420 is not detecting tilt.
- Solution: Verify the wiring connections, especially the
VCCandGNDpins. Ensure the power supply voltage is within the specified range (3.3V to 5V).
- Solution: Verify the wiring connections, especially the
Issue: The output is unstable or noisy.
- Solution: Add a pull-up resistor (10kΩ) to the
DOpin and a decoupling capacitor (0.1µF) betweenVCCandGNDto stabilize the signal.
- Solution: Add a pull-up resistor (10kΩ) to the
Issue: The Arduino does not respond to tilt events.
- Solution: Check the code to ensure the correct digital pin is being read. Use the
Serial.println()function to debug the tilt state.
- Solution: Check the code to ensure the correct digital pin is being read. Use the
Issue: False triggers occur due to vibrations.
- Solution: Mount the SW420 securely and consider adding software debounce logic to filter out rapid state changes.
FAQs
Q: Can the SW420 detect small tilts?
A: The SW420 is designed to detect tilts within a threshold angle of 15° to 45°. For smaller tilt detection, consider using a more sensitive sensor like an accelerometer.Q: Is the SW420 suitable for outdoor use?
A: The SW420 is not waterproof or weatherproof. If used outdoors, it must be enclosed in a protective casing.Q: Can I use the SW420 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the SW420 operates within a voltage range of 3.3V to 5V, making it compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the SW420 tilt switch into your projects and troubleshoot any issues that arise.