
How to Use Solar pannel: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
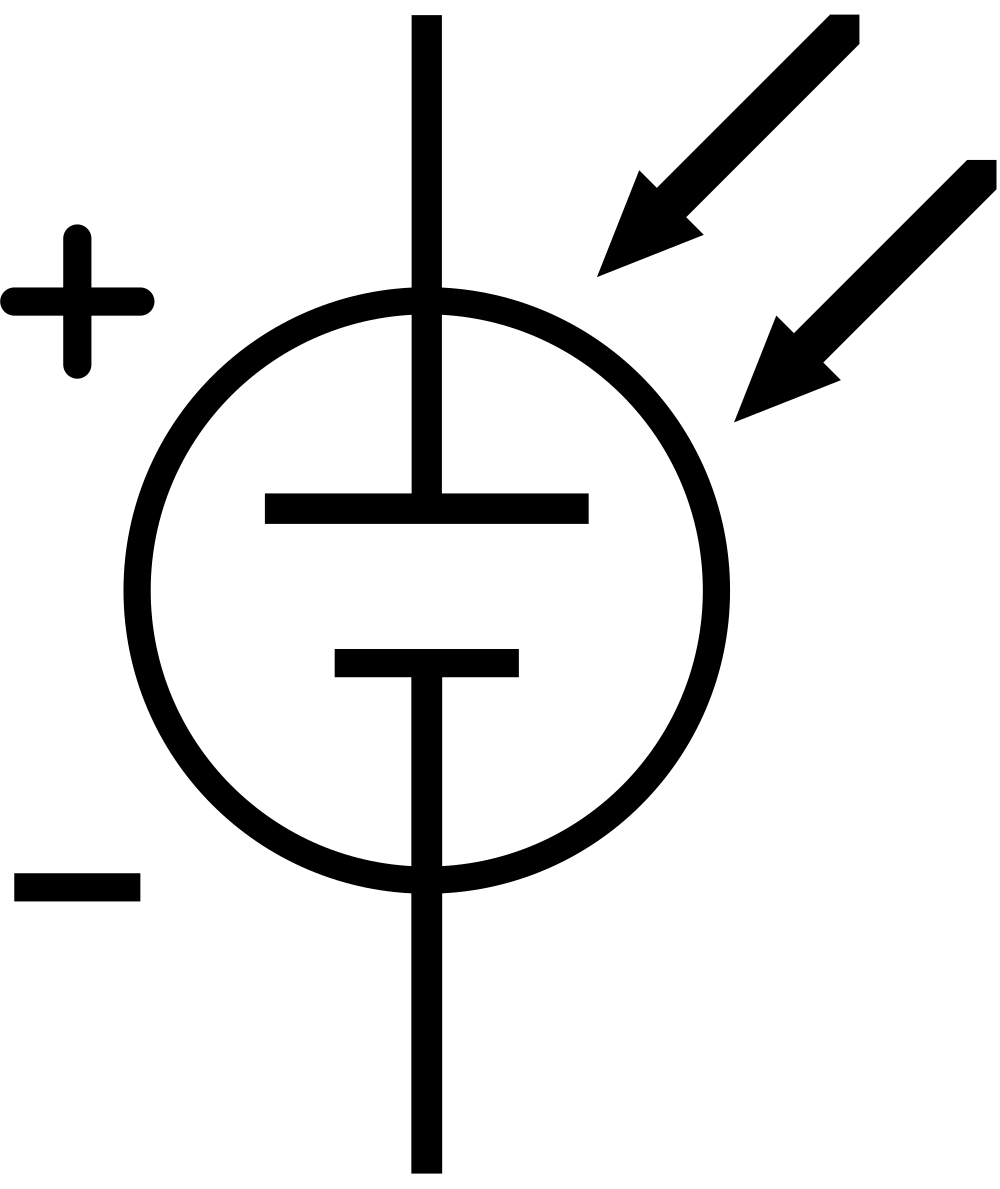
 Design with Solar pannel in Cirkit Designer
Design with Solar pannel in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electrical energy using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells are made of semiconductor materials that generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. Solar panels are widely used in renewable energy systems to provide clean and sustainable power.
Explore Projects Built with Solar pannel
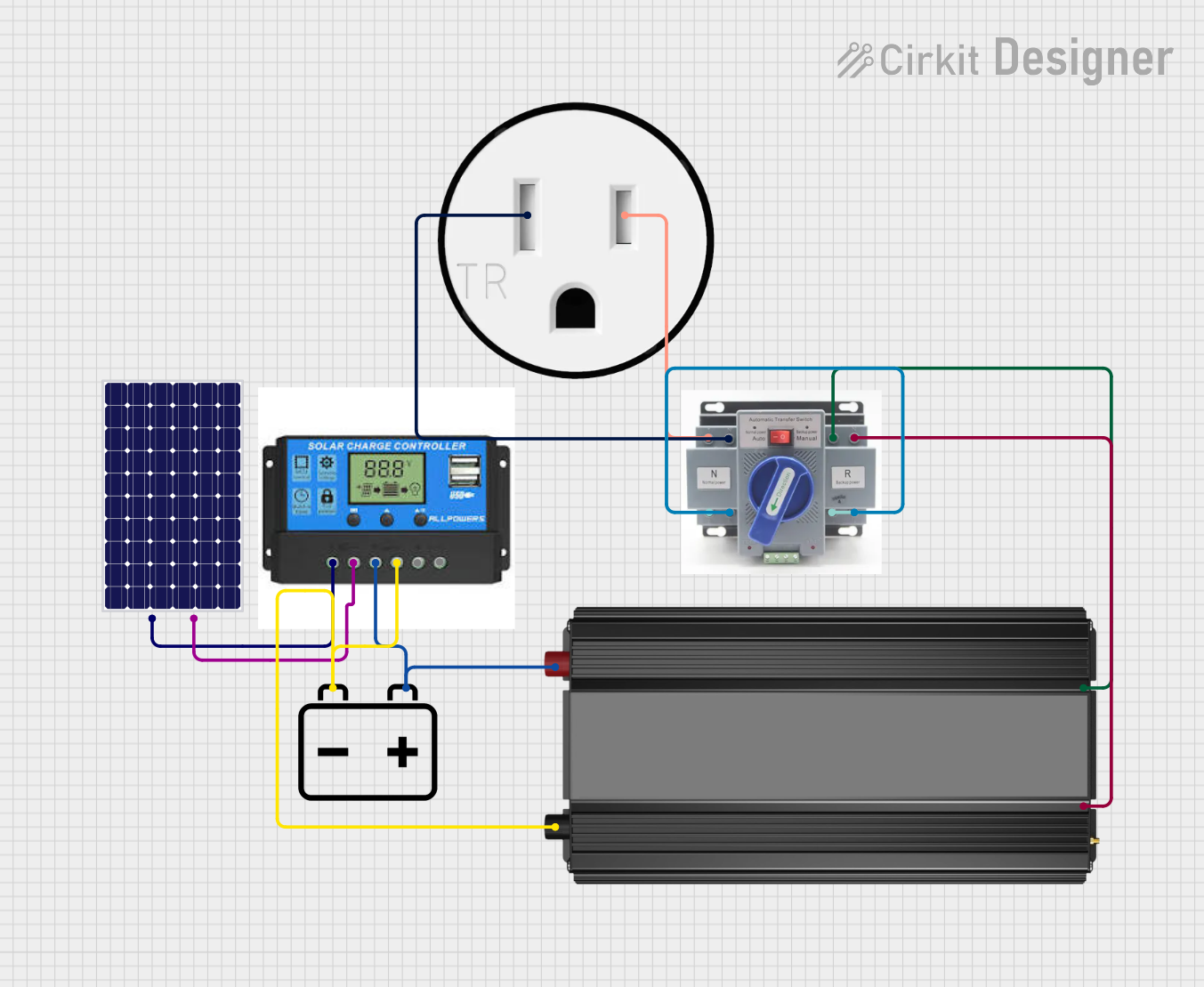
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer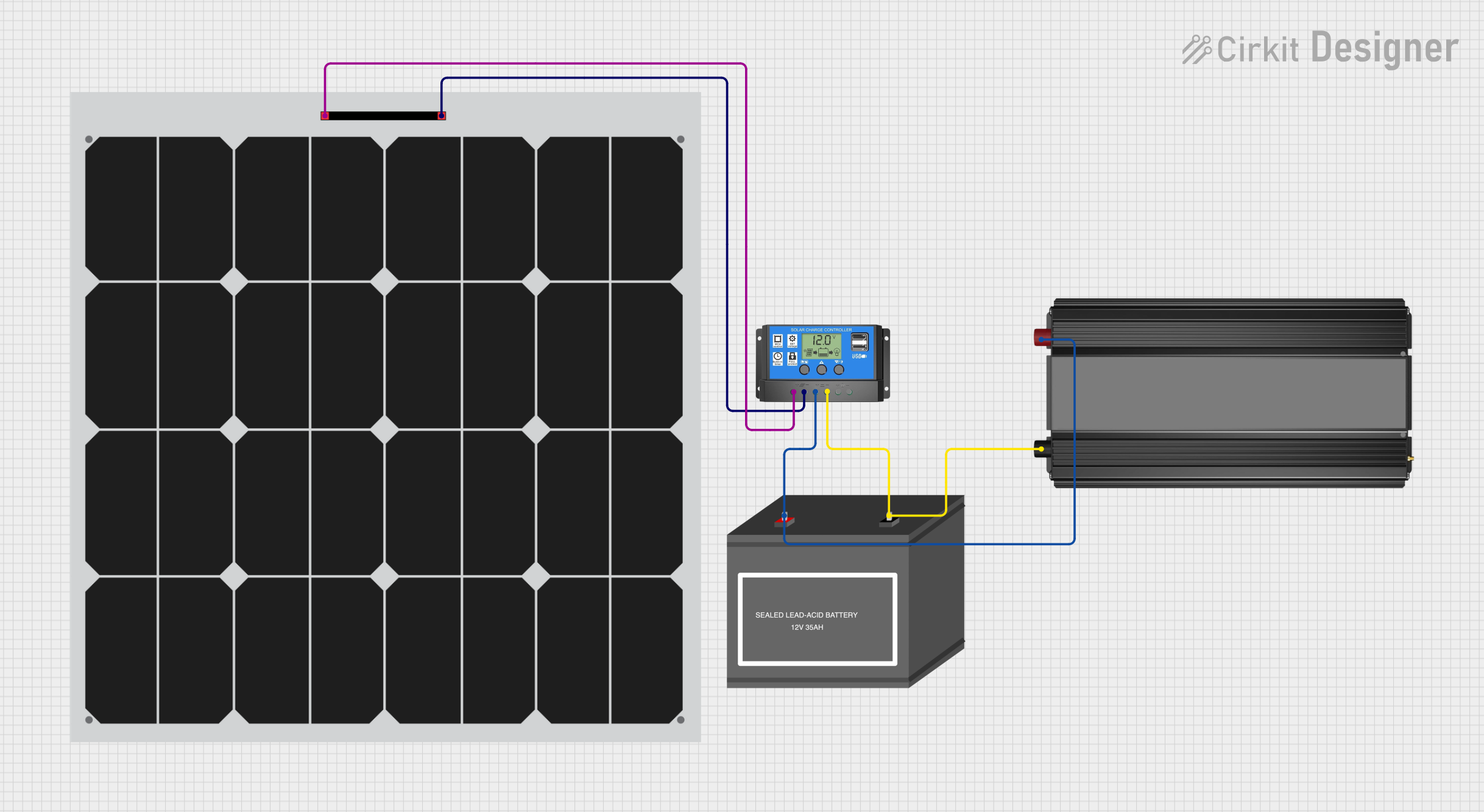
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer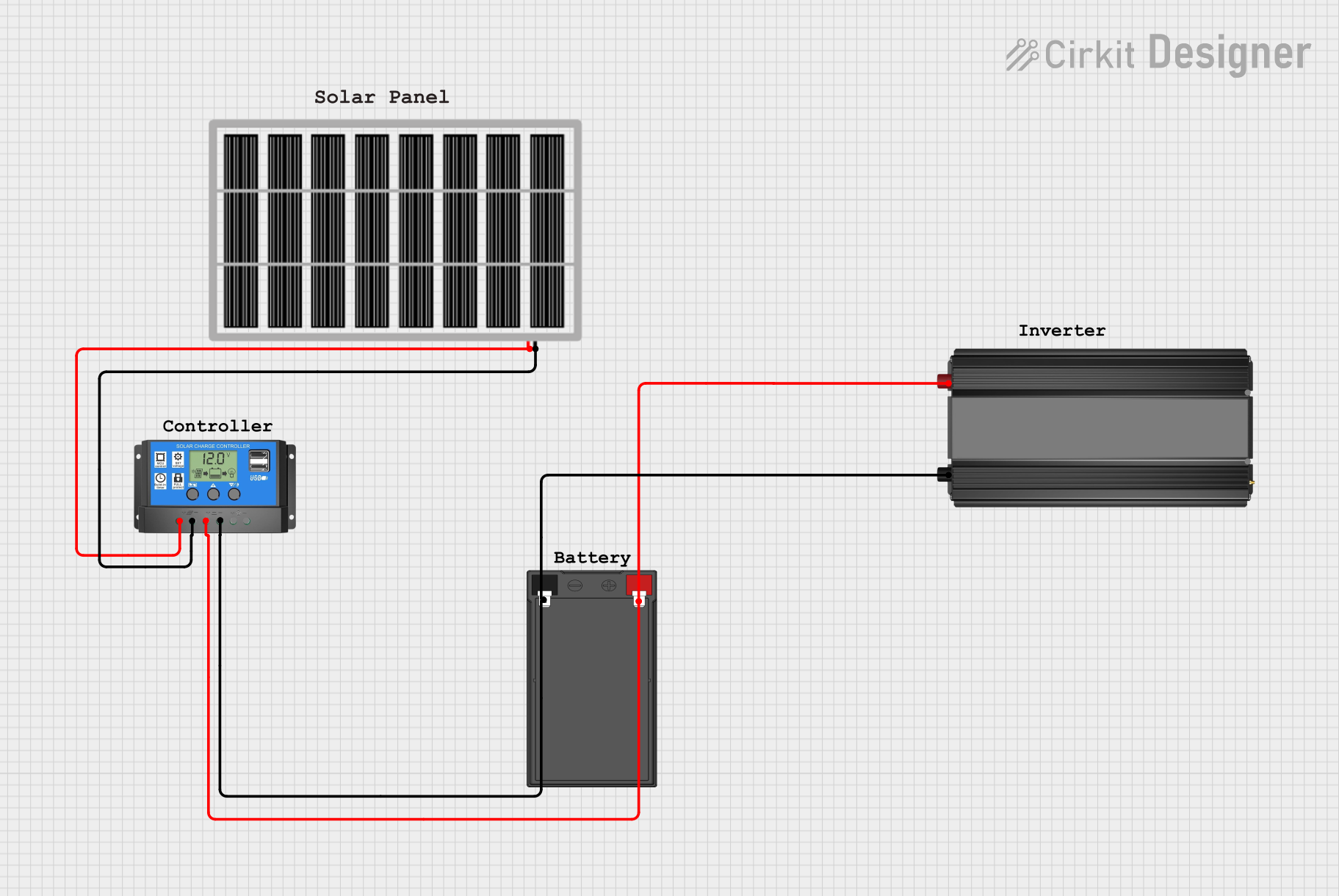
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Solar pannel

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential and commercial solar power systems
- Off-grid power solutions for remote areas
- Solar-powered devices (e.g., calculators, lights, and chargers)
- Integration with battery storage systems
- Solar water pumping systems
- Portable solar chargers for outdoor activities
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard solar panel. Note that actual values may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer.
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Power Output | 10W to 400W (varies by model) |
| Voltage (Open Circuit) | 18V to 45V |
| Voltage (Nominal) | 12V or 24V |
| Current (Short Circuit) | 0.5A to 10A |
| Efficiency | 15% to 22% |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | Varies (e.g., 1.6m x 1m for 300W) |
| Weight | Varies (e.g., ~20kg for 300W) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Solar panels typically have two output terminals for electrical connections:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | The positive terminal of the panel. Connects to the positive input of the load or charge controller. |
| Negative (-) | The negative terminal of the panel. Connects to the negative input of the load or charge controller. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Solar Panel in a Circuit
- Positioning the Panel: Place the solar panel in a location with maximum sunlight exposure. Ensure it is angled correctly based on your geographic location to optimize energy generation.
- Connecting to a Charge Controller:
- Connect the positive terminal of the solar panel to the positive input of the charge controller.
- Connect the negative terminal of the solar panel to the negative input of the charge controller.
- Connecting to a Battery (Optional): If using a battery, connect the charge controller's output terminals to the battery's positive and negative terminals.
- Connecting the Load: Attach the load (e.g., lights, appliances) to the output terminals of the charge controller or directly to the battery, depending on the system design.
- Monitoring: Use a multimeter or monitoring system to check the voltage and current output of the panel.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Shading: Even partial shading can significantly reduce the panel's efficiency.
- Use a Charge Controller: Always use a charge controller to prevent overcharging or deep discharging of the battery.
- Proper Wiring: Use appropriately rated wires and connectors to handle the current and voltage.
- Series or Parallel Connections: For higher voltage, connect panels in series. For higher current, connect panels in parallel.
- Maintenance: Clean the panel surface regularly to remove dirt, dust, and debris that can block sunlight.
Example: Connecting a Solar Panel to an Arduino UNO
To measure the voltage output of a solar panel using an Arduino UNO, you can use a voltage divider circuit. Below is an example code:
// Example code to measure solar panel voltage using Arduino UNO
// Ensure the voltage divider reduces the panel's voltage to within 0-5V range
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
float voltage = 0.0; // Variable to store the measured voltage
const float R1 = 10000.0; // Resistor R1 value in ohms
const float R2 = 10000.0; // Resistor R2 value in ohms
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read analog value
float adcVoltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to voltage
voltage = adcVoltage * ((R1 + R2) / R2); // Calculate actual panel voltage
// Print the measured voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Solar Panel Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Low Power Output:
- Cause: Insufficient sunlight or shading.
- Solution: Ensure the panel is in direct sunlight and free from obstructions.
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Check all connections and ensure proper polarity.
Overheating:
- Cause: Poor ventilation or excessive ambient temperature.
- Solution: Install the panel in a well-ventilated area and avoid placing it on heat-absorbing surfaces.
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Faulty charge controller or incorrect connections.
- Solution: Verify the charge controller's functionality and check the wiring.
FAQs
Can I connect a solar panel directly to a battery?
- It is not recommended. Always use a charge controller to prevent overcharging or damaging the battery.
How do I calculate the number of panels needed for my system?
- Determine your daily energy consumption (in watt-hours) and divide it by the panel's daily energy output (considering sunlight hours and efficiency).
Can solar panels work on cloudy days?
- Yes, but the output will be significantly reduced due to lower sunlight intensity.
Do solar panels require maintenance?
- Minimal maintenance is required. Regular cleaning and occasional inspections are sufficient to ensure optimal performance.