
How to Use ICM20948_変換モジュール: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ICM20948_変換モジュール in Cirkit Designer
Design with ICM20948_変換モジュール in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ICM20948_変換モジュール is a 9-axis motion tracking device manufactured by InvenSense. It integrates a 3-axis gyroscope, a 3-axis accelerometer, and a 3-axis magnetometer into a single compact module. This component is designed for applications requiring precise motion sensing and orientation detection, making it ideal for robotics, drones, wearable devices, and gaming peripherals.
The module provides high accuracy and low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered devices. It communicates via I²C or SPI interfaces, allowing seamless integration with microcontrollers and development boards like the Arduino UNO.
Explore Projects Built with ICM20948_変換モジュール

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer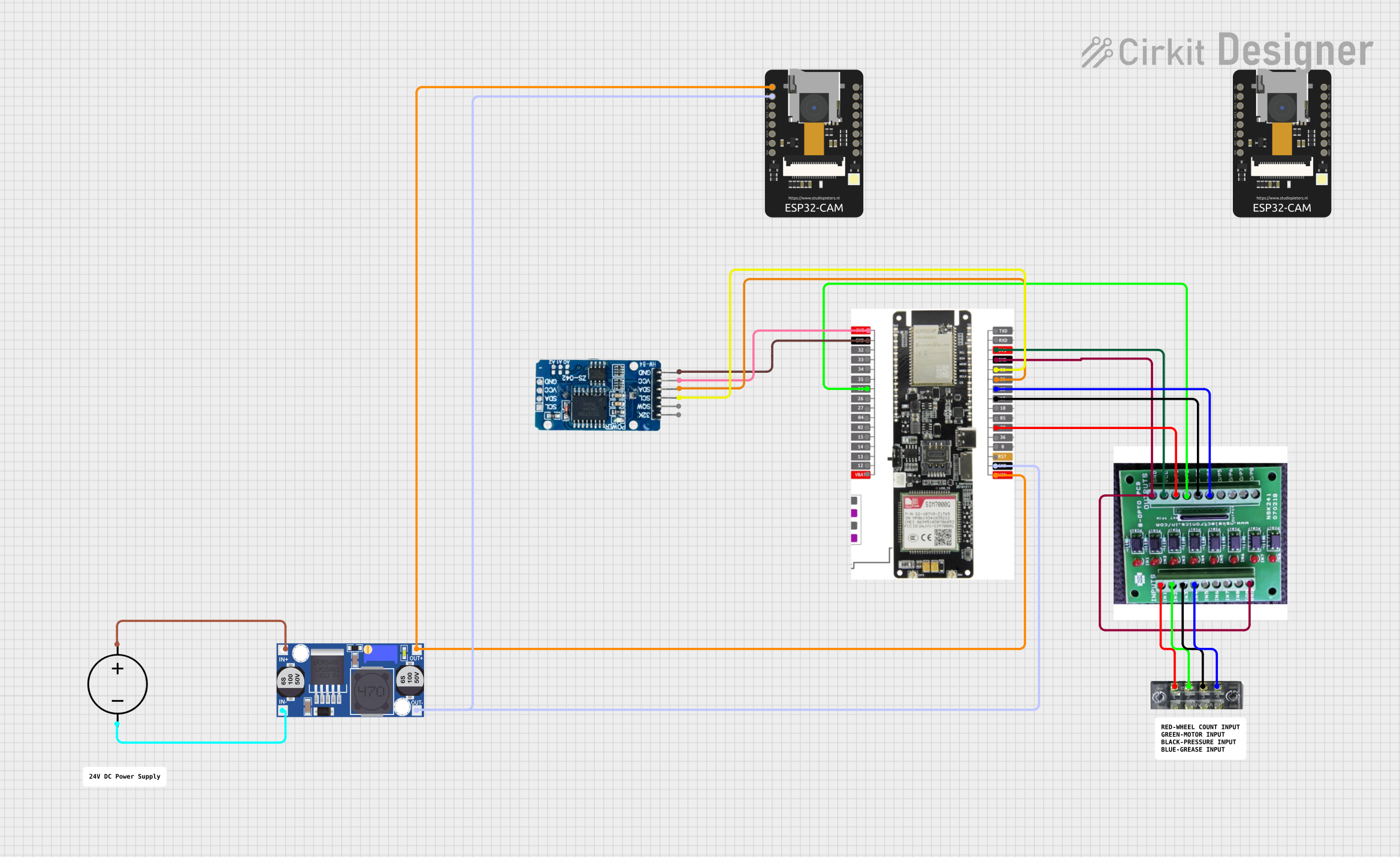
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer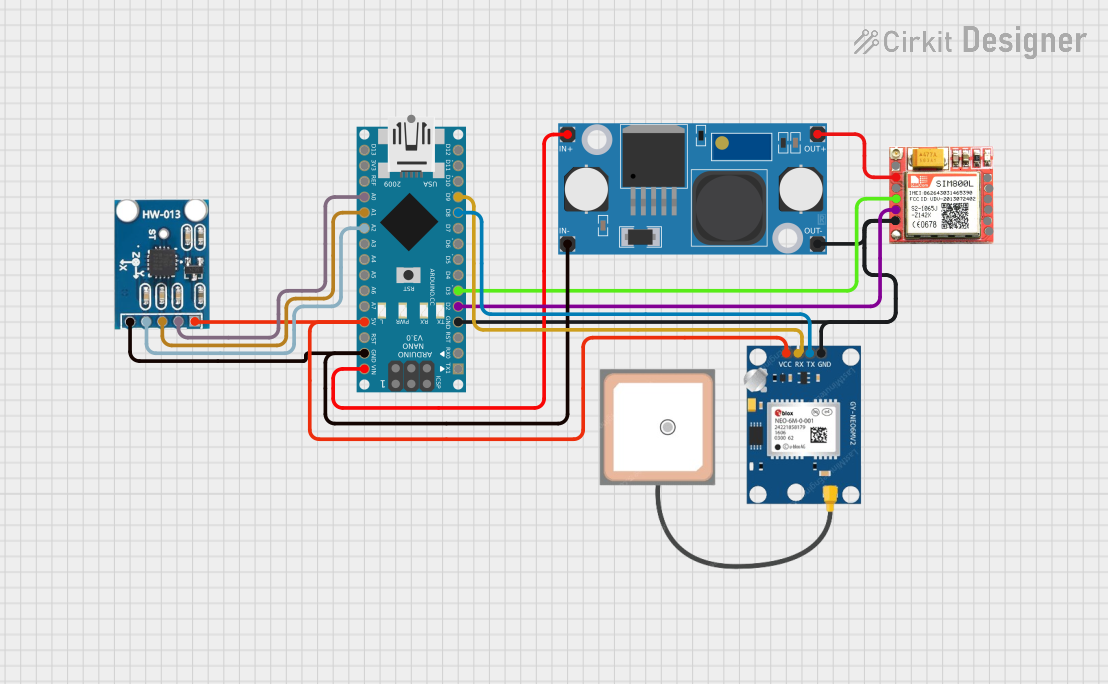
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ICM20948_変換モジュール

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | InvenSense |
| Sensor Type | 9-axis motion tracking |
| Gyroscope Range | ±250, ±500, ±1000, ±2000 dps |
| Accelerometer Range | ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, ±16g |
| Magnetometer Range | ±4900 µT |
| Operating Voltage | 1.8V (core), 3.3V (I/O) |
| Communication Interface | I²C (up to 400 kHz), SPI (up to 7 MHz) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Power Consumption | 2.5 mA (typical, full operation) |
| Dimensions | 3 mm x 3 mm x 1 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ICM20948_変換モジュール typically comes with a breakout board for easier integration. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power supply input (3.3V recommended) |
| GND | 2 | Ground |
| SDA | 3 | I²C data line |
| SCL | 4 | I²C clock line |
| CS | 5 | Chip select for SPI (active low) |
| SDO | 6 | SPI data output / I²C address selection |
| INT | 7 | Interrupt output |
| RST | 8 | Reset pin (active low) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Communication Interface:
- For I²C: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I²C pins on your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ) on both lines.
- For SPI: Connect the CS, SDO, and SCL pins to the SPI interface of your microcontroller.
- Interrupts: If needed, connect the INT pin to a GPIO pin on your microcontroller to handle interrupts.
- Reset: Optionally, connect the RST pin to a GPIO pin for manual or software-controlled resets.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure the I/O voltage levels of your microcontroller match the module's requirements (3.3V logic).
- Bypass Capacitors: Place a 0.1 µF capacitor close to the VCC pin to stabilize the power supply.
- Magnetometer Calibration: Perform a calibration routine to account for magnetic interference in your environment.
- Mounting Orientation: Ensure the module is mounted securely and aligned correctly for accurate motion tracking.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the ICM20948_変換モジュール with an Arduino UNO using the I²C interface:
#include <Wire.h>
// ICM20948 I²C address (default: 0x68 if SDO is low, 0x69 if SDO is high)
#define ICM20948_ADDR 0x68
// Register addresses
#define WHO_AM_I 0x00 // WHO_AM_I register address
#define PWR_MGMT_1 0x06 // Power management register
#define ACCEL_XOUT_H 0x2D // Accelerometer X-axis high byte
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I²C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Wake up the ICM20948
Wire.beginTransmission(ICM20948_ADDR);
Wire.write(PWR_MGMT_1); // Access power management register
Wire.write(0x01); // Set clock source
Wire.endTransmission();
// Verify communication
Wire.beginTransmission(ICM20948_ADDR);
Wire.write(WHO_AM_I); // Access WHO_AM_I register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(ICM20948_ADDR, 1); // Request 1 byte
if (Wire.available()) {
byte whoAmI = Wire.read();
Serial.print("WHO_AM_I: 0x");
Serial.println(whoAmI, HEX); // Print WHO_AM_I value
}
}
void loop() {
// Read accelerometer data
Wire.beginTransmission(ICM20948_ADDR);
Wire.write(ACCEL_XOUT_H); // Access accelerometer X-axis high byte
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(ICM20948_ADDR, 2); // Request 2 bytes (high and low)
if (Wire.available() == 2) {
int16_t accelX = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Combine high and low bytes
Serial.print("Accel X: ");
Serial.println(accelX); // Print accelerometer X-axis value
}
delay(500); // Delay for readability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Response from the Module:
- Ensure the module is powered correctly (check VCC and GND connections).
- Verify the I²C address (default is 0x68 or 0x69 depending on the SDO pin state).
- Check for proper pull-up resistors on the SDA and SCL lines.
Incorrect or No Sensor Data:
- Confirm that the module is initialized correctly (check the PWR_MGMT_1 register).
- Verify the mounting orientation of the module.
- Perform a calibration routine for the accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer.
Communication Errors:
- Ensure the I²C or SPI connections are secure and free of noise.
- Check the clock speed of the communication interface (I²C: max 400 kHz, SPI: max 7 MHz).
FAQs
Q: Can the ICM20948_変換モジュール be used with 5V logic?
A: No, the module operates at 3.3V logic. Use a level shifter if interfacing with a 5V microcontroller.Q: How do I calibrate the magnetometer?
A: Perform a figure-eight motion with the module while collecting data to calculate offsets and scale factors.Q: What is the maximum sampling rate?
A: The maximum sampling rate is 1 kHz for the accelerometer and gyroscope.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the ICM20948_変換モジュール effectively in your projects.