
How to Use 555 Timer: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 555 Timer in Cirkit Designer
Design with 555 Timer in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 555 Timer is a highly versatile integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by Texas Instruments under the part ID LM555. It is widely used for timing, pulse generation, and oscillation purposes. The 555 Timer can operate in three primary modes: monostable, astable, and bistable, making it a staple in both analog and digital electronics.
Explore Projects Built with 555 Timer
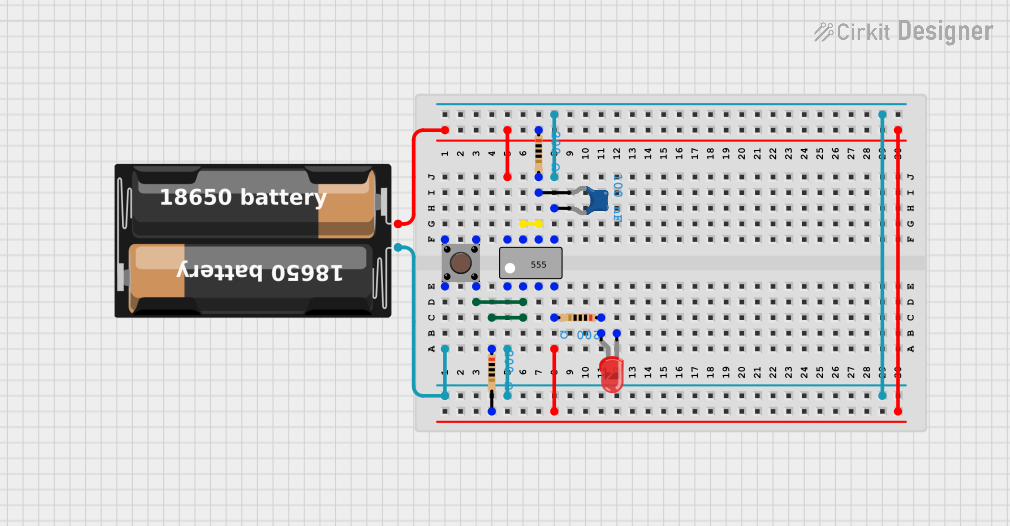
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer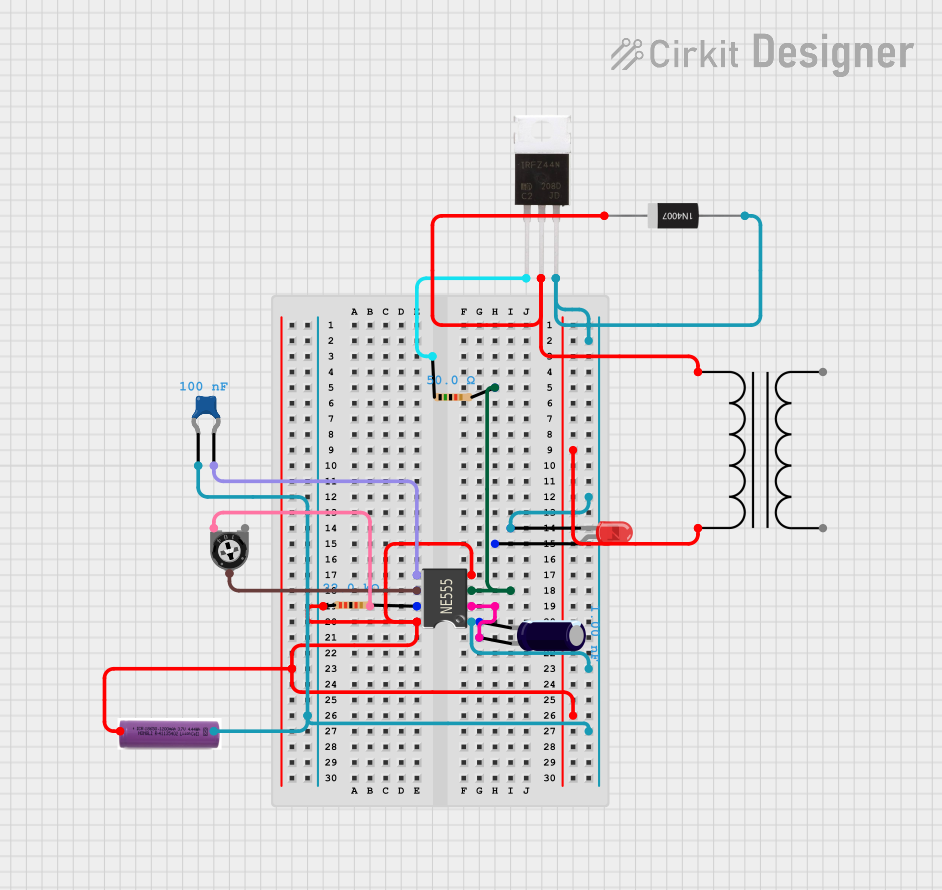
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer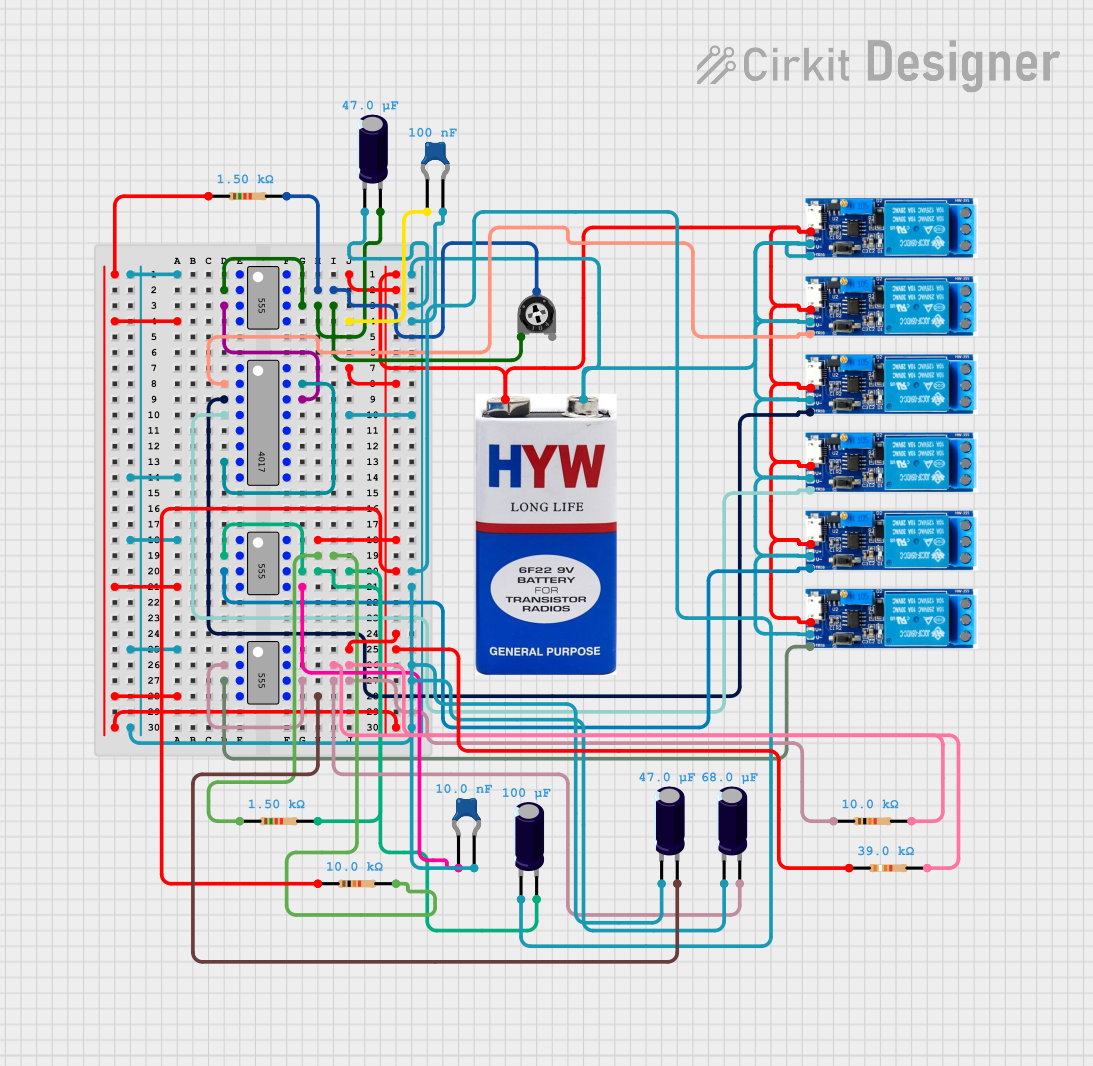
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer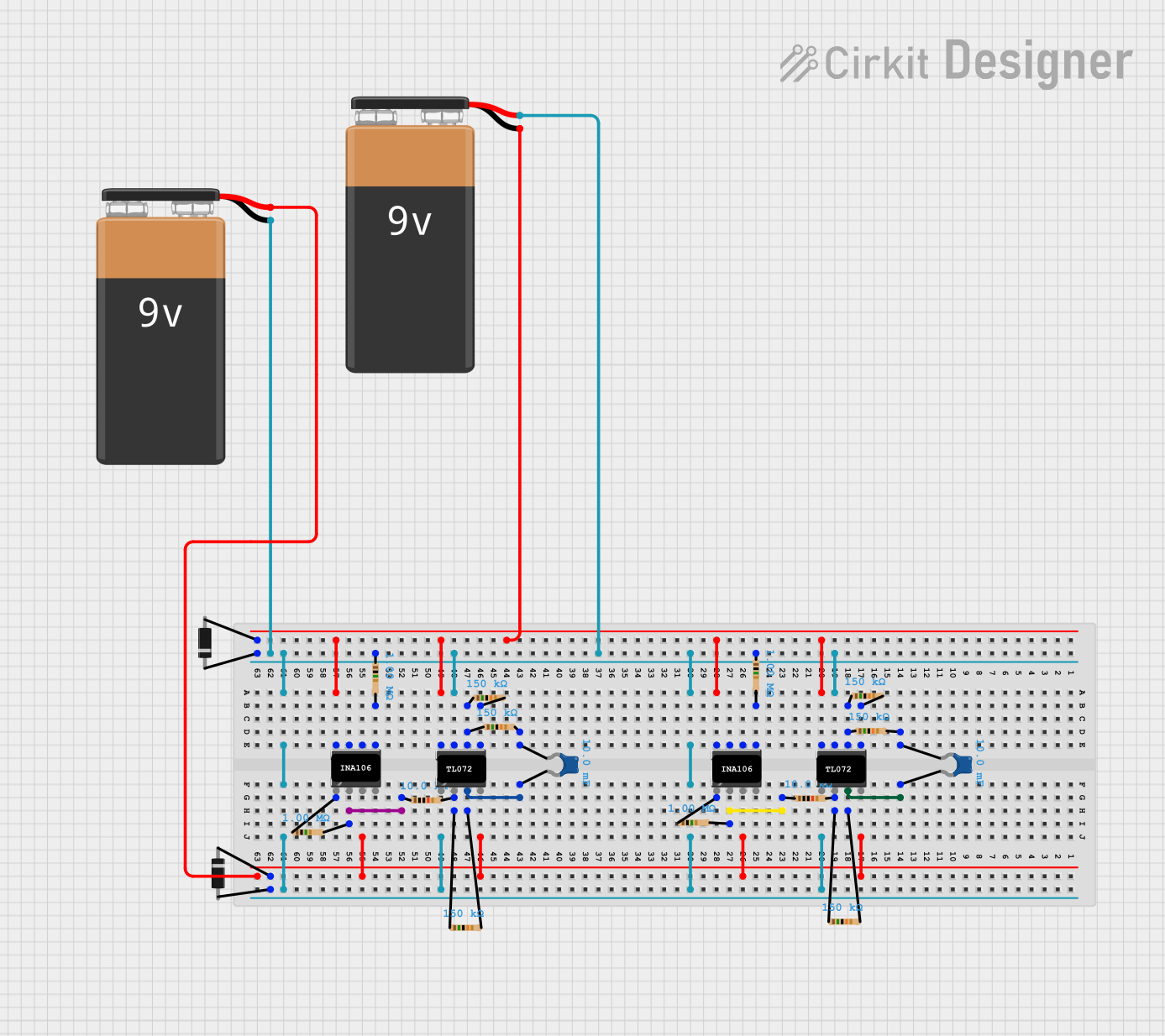
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 555 Timer

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Monostable Mode: Used for creating time delays, such as in timers or one-shot pulse generators.
- Astable Mode: Used for generating square waves, pulse-width modulation (PWM), and frequency generation.
- Bistable Mode: Functions as a flip-flop or basic memory element.
- Other Applications: LED flashers, tone generators, frequency dividers, and more.
Technical Specifications
The LM555 Timer is designed to operate under a wide range of conditions, making it suitable for various applications. Below are its key technical details and pin configuration.
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 4.5V to 16V |
| Supply Current (Typical) | 3 mA at 5V |
| Output Current (Max) | 200 mA |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to 125°C |
| Timing Accuracy | ±1% |
| Frequency Range | Up to 500 kHz |
| Package Types | DIP-8, SOIC-8, and others |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The LM555 Timer is an 8-pin IC. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the negative terminal of the power supply. |
| 2 | TRIG | Trigger input. A low voltage (<1/3 Vcc) on this pin starts the timing cycle. |
| 3 | OUT | Output pin. Provides the output signal (high or low). |
| 4 | RESET | Reset pin. Active low; resets the timer when pulled to ground. |
| 5 | CTRL | Control voltage. Used to adjust the threshold voltage (optional). |
| 6 | THR | Threshold input. Ends the timing cycle when voltage exceeds 2/3 Vcc. |
| 7 | DISCH | Discharge pin. Used to discharge the timing capacitor. |
| 8 | Vcc | Supply voltage. Connect to the positive terminal of the power supply. |
Usage Instructions
The LM555 Timer can be configured in different modes depending on the application. Below are instructions for using it in monostable and astable modes.
Monostable Mode (One-Shot Timer)
In monostable mode, the 555 Timer generates a single pulse of a specific duration when triggered. The pulse width is determined by an external resistor (R) and capacitor (C).
Circuit Setup:
- Connect Pin 1 (GND) to ground and Pin 8 (Vcc) to the power supply.
- Connect a resistor (R) between Pin 7 (DISCH) and Vcc.
- Connect a capacitor (C) between Pin 6 (THR) and ground.
- Connect Pin 2 (TRIG) to the trigger signal source.
- Leave Pin 5 (CTRL) unconnected or connect it to ground via a 0.01 µF capacitor for noise filtering.
- Connect Pin 4 (RESET) to Vcc to enable normal operation.
Pulse Width Calculation: The pulse width (T) is given by:
T = 1.1 * R * Cwhere T is in seconds, R is in ohms, and C is in farads.
Triggering: Apply a low pulse (<1/3 Vcc) to Pin 2 to start the timing cycle. The output (Pin 3) will go high for the duration of T.
Astable Mode (Oscillator)
In astable mode, the 555 Timer generates a continuous square wave. The frequency and duty cycle are determined by two resistors (R1, R2) and a capacitor (C).
Circuit Setup:
- Connect Pin 1 (GND) to ground and Pin 8 (Vcc) to the power supply.
- Connect a resistor (R1) between Pin 7 (DISCH) and Vcc.
- Connect a resistor (R2) between Pin 7 (DISCH) and Pin 6 (THR).
- Connect a capacitor (C) between Pin 6 (THR) and ground.
- Connect Pin 5 (CTRL) to ground via a 0.01 µF capacitor for noise filtering.
- Connect Pin 4 (RESET) to Vcc to enable normal operation.
Frequency and Duty Cycle Calculation: The frequency (f) and duty cycle (D) are given by:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C) D = (R1 + R2) / (R1 + 2 * R2)where f is in Hz, R1 and R2 are in ohms, and C is in farads.
Output: The output (Pin 3) will alternate between high and low states, creating a square wave.
Example: Using the LM555 with Arduino UNO
The LM555 Timer can be used with an Arduino UNO to generate a PWM signal. Below is an example code to read the output of the 555 Timer:
// Example: Reading 555 Timer Output with Arduino UNO
const int timerOutputPin = 2; // Connect 555 Timer output (Pin 3) to Arduino Pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Onboard LED for visual feedback
void setup() {
pinMode(timerOutputPin, INPUT); // Set 555 Timer output pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int timerState = digitalRead(timerOutputPin); // Read 555 Timer output state
digitalWrite(ledPin, timerState); // Reflect state on LED
Serial.println(timerState); // Print state to Serial Monitor
delay(100); // Small delay for stability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Output Signal:
- Ensure the power supply is connected correctly (Pin 8 to Vcc, Pin 1 to GND).
- Verify that the external components (resistors, capacitors) are connected as per the desired mode.
- Check if Pin 4 (RESET) is connected to Vcc.
Incorrect Timing or Frequency:
- Double-check the resistor and capacitor values used in the circuit.
- Ensure the formula for pulse width or frequency is applied correctly.
Unstable Operation:
- Add a 0.01 µF capacitor between Pin 5 (CTRL) and ground to reduce noise.
- Verify that the power supply voltage is within the specified range (4.5V to 16V).
FAQs
Q1: Can the LM555 Timer drive high-current loads?
A1: Yes, the LM555 Timer can source or sink up to 200 mA, making it suitable for driving LEDs, relays, and small motors directly.
Q2: What is the purpose of the control voltage pin (Pin 5)?
A2: Pin 5 allows external adjustment of the threshold voltage, enabling fine-tuning of the timing cycle. It is optional and can be left unconnected or grounded via a capacitor.
Q3: Can the LM555 Timer operate at low voltages?
A3: Yes, the LM555 can operate with a supply voltage as low as 4.5V, but ensure the connected components are compatible with the chosen voltage.
Q4: How do I calculate the duty cycle in astable mode?
A4: Use the formula:
D = (R1 + R2) / (R1 + 2 * R2)
where R1 and R2 are the resistors in the circuit.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the LM555 Timer in a variety of applications.