
How to Use Power Supply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Power Supply in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Supply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Power Supply is an essential component in any electronic system. It converts electrical power from a source, such as the mains AC (Alternating Current) or a battery, into a stable DC (Direct Current) voltage and current to operate a variety of electronic devices and circuits. Power supplies are used in everything from consumer electronics to industrial machinery, ensuring that devices receive the correct voltage and current for their operation.
Explore Projects Built with Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer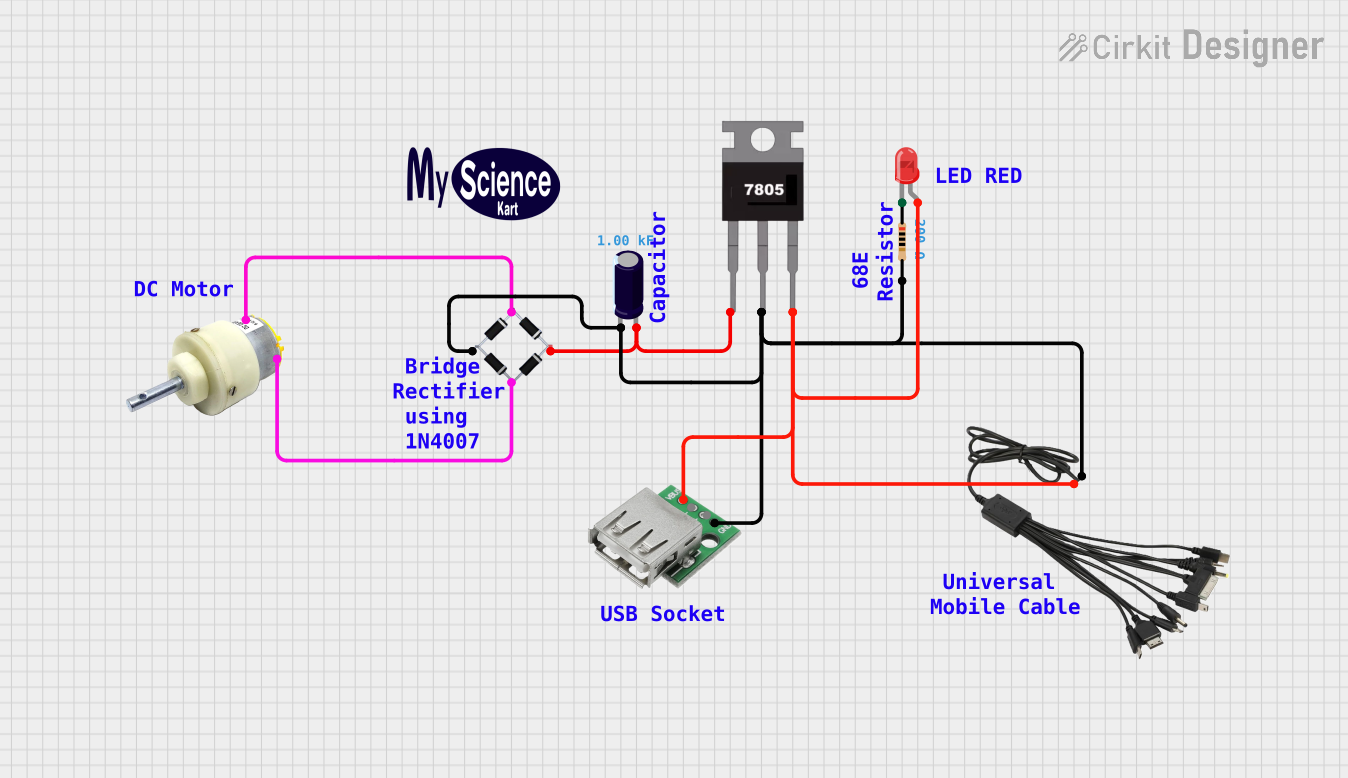
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer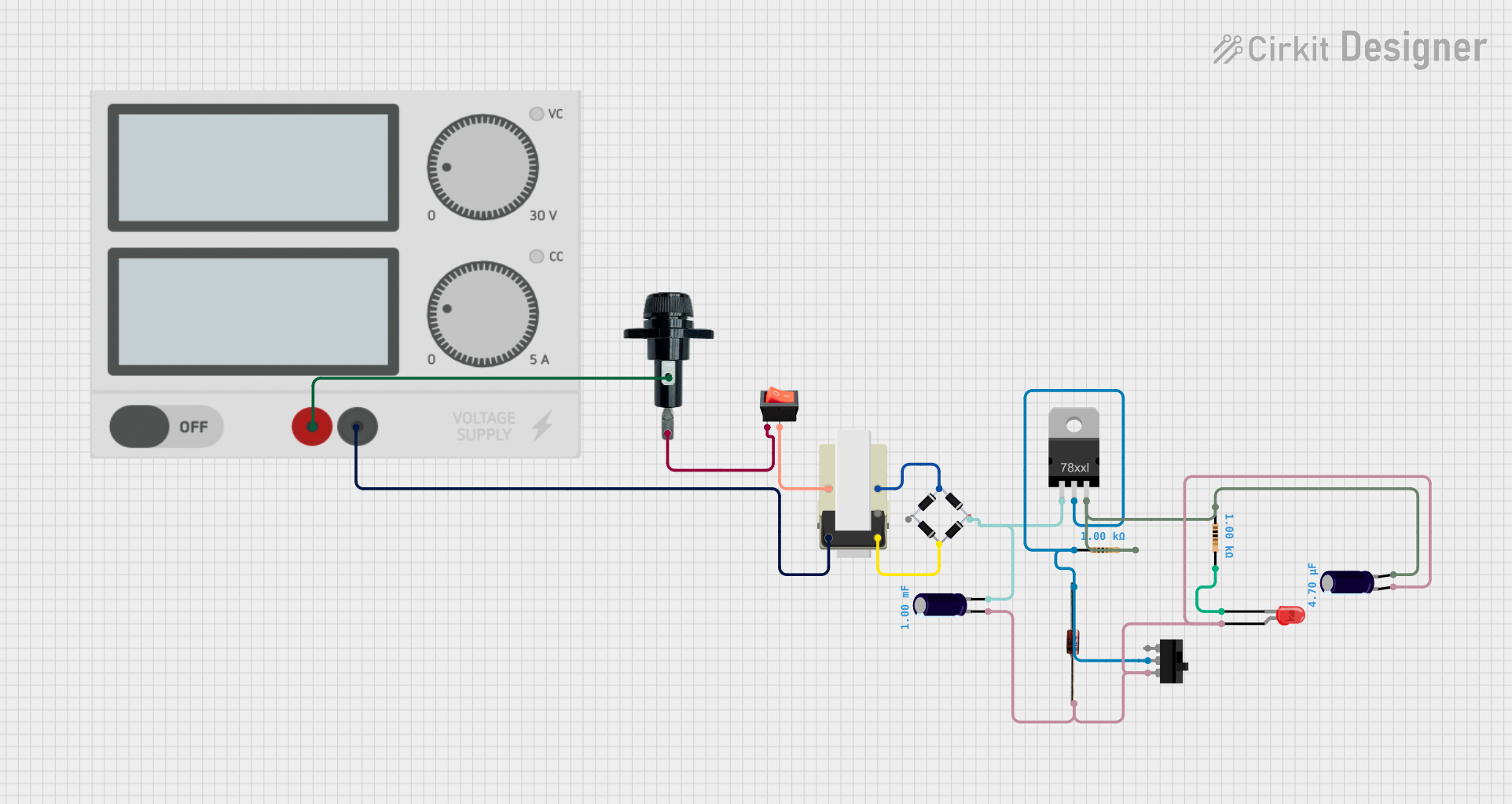
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Personal computers and servers
- Consumer electronics (TVs, radios, gaming consoles)
- Industrial control systems
- Telecommunication equipment
- Medical devices
- Laboratory and test equipment
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: The range of voltages the power supply can accept.
- Output Voltage Range: The range of voltages the power supply can deliver.
- Current Rating: The maximum current the power supply can provide.
- Power Rating: The maximum power the power supply can deliver, typically in watts.
- Efficiency: The ratio of output power to input power, expressed as a percentage.
- Ripple and Noise: The amount of unwanted variation in the output voltage.
- Protection Features: Overvoltage, overcurrent, short-circuit, and thermal protections.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AC Input | Connect to AC mains or source |
| 2 | Ground (Earth) | Safety ground connection |
| 3 | DC Output Positive | Positive voltage output |
| 4 | DC Output Negative | Ground or negative voltage output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Power Supply in a Circuit
- Connect the AC Input: Ensure the power supply is not plugged into an AC source. Connect the AC input pins to your AC source, respecting the correct voltage and polarity.
- Grounding: Connect the ground pin to the earth ground in your system for safety and noise reduction.
- Connect the DC Output: Attach the positive and negative outputs to your circuit, ensuring that the voltage and current ratings are within the specifications of your device.
- Power On: Once all connections are secure, plug the power supply into the AC source and switch it on.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Load Requirements: Ensure the power supply meets or exceeds the voltage and current requirements of your load.
- Ventilation: Provide adequate ventilation around the power supply to prevent overheating.
- Safety: Always follow electrical safety standards and regulations when installing and operating the power supply.
- Compatibility: Check that the output voltage is compatible with the devices being powered.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Insufficient Power Output: Ensure the power supply's ratings are not exceeded by the load.
- Overheating: Check for adequate ventilation and that the ambient temperature is within the specified limits.
- Unexpected Shutdowns: This could be due to overcurrent protection. Check if the load is drawing too much current.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Loose or incorrect connections can cause various issues. Verify all connections are secure and correct.
- Measure Output Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the output voltage is within the expected range.
- Load Testing: Disconnect the load and test the power supply independently to ensure it is functioning correctly.
FAQs
Q: Can I adjust the output voltage of the power supply?
- A: This depends on the model. Some power supplies have adjustable outputs, while others are fixed.
Q: What should I do if the power supply is making noise?
- A: Some noise can be normal, but excessive noise may indicate an issue with the fan or internal components. Check for obstructions or contact support.
Q: How do I know if the power supply is efficient?
- A: Look at the efficiency rating in the technical specifications. Higher percentages indicate better efficiency.
Example Connection to an Arduino UNO
// No direct code is involved in connecting a power supply to an Arduino UNO.
// However, it is crucial to ensure that the power supply's output voltage
// matches the requirements of the Arduino UNO (typically 5V or 3.3V for logic).
// Always consult the Arduino UNO's specifications before connecting a power supply.
Note: The Arduino UNO can be powered via the USB connection, the barrel jack, or the VIN pin. When using an external power supply, ensure it complies with the Arduino's input voltage specifications (6-20V for barrel jack, recommended 7-12V).
Remember, this documentation is a generic guide and may not cover all aspects of your specific power supply model. Always consult the manufacturer's datasheet for precise information.