
How to Use Potentiometer: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Potentiometer in Cirkit Designer
Design with Potentiometer in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
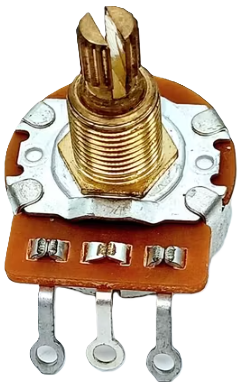
The PR-Rotary Potentiometer is a variable resistor designed to adjust voltage levels in a circuit. By varying its resistance, it allows for precise control of current flow and signal levels. This component is widely used in applications such as volume control in audio devices, brightness adjustment in lighting systems, and as an input device in microcontroller-based projects.
Explore Projects Built with Potentiometer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer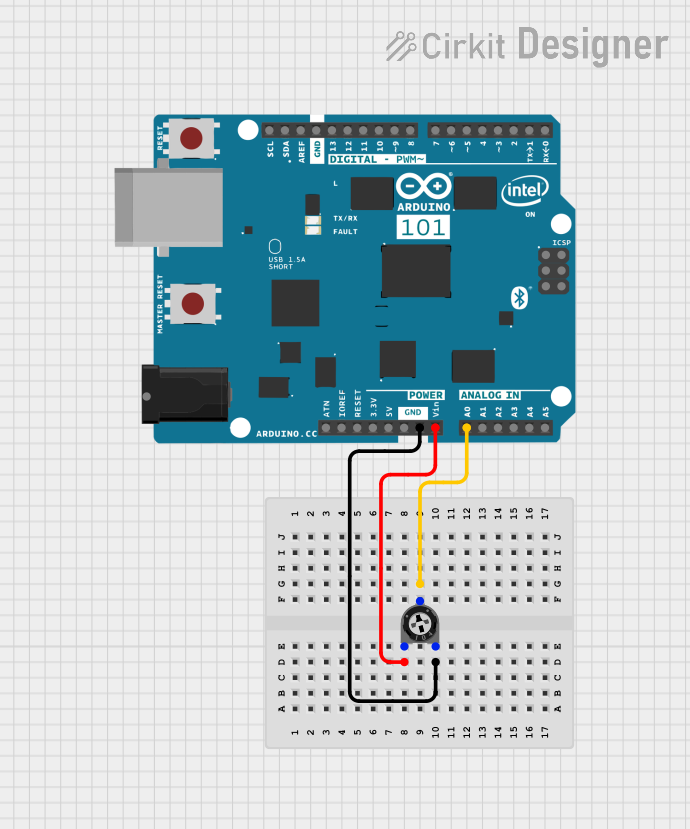
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer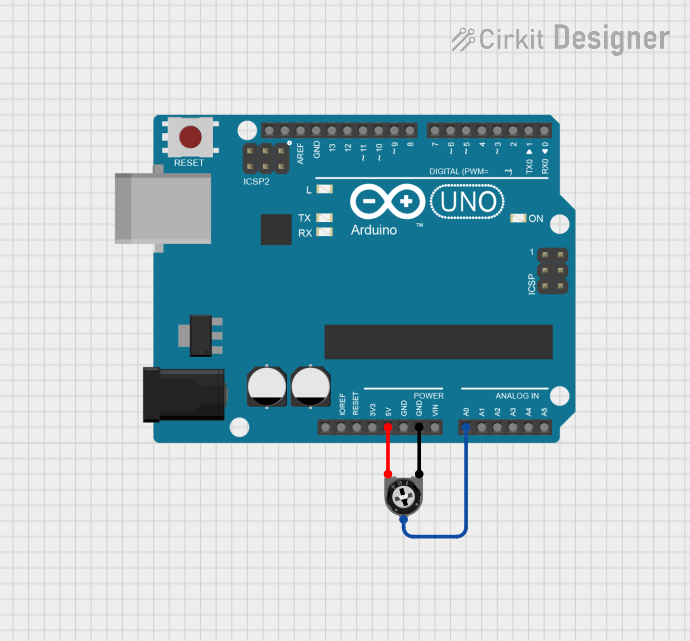
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer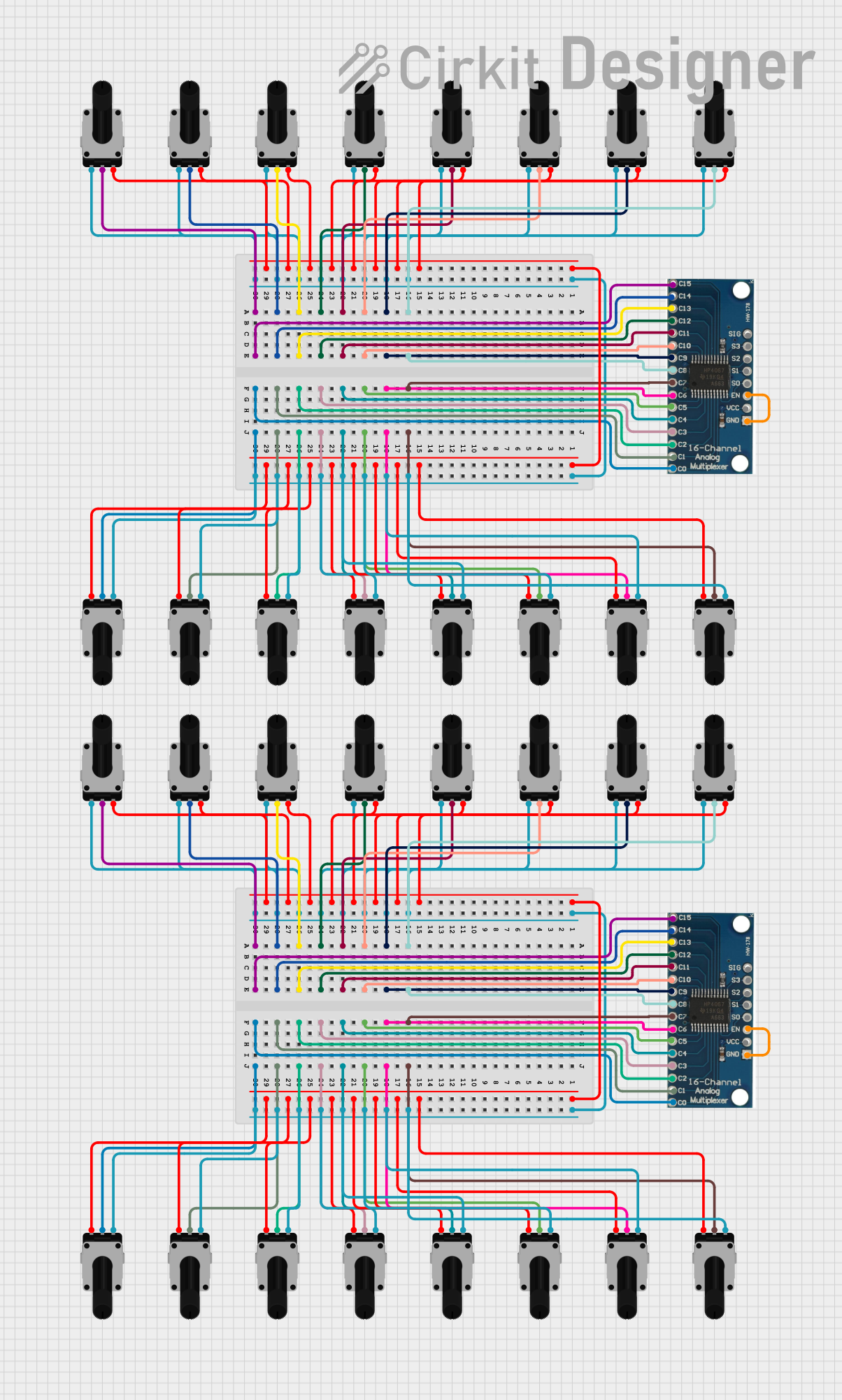
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Potentiometer

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Audio volume control
- Brightness adjustment in LED circuits
- Sensor calibration
- Voltage divider circuits
- User input for microcontroller projects (e.g., Arduino)
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the PR-Rotary Potentiometer:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | PR-Rotary Potentiometer |
| Resistance Range | 1 kΩ to 1 MΩ (varies by model) |
| Tolerance | ±10% |
| Power Rating | 0.25 W (250 mW) |
| Maximum Voltage | 250 V DC |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Rotational Life | 10,000 cycles |
| Shaft Rotation Angle | 300° ± 5° |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The potentiometer typically has three pins, as described below:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Terminal 1 | One end of the resistive track. Connect to the circuit's voltage source. |
| 2 | Wiper | The adjustable middle pin. Outputs the variable voltage based on rotation. |
| 3 | Terminal 2 | The other end of the resistive track. Connect to ground or another circuit. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Potentiometer in a Circuit
Basic Voltage Divider Configuration:
- Connect Pin 1 to the positive voltage supply (e.g., 5V).
- Connect Pin 3 to ground (GND).
- Use Pin 2 (Wiper) to output a variable voltage between 0V and the supply voltage.
Adjusting Resistance:
- Rotate the potentiometer's shaft to change the resistance between the wiper and the two terminals.
- Clockwise rotation typically increases the resistance between Pin 2 and Pin 3, while decreasing it between Pin 2 and Pin 1.
Microcontroller Input:
- Connect the wiper (Pin 2) to an analog input pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- Use the potentiometer to provide a variable input signal for controlling parameters like brightness or motor speed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid exceeding the maximum voltage and power ratings to prevent damage.
- Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) across the potentiometer terminals in sensitive circuits to reduce noise.
- Ensure proper mechanical mounting to avoid stress on the shaft during operation.
- For long-term reliability, avoid operating the potentiometer near its maximum temperature limit.
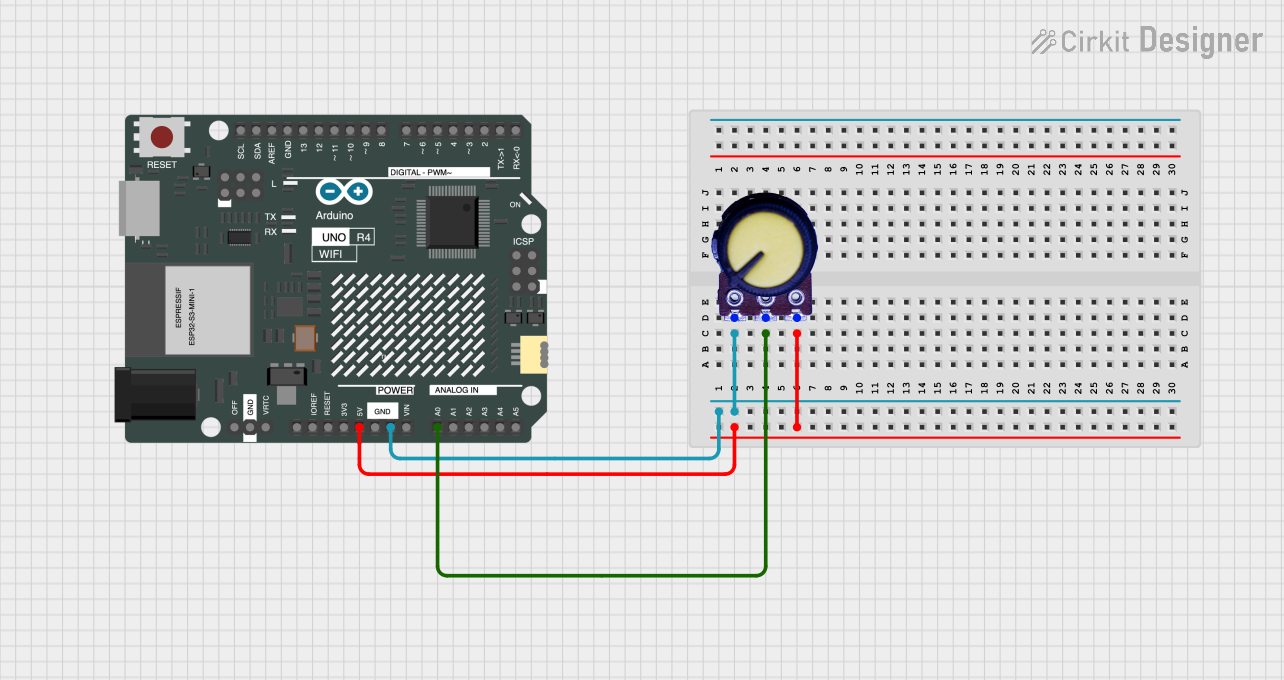
Example: Using the Potentiometer with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the potentiometer to read analog values with an Arduino UNO:
// Example: Reading potentiometer values with Arduino UNO
const int potPin = A0; // Connect the wiper (Pin 2) to analog pin A0
int potValue = 0; // Variable to store the potentiometer value
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
potValue = analogRead(potPin); // Read the analog value from the potentiometer
Serial.print("Potentiometer Value: ");
Serial.println(potValue); // Print the value to the Serial Monitor
delay(100); // Small delay for stability
}
Circuit Diagram
- Pin 1: Connect to 5V (Vcc).
- Pin 2 (Wiper): Connect to Arduino analog pin A0.
- Pin 3: Connect to GND.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Ensure the potentiometer is properly connected to the voltage source and ground.
- Verify that the wiper pin is connected to the correct circuit point.
Inconsistent or Noisy Output:
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
- Add a decoupling capacitor across the potentiometer terminals to reduce noise.
Potentiometer Not Responding to Rotation:
- Verify that the shaft is not physically damaged or stuck.
- Ensure the potentiometer is not worn out (check rotational life cycles).
Microcontroller Not Reading Values:
- Confirm that the wiper pin is connected to the correct analog input pin.
- Check the microcontroller's power supply and ensure the code is uploaded correctly.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the potentiometer to control an LED's brightness directly?
A: No, the potentiometer cannot directly drive an LED. Use it to control the input of a transistor or PWM signal for brightness adjustment.
Q: What happens if I exceed the power rating?
A: Exceeding the power rating can cause the potentiometer to overheat, potentially damaging the resistive track.
Q: Can I use the potentiometer as a fixed resistor?
A: Yes, by setting the wiper to one extreme position, the potentiometer can act as a fixed resistor between the wiper and one terminal.
Q: How do I clean a noisy potentiometer?
A: Use a contact cleaner spray to clean the internal resistive track. Avoid using excessive force on the shaft.
This concludes the documentation for the PR-Rotary Potentiometer.