
How to Use Diode: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Diode in Cirkit Designer
Design with Diode in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only, acting as a one-way valve for electrical current. It is one of the most fundamental components in electronics and is widely used in various applications. Diodes are essential for rectification, signal demodulation, voltage regulation, and circuit protection.
Explore Projects Built with Diode
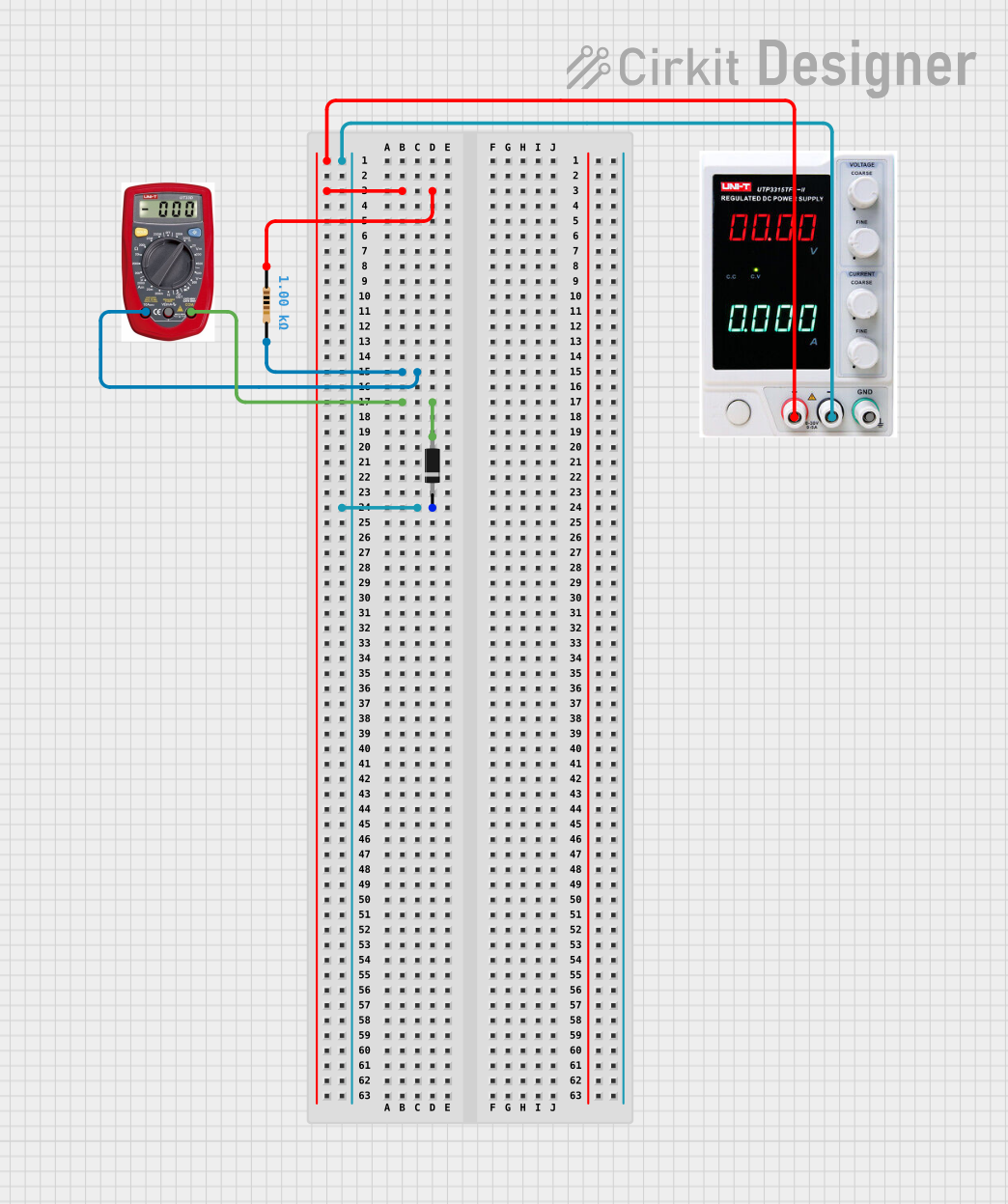
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer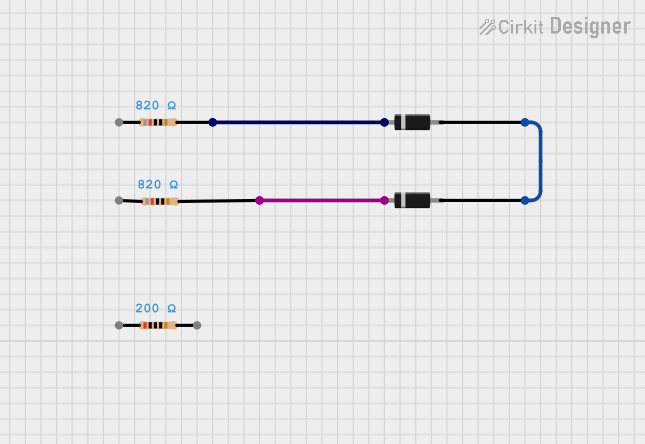
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer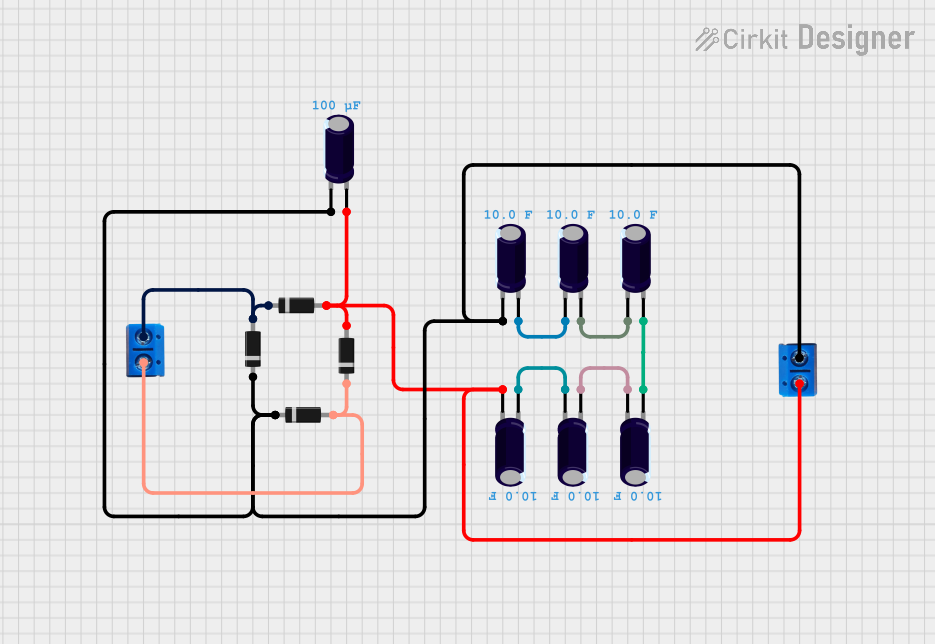
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer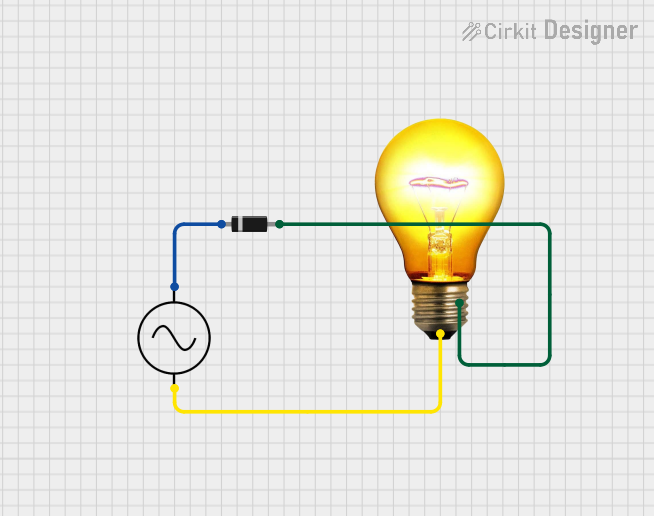
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Diode

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Rectification: Converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) in power supplies.
- Signal Demodulation: Extracting information from modulated signals in communication systems.
- Voltage Regulation: Stabilizing voltage levels in circuits.
- Circuit Protection: Preventing reverse polarity damage in sensitive components.
- LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes): Producing light in display and lighting applications.
Technical Specifications
The specifications of a diode can vary depending on its type and intended use. Below are the general technical details for a standard silicon diode (e.g., 1N4007):
Key Technical Details
- Forward Voltage Drop (Vf): ~0.7V (for silicon diodes), ~0.3V (for germanium diodes)
- Maximum Reverse Voltage (Vr): 50V to 1000V (depending on the diode type)
- Maximum Forward Current (If): 1A to 3A (for general-purpose diodes)
- Power Dissipation: Typically 1W or less
- Reverse Leakage Current (Ir): A few microamps (µA) under reverse bias
- Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Diodes typically have two terminals: Anode and Cathode. The cathode is marked with a stripe or band on the diode body.
| Pin Name | Description | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Anode | Positive terminal; current enters here in forward bias | A |
| Cathode | Negative terminal; current exits here in forward bias | K |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Diode in a Circuit
- Identify the Terminals: Locate the cathode (marked with a stripe) and the anode.
- Connect in Forward Bias: Connect the anode to the positive voltage and the cathode to the negative voltage for current to flow.
- Reverse Bias for Blocking: If the cathode is connected to the positive voltage and the anode to the negative voltage, the diode will block current flow.
- Use a Resistor if Necessary: When using a diode in series with an LED or other components, include a current-limiting resistor to prevent damage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Ratings: Ensure the diode's reverse voltage rating exceeds the maximum voltage in your circuit.
- Current Ratings: Verify that the diode can handle the maximum current in your application.
- Polarity: Always connect the diode with the correct polarity to avoid circuit malfunction.
- Heat Dissipation: For high-power applications, consider heat sinks or diodes with higher power ratings.
Example: Using a Diode with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of using a diode to protect an Arduino UNO from reverse polarity:
/*
* This example demonstrates how to use a diode to protect an Arduino UNO
* from reverse polarity. The diode is placed in series with the power supply.
*/
void setup() {
// No specific setup is required for the diode in this example.
// The diode is a passive component that protects the circuit.
}
void loop() {
// Your main code goes here.
// The diode ensures that the Arduino is protected from reverse polarity.
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Diode Not Conducting in Forward Bias:
- Cause: Insufficient forward voltage.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage exceeds the diode's forward voltage drop (e.g., 0.7V for silicon diodes).
Diode Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the diode's current or power rating.
- Solution: Use a diode with a higher current rating or add a heat sink.
Reverse Leakage Current:
- Cause: High reverse voltage or temperature.
- Solution: Verify that the reverse voltage is within the diode's rating and operate within the specified temperature range.
Circuit Not Working as Expected:
- Cause: Incorrect polarity connection.
- Solution: Double-check the anode and cathode connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I use any diode for rectification?
- A: Not all diodes are suitable for rectification. Use rectifier diodes like 1N4007 for power applications.
Q: What is the difference between a silicon and a germanium diode?
- A: Silicon diodes have a higher forward voltage drop (
0.7V) and are more common, while germanium diodes have a lower forward voltage drop (0.3V) and are used in specific applications like signal detection.
- A: Silicon diodes have a higher forward voltage drop (
Q: How do I test a diode?
- A: Use a multimeter in diode mode. Connect the positive probe to the anode and the negative probe to the cathode. A forward-biased diode will show a voltage drop (e.g., ~0.7V for silicon), while a reverse-biased diode will show no conduction.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use diodes in your electronic projects and troubleshoot common issues.