
How to Use Solenoid : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Solenoid in Cirkit Designer
Design with Solenoid in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into linear motion. It consists of a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This magnetic field moves a ferromagnetic plunger or core, enabling the solenoid to perform mechanical actions. Solenoids are widely used in applications requiring controlled linear motion, such as controlling valves, actuating mechanical systems, or locking mechanisms.
Explore Projects Built with Solenoid
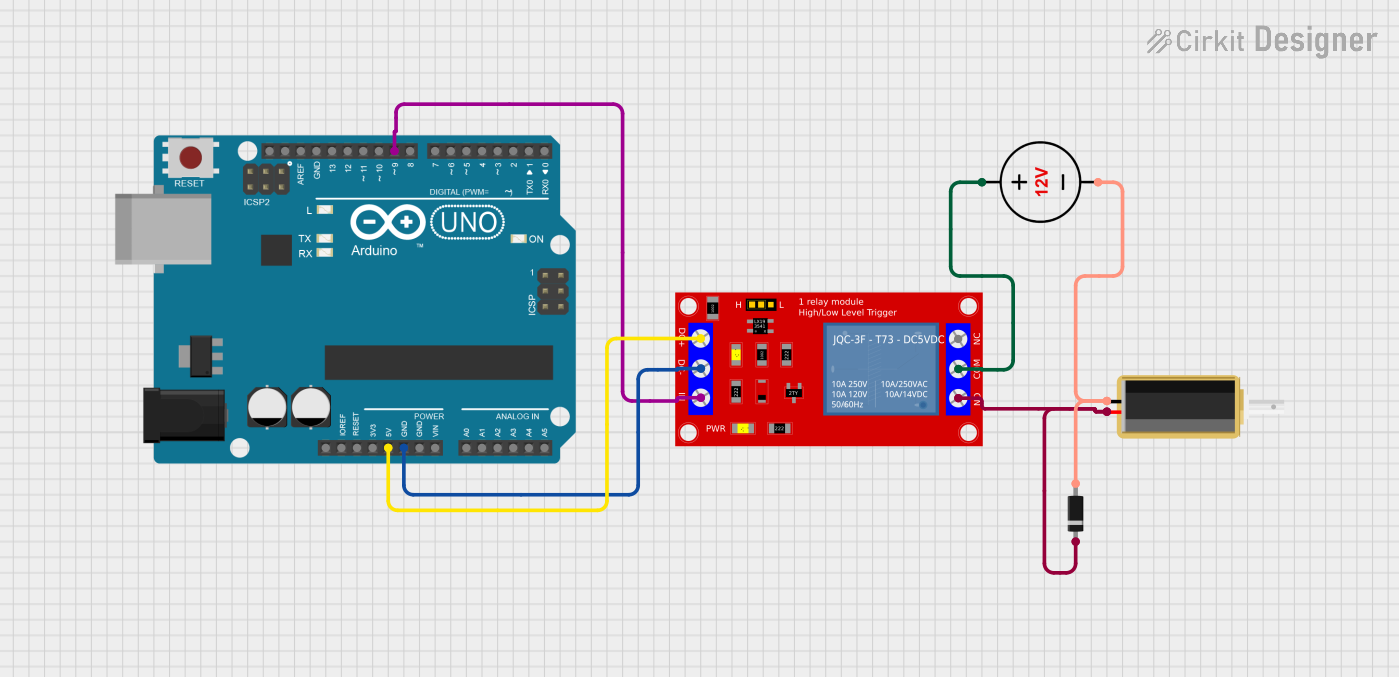
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer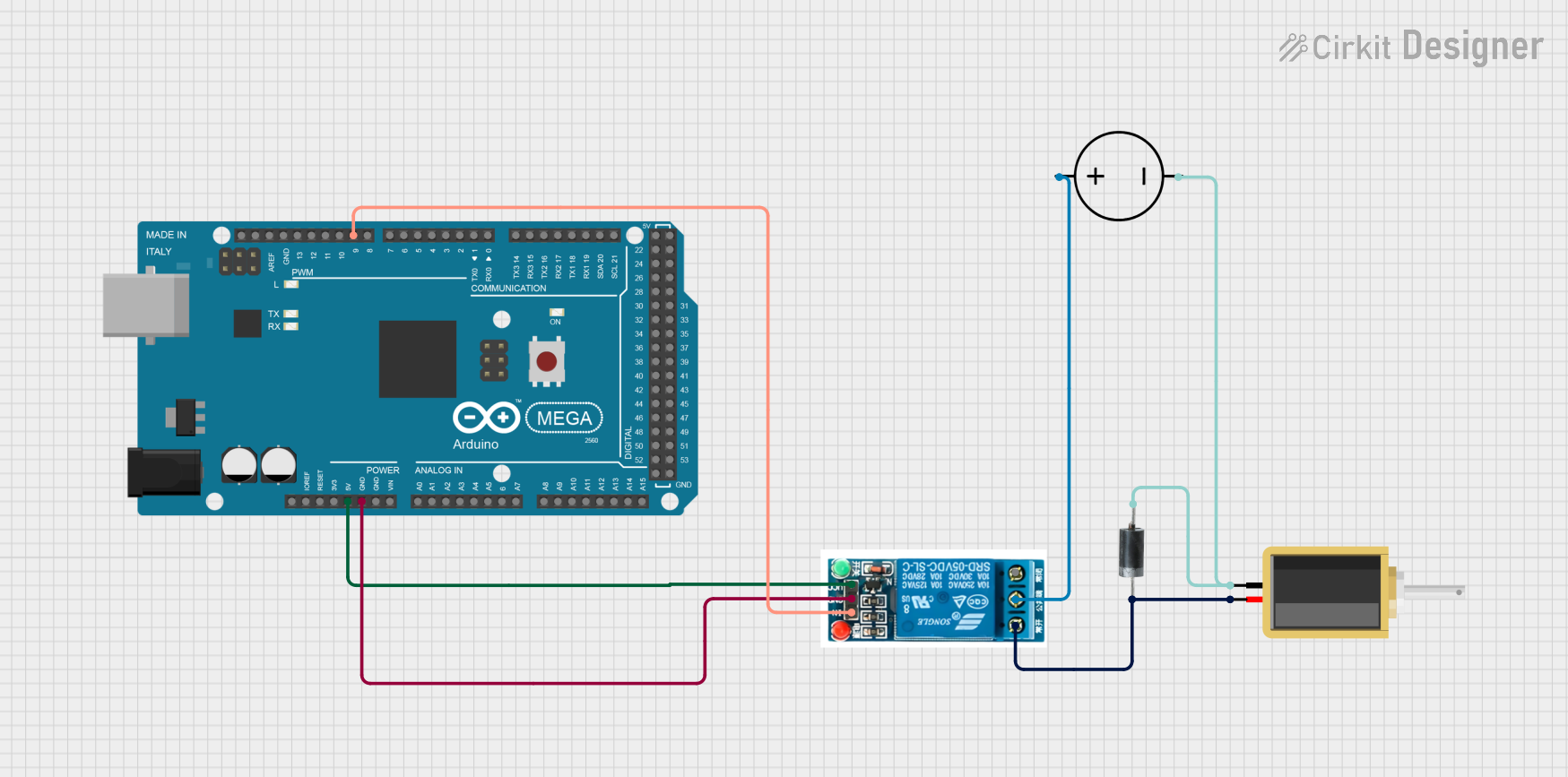
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer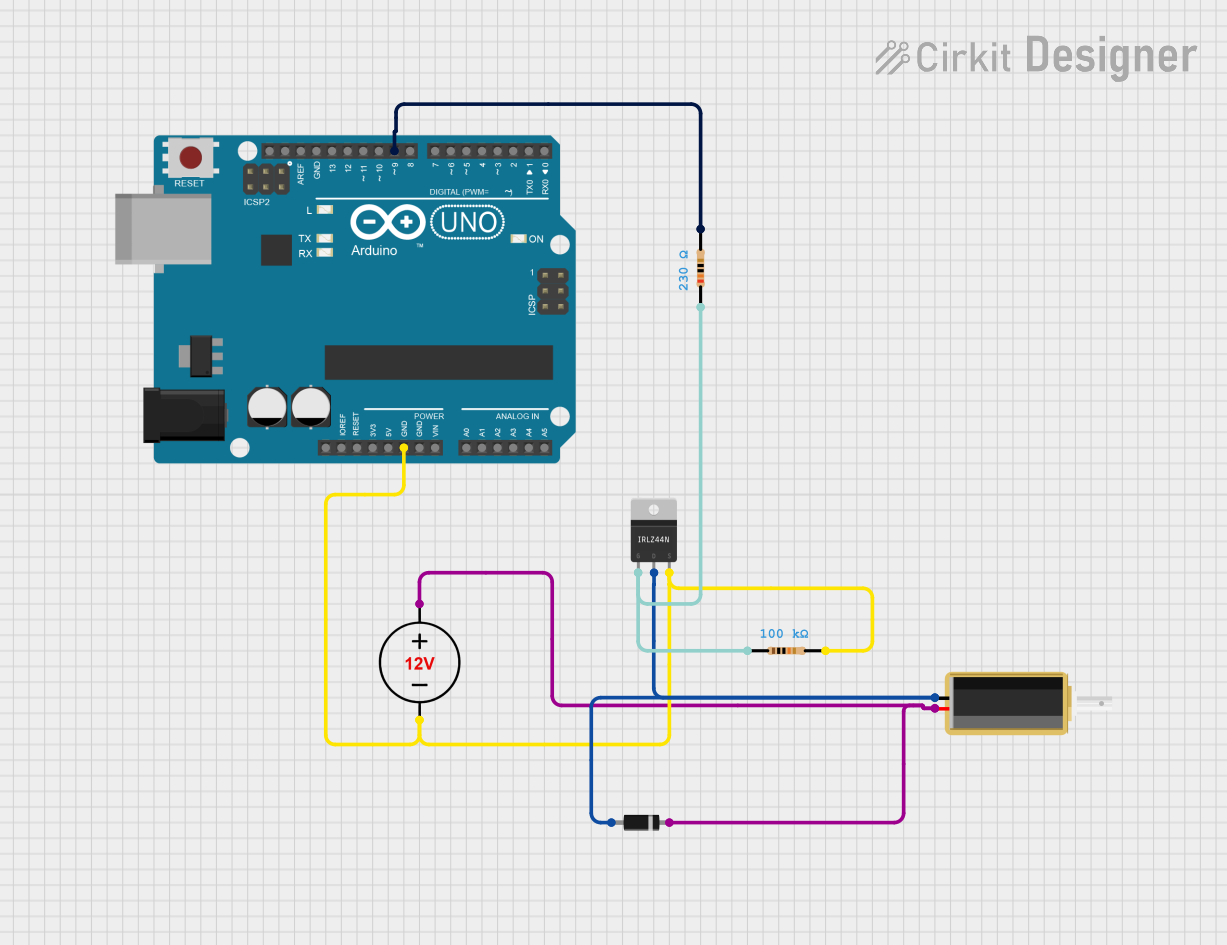
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Solenoid

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive Systems: Used in starter motors, fuel injectors, and door locks.
- Industrial Automation: Actuates valves, relays, and robotic mechanisms.
- Home Appliances: Found in washing machines, dishwashers, and vending machines.
- Access Control: Used in electronic locks and security systems.
- Prototyping and DIY Projects: Commonly used with microcontrollers like Arduino for automation tasks.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V to 24V (depending on the model) |
| Current Consumption | 0.5A to 2A (varies by size and type) |
| Stroke Length | 5mm to 30mm (model-dependent) |
| Force | 1N to 50N (varies by application) |
| Coil Resistance | 5Ω to 50Ω |
| Duty Cycle | 10% to 100% (check model specs) |
| Actuation Type | Push, Pull, or Push-Pull |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive | Connects to the positive terminal of the power supply. |
| Negative | Connects to the ground (GND) of the power supply. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the solenoid is powered by a voltage source within its operating range (e.g., 12V DC). Use a regulated power supply to avoid damage.
- Control Circuit: Use a transistor or MOSFET to control the solenoid, as it typically requires more current than a microcontroller can provide.
- Diode Protection: Always connect a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the solenoid terminals to protect the circuit from voltage spikes caused by the collapsing magnetic field when the solenoid is turned off.
- Microcontroller Interface: If using a microcontroller like Arduino, connect the control pin to the base/gate of the transistor or MOSFET through a resistor.
Example Circuit Diagram
- Components Needed:
- Solenoid
- NPN Transistor (e.g., 2N2222) or N-channel MOSFET
- Flyback Diode (e.g., 1N4007)
- Resistor (e.g., 1kΩ for the transistor base)
- External Power Supply (e.g., 12V DC)
Arduino Example Code
// Example code to control a solenoid with an Arduino UNO
// The solenoid is connected to pin 9 via a transistor or MOSFET
const int solenoidPin = 9; // Pin connected to the transistor's base/gate
void setup() {
pinMode(solenoidPin, OUTPUT); // Set the solenoid pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(solenoidPin, HIGH); // Activate the solenoid
delay(1000); // Keep it on for 1 second
digitalWrite(solenoidPin, LOW); // Deactivate the solenoid
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before repeating
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current for the solenoid.
- Heat Management: Avoid overheating by adhering to the solenoid's duty cycle rating.
- Flyback Diode: Always use a flyback diode to protect the circuit from voltage spikes.
- Mechanical Load: Ensure the solenoid's force and stroke length are suitable for your application.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Solenoid does not activate | Insufficient power supply | Check the voltage and current ratings. |
| Faulty connections | Verify all wiring and connections. | |
| Transistor/MOSFET not functioning | Test and replace the transistor/MOSFET. | |
| Solenoid overheats | Exceeding duty cycle | Reduce activation time or increase rest time. |
| Incorrect voltage applied | Use a regulated power supply within specs. | |
| Circuit damage after use | Missing flyback diode | Add a flyback diode across solenoid terminals. |
| Solenoid is weak or slow | Insufficient current | Use a power supply with higher current capacity. |
FAQs
Can I connect a solenoid directly to an Arduino?
- No, solenoids typically require more current than an Arduino pin can provide. Use a transistor or MOSFET as a switch.
What is a flyback diode, and why is it necessary?
- A flyback diode protects the circuit from voltage spikes caused by the collapsing magnetic field when the solenoid is turned off.
How do I choose the right solenoid for my project?
- Consider the required voltage, current, stroke length, force, and duty cycle for your application.
Can I use a solenoid for continuous operation?
- Only if the solenoid is rated for a 100% duty cycle. Otherwise, limit the activation time to prevent overheating.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, using, and troubleshooting solenoids in various applications.