
How to Use DC Circuit breaker: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DC Circuit breaker in Cirkit Designer
Design with DC Circuit breaker in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A DC circuit breaker is a protective device designed to automatically interrupt the flow of direct current (DC) in an electrical circuit. It serves as a safeguard against potential damage caused by overloads, short circuits, or other electrical faults. Unlike fuses, which need to be replaced after a fault, DC circuit breakers can be reset and reused, making them a more convenient and cost-effective solution.
Explore Projects Built with DC Circuit breaker

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer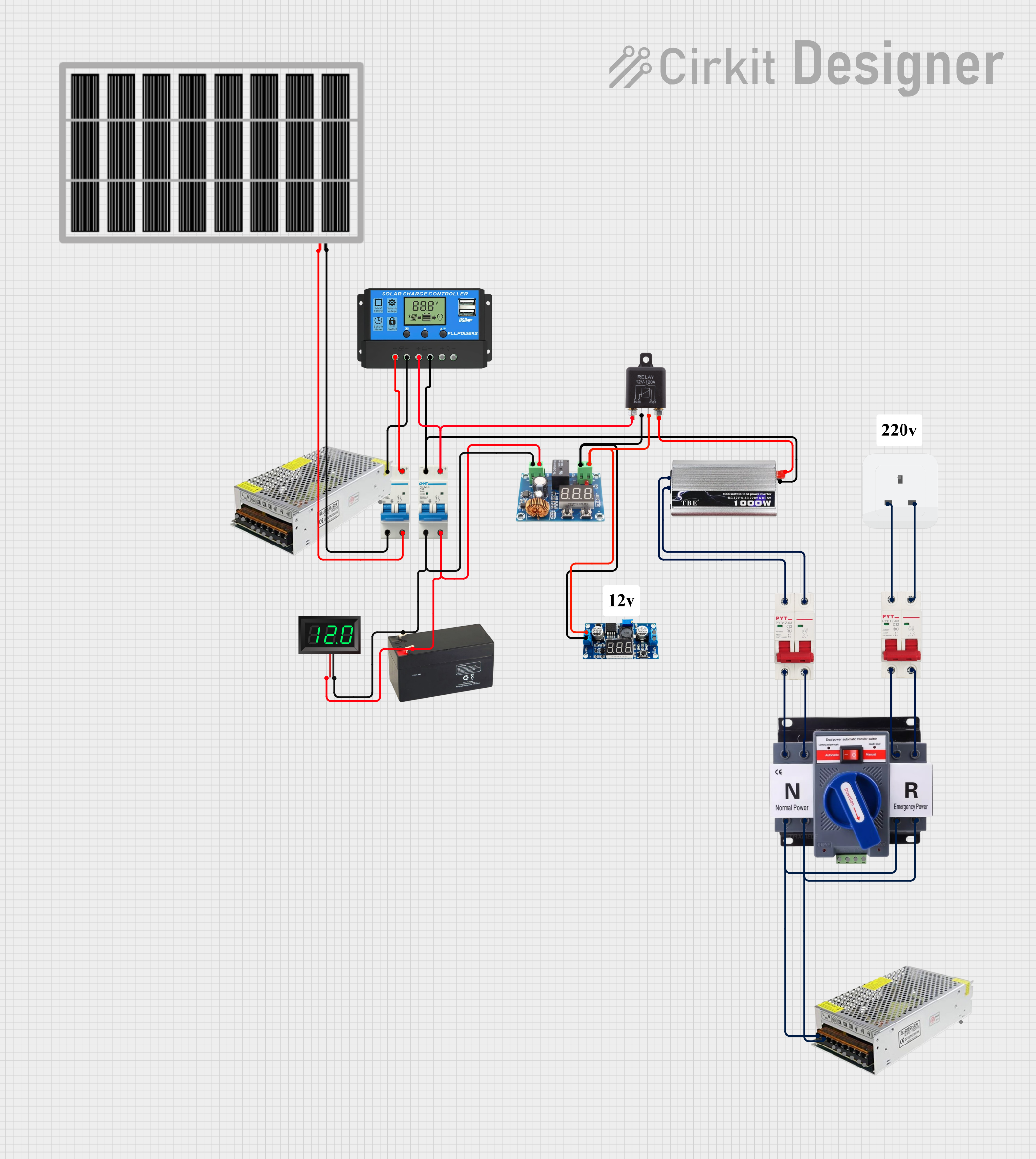
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer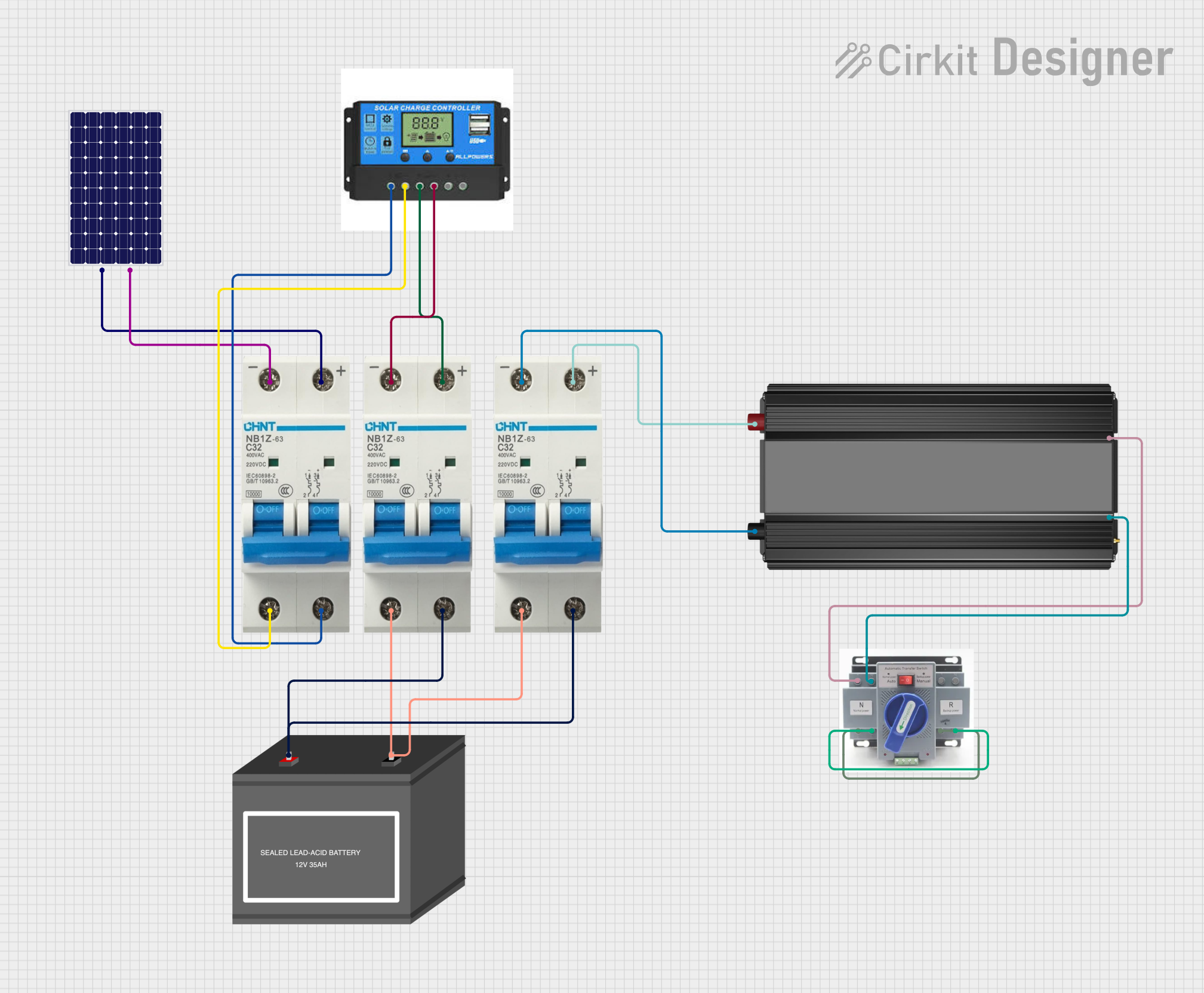
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer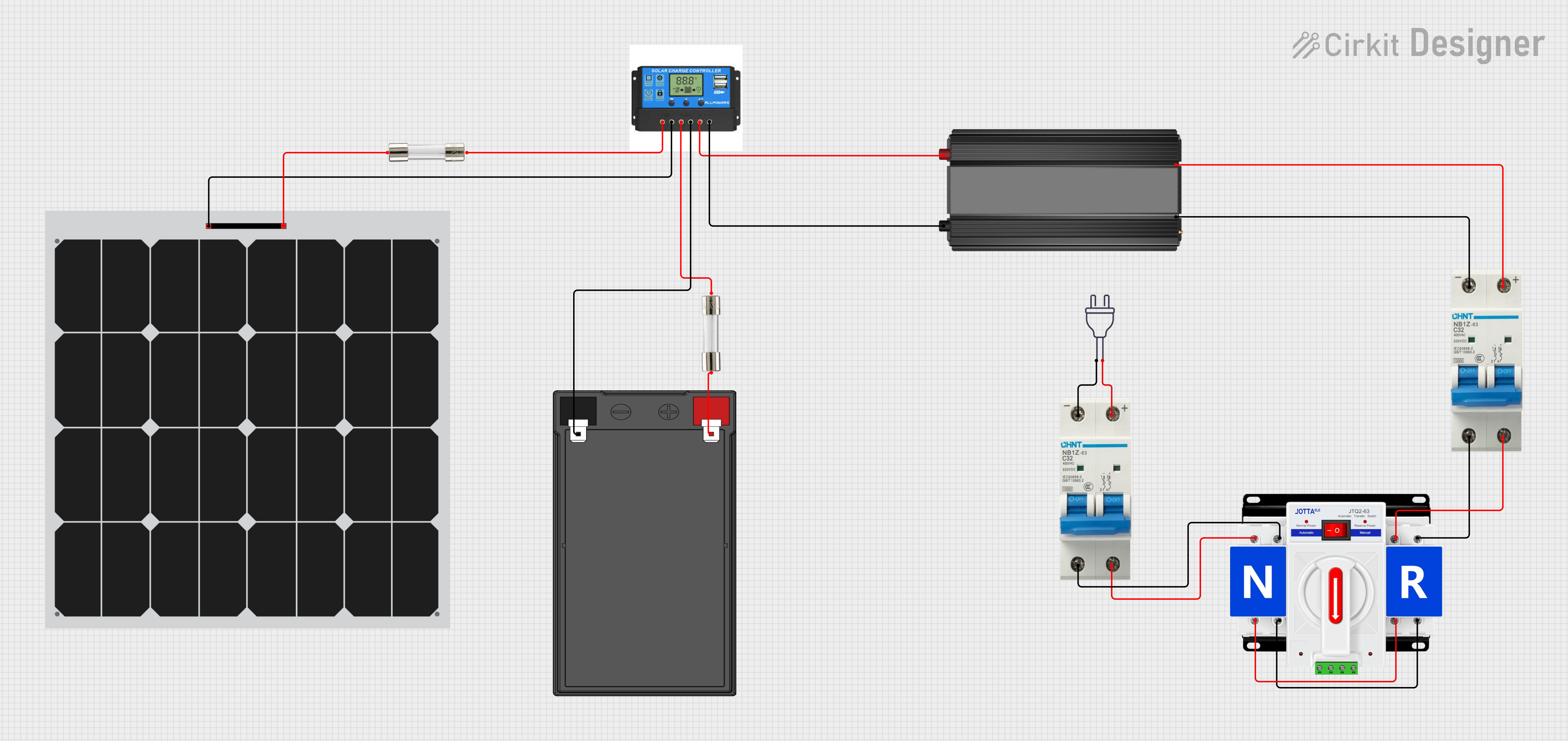
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DC Circuit breaker

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Solar Power Systems: Protecting photovoltaic (PV) panels and inverters from overcurrent conditions.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Ensuring safe operation of high-current DC circuits in EVs.
- Battery Management Systems: Preventing damage to batteries and associated electronics.
- Industrial Equipment: Protecting DC motors, drives, and other machinery.
- Telecommunication Systems: Safeguarding DC power supplies and distribution networks.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a typical DC circuit breaker:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 12V, 24V, 48V, 100V, or higher |
| Rated Current | 1A to 1000A (varies by model) |
| Breaking Capacity | 6kA to 10kA (depends on model) |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +70°C |
| Reset Type | Manual or Automatic |
| Mounting Style | DIN rail or panel-mounted |
| Poles | 1P, 2P, or 3P |
| Compliance Standards | IEC 60947-2, UL 489, or equivalent |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
DC circuit breakers typically have input and output terminals for connecting to the circuit. Below is a general description:
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Line (Input) | Connects to the positive terminal of the DC power source. |
| Load (Output) | Connects to the load or downstream circuit. |
| Ground (Optional) | Provides grounding for safety (if applicable). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Determine the Specifications: Select a DC circuit breaker with a voltage and current rating suitable for your application.
- Connect the Input: Attach the positive terminal of the DC power source to the "Line" terminal of the circuit breaker.
- Connect the Output: Connect the "Load" terminal to the downstream circuit or device.
- Secure the Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and secure to prevent arcing or loose contacts.
- Mount the Breaker: Install the circuit breaker on a DIN rail or panel, as per the mounting style.
- Test the Circuit: Power on the system and verify that the circuit breaker operates correctly under normal conditions.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Polarity: Ensure correct polarity when connecting the circuit breaker, as DC devices are polarity-sensitive.
- Breaking Capacity: Verify that the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker exceeds the maximum fault current of your system.
- Environmental Conditions: Avoid installing the breaker in environments with excessive moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect the breaker for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Resetting After a Trip: If the breaker trips, identify and resolve the fault before resetting it.
Example: Using a DC Circuit Breaker with an Arduino UNO
While DC circuit breakers are not directly interfaced with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, they can be used to protect circuits powered by the Arduino. Below is an example of a simple setup:
// Example: Monitoring a DC circuit breaker's status with Arduino UNO
// This code assumes the breaker has an auxiliary contact for status monitoring.
const int breakerStatusPin = 2; // Pin connected to the auxiliary contact
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED to indicate breaker status
void setup() {
pinMode(breakerStatusPin, INPUT_PULLUP); // Configure the status pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Configure the LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int breakerStatus = digitalRead(breakerStatusPin); // Read the breaker's status
if (breakerStatus == HIGH) {
// Breaker is closed (normal operation)
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
Serial.println("Breaker Status: Closed");
} else {
// Breaker is open (tripped or manually opened)
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off the LED
Serial.println("Breaker Status: Open");
}
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next status check
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Breaker trips frequently | Overload or short circuit in the circuit | Check the load and wiring for faults. |
| Breaker does not reset | Fault condition still present | Resolve the fault before resetting. |
| Breaker overheats | Exceeding rated current or poor ventilation | Reduce load or improve ventilation. |
| Loose connections | Improper wiring or terminal tightening | Recheck and secure all connections. |
FAQs
Can I use an AC circuit breaker for DC circuits?
- No, AC and DC circuit breakers are designed differently. Using an AC breaker in a DC circuit may result in improper operation or failure.
What happens if I exceed the breaker's rated current?
- The breaker will trip to protect the circuit. Repeated overcurrent conditions can damage the breaker.
How do I choose the right DC circuit breaker?
- Consider the voltage, current, and breaking capacity requirements of your system. Ensure compliance with relevant standards.
Can I use a DC circuit breaker in a solar power system?
- Yes, DC circuit breakers are commonly used in solar systems to protect PV panels and inverters.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use a DC circuit breaker to protect your electrical systems and ensure safe operation.