
How to Use Potentiometer onboard: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
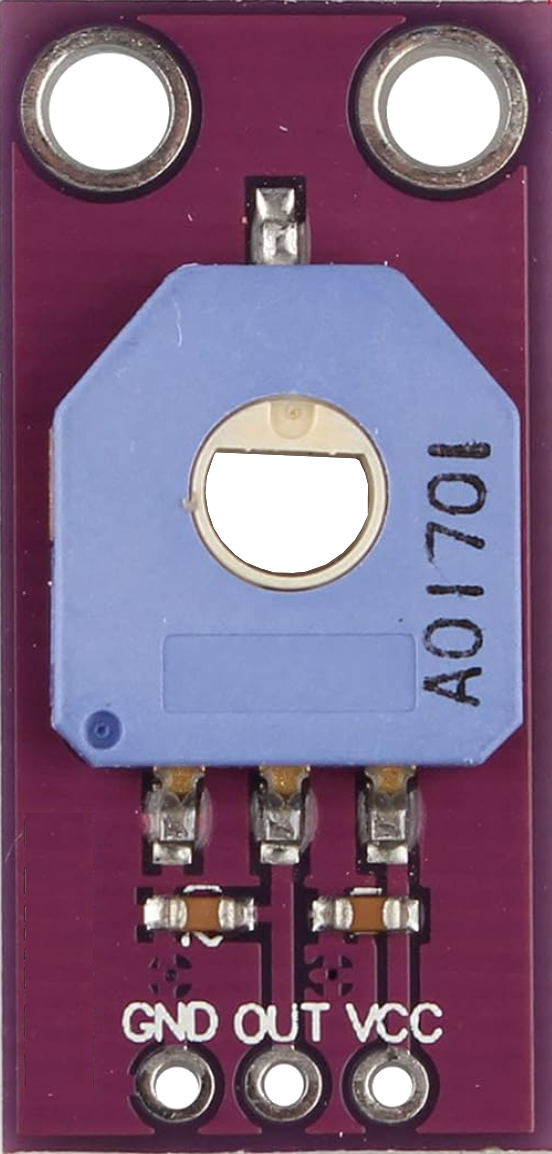
 Design with Potentiometer onboard in Cirkit Designer
Design with Potentiometer onboard in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A potentiometer onboard is a variable resistor integrated into a circuit board, designed to adjust voltage levels by varying resistance. It is commonly used to control current flow and serves as a user interface for settings such as volume, brightness, or other adjustable parameters. The onboard design makes it compact and easy to integrate into electronic projects.
Explore Projects Built with Potentiometer onboard
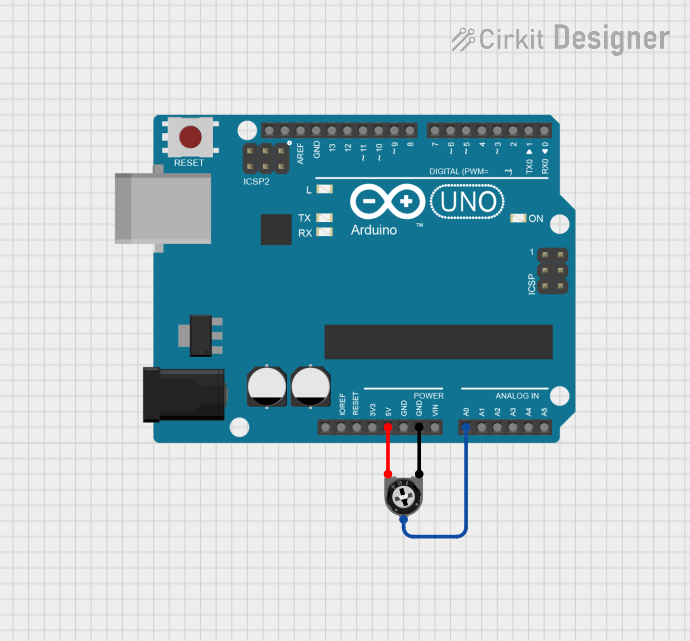
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer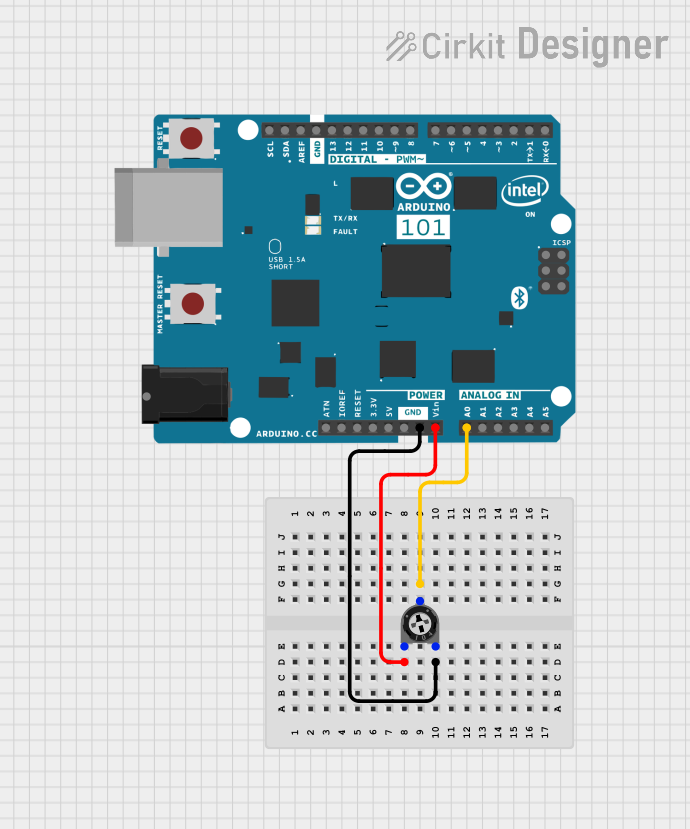
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer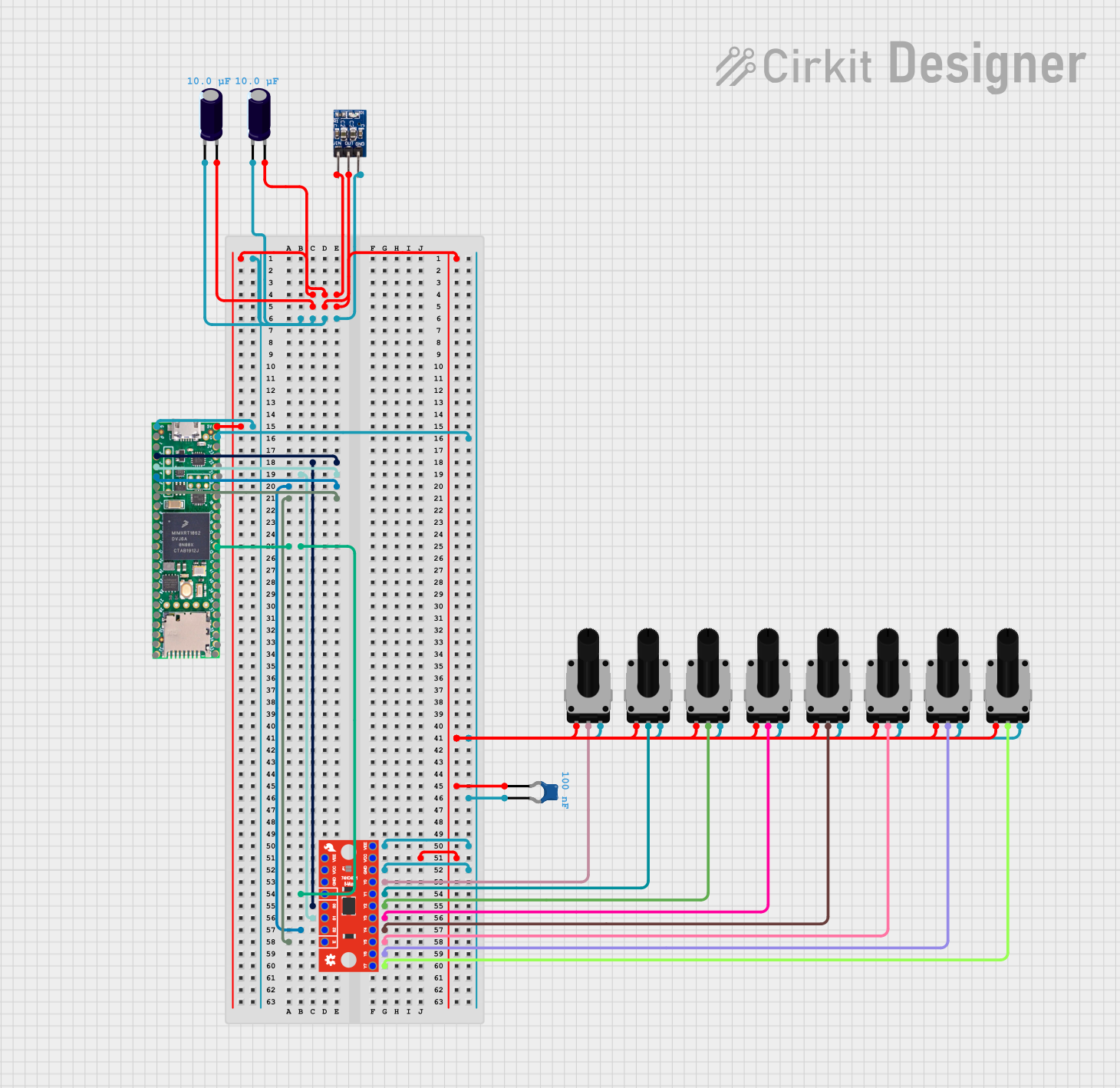
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer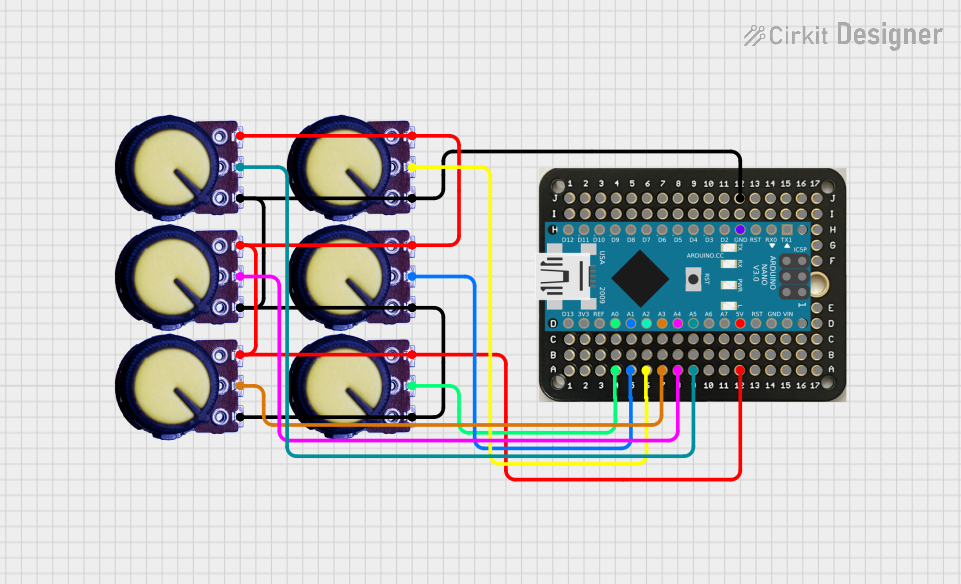
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Potentiometer onboard

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Volume control in audio devices
- Brightness adjustment in LED circuits
- Calibration of sensors
- User input for microcontroller-based projects
- Fine-tuning resistance in analog circuits
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical potentiometer onboard:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Resistance Range | 1 kΩ to 100 kΩ (varies by model) |
| Tolerance | ±10% |
| Power Rating | 0.1 W to 0.5 W |
| Adjustment Type | Rotary or slide |
| Operating Voltage | 0 V to 50 V |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Lifespan | 10,000 to 50,000 cycles |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The potentiometer onboard typically has three pins:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC/Input | Connects to the input voltage or power source. |
| 2 | Wiper/Output | Provides the adjustable output voltage based on the wiper's position. |
| 3 | GND | Connects to ground (0 V). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Potentiometer Onboard in a Circuit
Connect the Pins:
- Pin 1 (VCC/Input): Connect to the positive voltage source.
- Pin 3 (GND): Connect to the ground of the circuit.
- Pin 2 (Wiper/Output): Connect to the input of the device or circuit where the adjustable voltage is required.
Adjust the Resistance:
- Rotate the knob (for rotary types) or slide the control (for slide types) to change the resistance and adjust the output voltage.
Test the Output:
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the wiper pin (Pin 2) to ensure it meets your requirements.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Rating: Ensure the potentiometer's power rating is not exceeded to avoid damage.
- Debouncing: For applications involving microcontrollers, consider software debouncing to handle noise caused by mechanical movement.
- Mounting: Secure the potentiometer onboard to prevent accidental movement or damage during operation.
- Voltage Limits: Do not exceed the specified operating voltage to avoid damaging the component.
Example: Using a Potentiometer Onboard with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a potentiometer onboard to control the brightness of an LED using an Arduino UNO:
// Define pin connections
const int potPin = A0; // Potentiometer connected to analog pin A0
const int ledPin = 9; // LED connected to digital pin 9 (PWM)
// Variable to store potentiometer value
int potValue = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
// Read the potentiometer value (0-1023)
potValue = analogRead(potPin);
// Map the potentiometer value to PWM range (0-255)
int ledBrightness = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// Set the LED brightness
analogWrite(ledPin, ledBrightness);
// Print the potentiometer value and brightness for debugging
Serial.print("Potentiometer Value: ");
Serial.print(potValue);
Serial.print(" | LED Brightness: ");
Serial.println(ledBrightness);
delay(100); // Small delay for stability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the pin connections and ensure they are secure.
Inconsistent Output:
- Cause: Dust or wear on the potentiometer's internal track.
- Solution: Clean the potentiometer or replace it if worn out.
Component Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the power rating.
- Solution: Use a potentiometer with a higher power rating or reduce the load.
Microcontroller Not Responding:
- Cause: Noise or lack of debouncing.
- Solution: Implement software debouncing in your code.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use a potentiometer onboard to control AC voltage?
A1: No, potentiometers are designed for low-power DC applications. For AC voltage control, use a specialized component like a dimmer circuit.
Q2: How do I choose the right resistance value for my application?
A2: Select a resistance value that matches the input impedance of the circuit you are controlling. For general use, 10 kΩ is a common choice.
Q3: Can I use the potentiometer onboard as a fixed resistor?
A3: Yes, by setting the wiper to a specific position and not adjusting it, the potentiometer can act as a fixed resistor.
Q4: What is the lifespan of a potentiometer onboard?
A4: The lifespan typically ranges from 10,000 to 50,000 cycles, depending on the quality and usage conditions.