
How to Use JST XH 6P: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with JST XH 6P in Cirkit Designer
Design with JST XH 6P in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The JST XH 6P is a 6-position connector from JST's XH series, featuring a 2.5mm pitch. It is widely used in electronic circuits for connecting wires to PCBs, modules, or other components. Known for its compact design and reliable connections, the JST XH 6P is ideal for applications requiring secure and durable wire-to-board or wire-to-wire connections.
Explore Projects Built with JST XH 6P
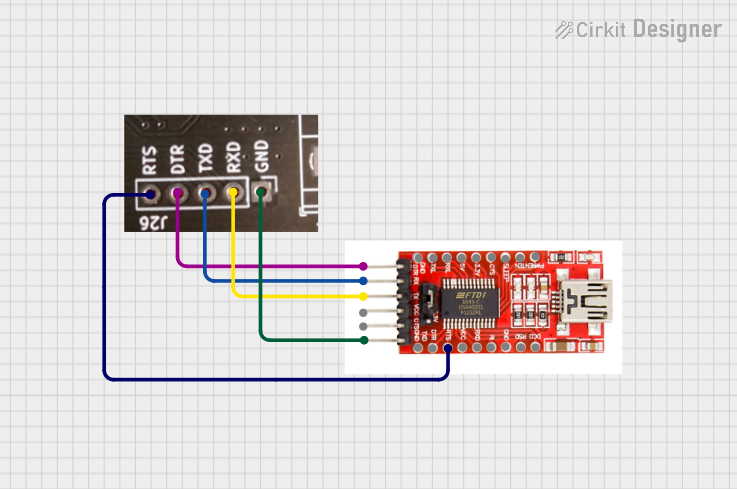
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer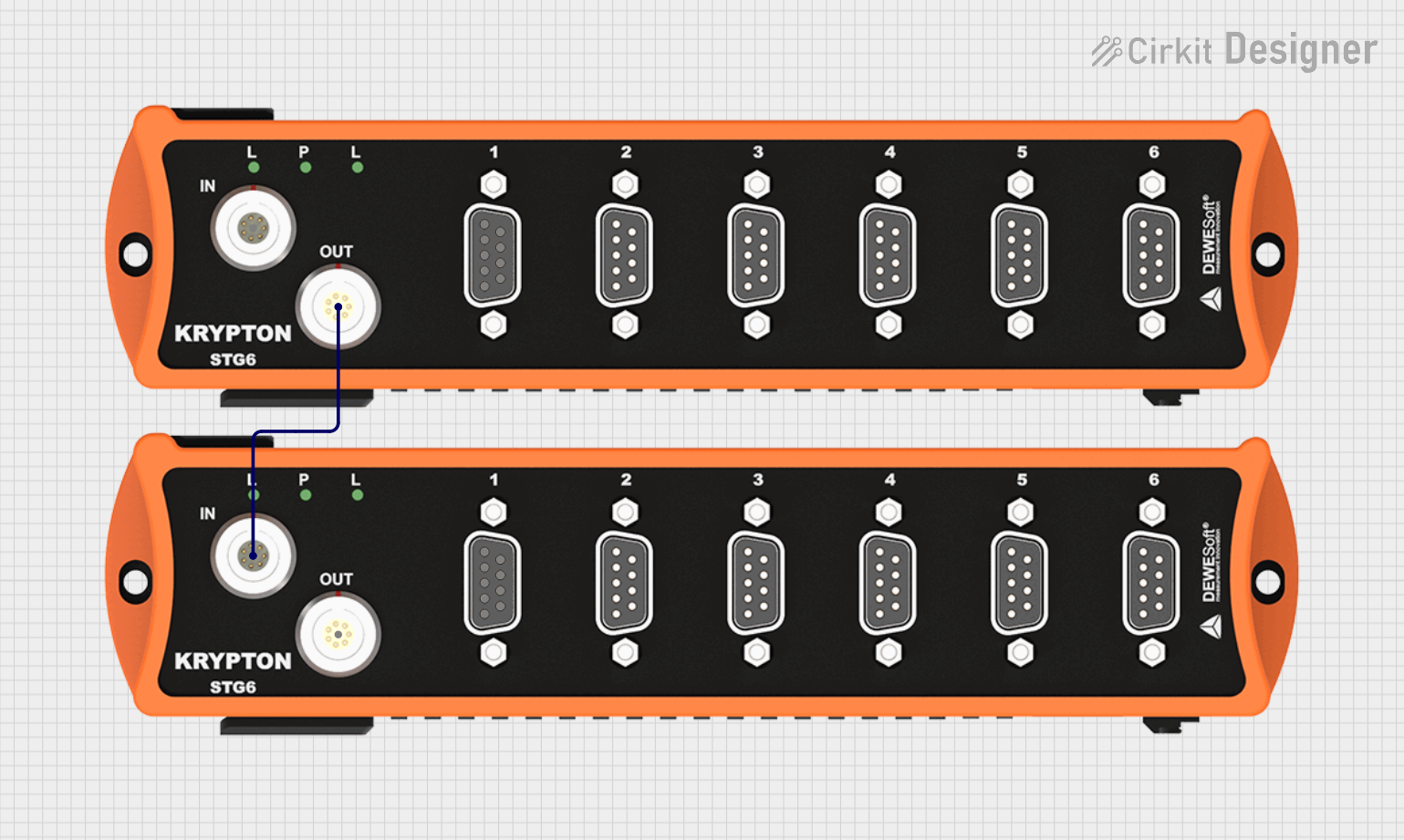
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer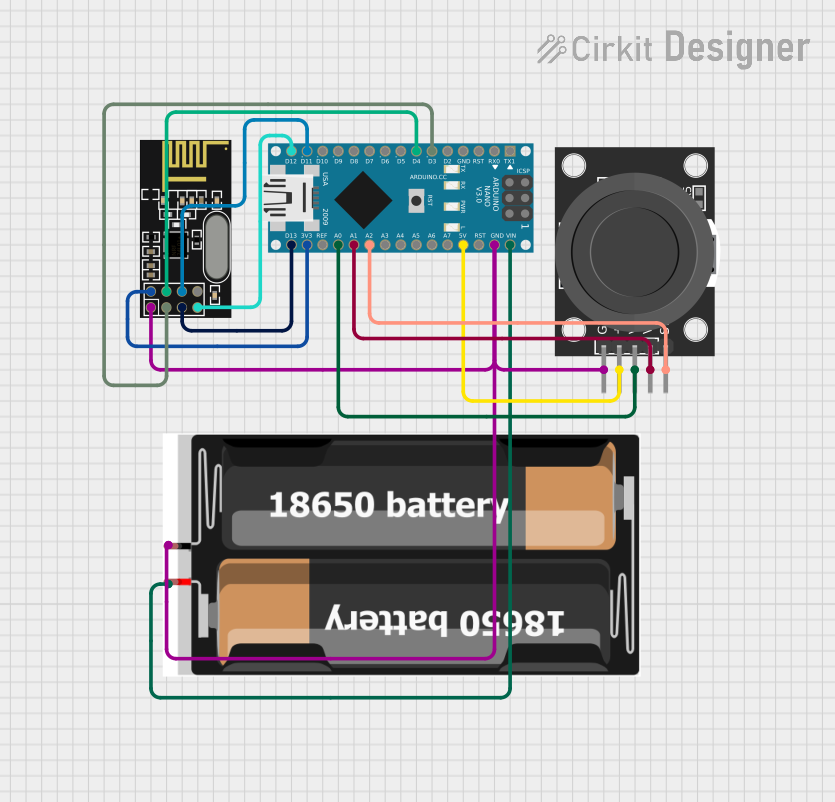
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with JST XH 6P

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power supply connections in small electronic devices
- Signal transmission in sensors and modules
- Battery pack connections
- Consumer electronics, such as RC vehicles and drones
- Industrial control systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the JST XH 6P connector:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Positions | 6 |
| Pitch | 2.5mm |
| Rated Voltage | 250V AC/DC |
| Rated Current | 3A |
| Contact Resistance | ≤ 10mΩ |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥ 1000MΩ |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +85°C |
| Material (Housing) | Nylon 66 (UL94V-0 rated) |
| Material (Contacts) | Phosphor bronze with tin plating |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The JST XH 6P connector has six pins, each corresponding to a specific position. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Signal/Power Line 1 |
| 2 | Signal/Power Line 2 |
| 3 | Signal/Power Line 3 |
| 4 | Signal/Power Line 4 |
| 5 | Signal/Power Line 5 |
| 6 | Signal/Power Line 6 |
Note: The specific function of each pin depends on the application and circuit design.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the JST XH 6P in a Circuit
Connector Assembly:
- Use compatible crimp terminals (e.g., JST SXH-001T-P0.6) to attach wires to the connector.
- Ensure the wires are stripped to the appropriate length (approximately 1.0–1.5mm) before crimping.
- Insert the crimped terminals into the housing until they click into place.
PCB Mounting:
- Use a matching JST XH 6P header (straight or right-angle) for PCB mounting.
- Solder the header onto the PCB, ensuring proper alignment and secure connections.
Mating the Connector:
- Align the JST XH 6P connector with the header and gently push it in until it locks.
- To disconnect, press the locking tab and pull the connector out carefully.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Wire Gauge: Use wires with a gauge of 22–28 AWG for optimal performance.
- Current Rating: Do not exceed the rated current of 3A to avoid overheating.
- Secure Connections: Ensure the crimp terminals are properly secured to prevent loose connections.
- Environmental Conditions: Avoid exposing the connector to temperatures or voltages beyond its rated limits.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The JST XH 6P can be used to connect sensors or modules to an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of wiring and code for reading data from a sensor connected via the JST XH 6P.
Wiring Diagram
- Pin 1: VCC (5V from Arduino)
- Pin 2: GND (Ground)
- Pin 3: Signal (e.g., analog input to Arduino A0)
- Pins 4–6: Unused (or additional signals as needed)
Arduino Code Example
// Example code for reading an analog sensor connected via JST XH 6P
const int sensorPin = A0; // Pin A0 is connected to the sensor's signal line
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as an input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the analog value from the sensor
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Note: Ensure the sensor's power and ground lines are properly connected to the Arduino.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Loose Connections:
- Issue: The connector feels loose or disconnects easily.
- Solution: Verify that the crimp terminals are fully inserted into the housing and that the locking tab is engaged.
Overheating:
- Issue: The connector becomes hot during operation.
- Solution: Check that the current does not exceed the 3A rating. Use thicker wires if necessary.
Signal Interference:
- Issue: Unstable or noisy signals.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for signal lines and ensure proper grounding.
Connector Damage:
- Issue: The housing or pins are damaged.
- Solution: Replace the damaged connector and ensure proper handling during assembly.
FAQs
Q1: Can the JST XH 6P be used for high-power applications?
A1: No, the JST XH 6P is rated for a maximum current of 3A. For high-power applications, consider connectors with higher current ratings.
Q2: Is the JST XH 6P compatible with other JST series connectors?
A2: No, the JST XH 6P is specifically designed for the XH series and may not be compatible with other series due to differences in pitch and design.
Q3: How do I remove a crimp terminal from the housing?
A3: Use a small flathead screwdriver or a terminal removal tool to gently release the locking tab and pull the terminal out.
Q4: Can I use the JST XH 6P in outdoor applications?
A4: The JST XH 6P is not waterproof. For outdoor use, consider using waterproof connectors or additional sealing methods.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the JST XH 6P connector in your electronic projects.