
How to Use 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna in Cirkit Designer
Design with 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna is a specialized component designed to operate within the frequency range of 1.2 to 1.3 GHz. It is widely used in wireless communication applications, including RFID systems, remote sensing, telemetry, and amateur radio. This antenna is optimized for high-frequency signal transmission and reception, ensuring reliable performance in various environments.
Common applications and use cases:
- RFID systems: Used for tracking and identification in industrial and commercial settings.
- Remote sensing: Supports data collection in environmental monitoring and scientific research.
- Telemetry: Enables wireless data transmission in aerospace, automotive, and medical fields.
- Amateur radio: Popular among hobbyists for long-range communication.
Explore Projects Built with 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna
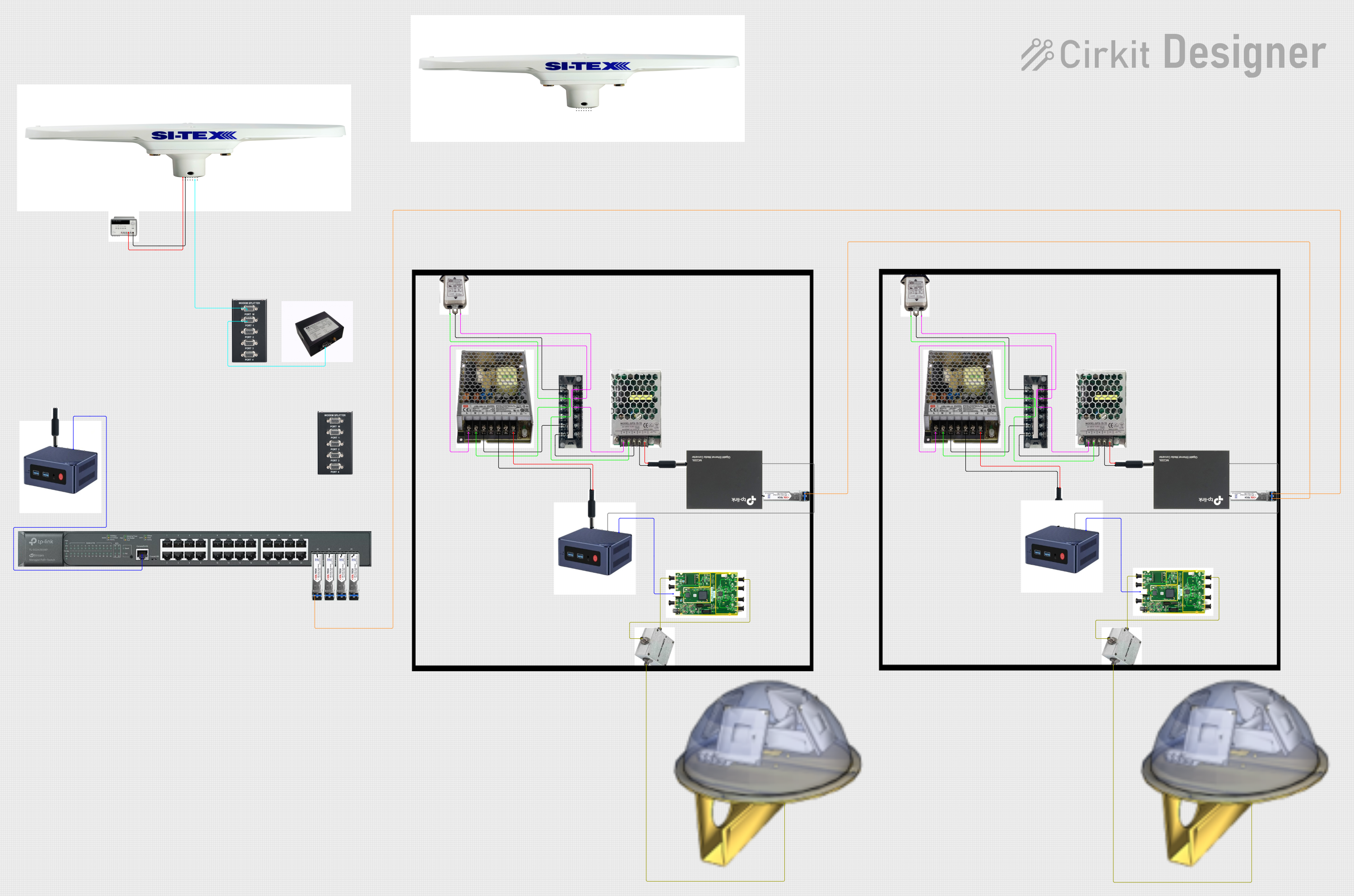
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer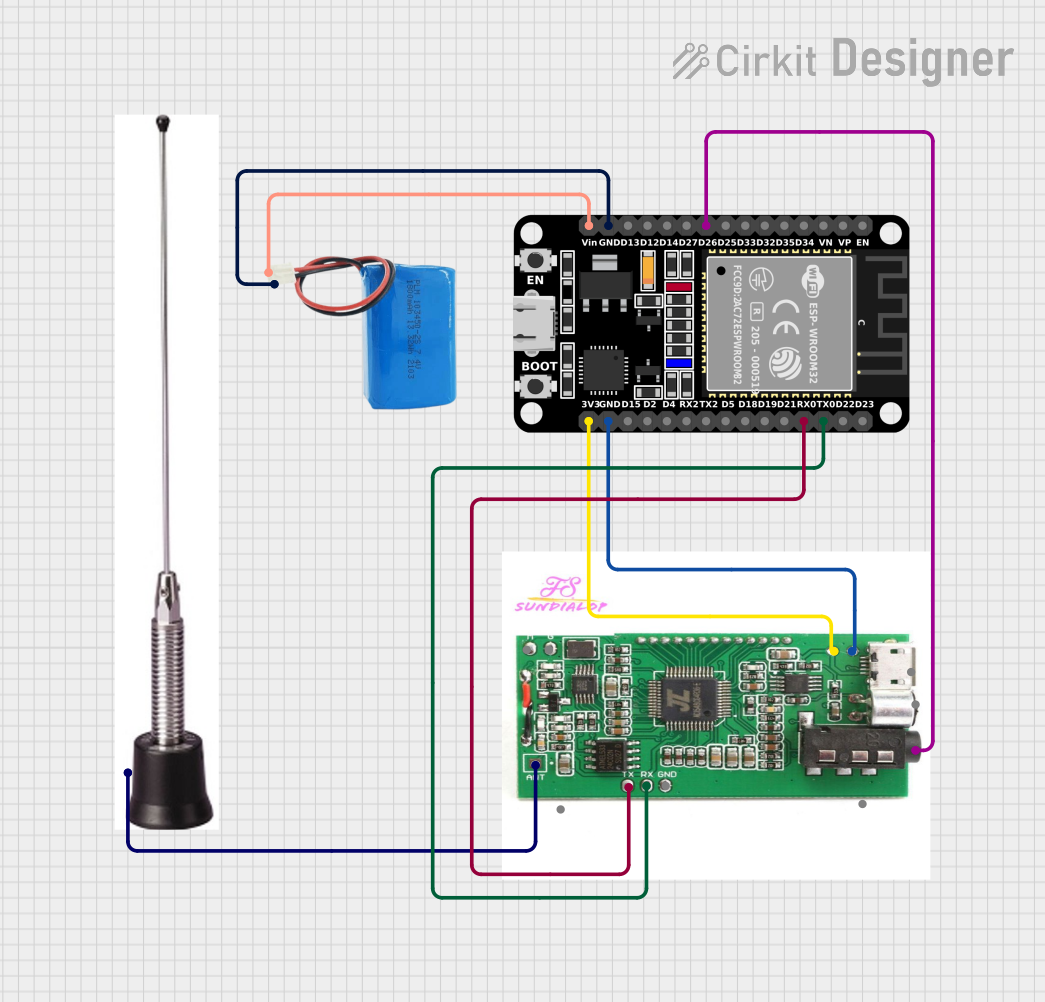
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 1.2 GHz to 1.3 GHz |
| Gain | 6 dBi to 12 dBi (varies by model) |
| Polarization | Linear or Circular |
| Impedance | 50 Ω |
| VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) | ≤ 1.5:1 |
| Connector Type | SMA, N-Type, or custom |
| Power Handling Capacity | Up to 50 W |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | Varies (e.g., 20 cm to 50 cm length) |
| Weight | Typically 200 g to 500 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna typically has a single RF connector for interfacing with the circuit or device. Below is a description of the connector pin:
| Pin/Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| RF Connector | Connects the antenna to the transmitter or receiver. Common types include SMA and N-Type. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Antenna in a Circuit
- Select a compatible RF connector: Ensure the antenna's connector type (e.g., SMA or N-Type) matches the connector on your device or circuit.
- Mount the antenna: Position the antenna in a location with minimal obstructions to maximize signal strength. For outdoor use, ensure the antenna is weatherproofed.
- Connect to the RF circuit: Attach the antenna to the transmitter or receiver using a low-loss coaxial cable. Maintain a secure connection to minimize signal loss.
- Tune the system: Verify that the operating frequency of your transmitter or receiver is within the 1.2 to 1.3 GHz range. Adjust the system settings as needed to optimize performance.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Impedance matching: Ensure the antenna impedance (50 Ω) matches the impedance of your RF circuit to prevent signal reflection and power loss.
- Minimize VSWR: Use high-quality cables and connectors to maintain a low VSWR (≤ 1.5:1) for efficient signal transmission.
- Avoid interference: Place the antenna away from sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI), such as power lines or other RF devices.
- Secure mounting: Use appropriate mounting hardware to prevent the antenna from shifting or falling during operation.
- Weatherproofing: For outdoor installations, use weatherproof enclosures or coatings to protect the antenna from environmental damage.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
While the 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna is not directly connected to an Arduino UNO, it can be used with RF modules (e.g., LoRa or telemetry modules) that interface with the Arduino. Below is an example of using an RF module with the antenna and Arduino:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <LoRa.h>
// Define LoRa module pins
#define SCK 5 // Clock pin
#define MISO 19 // Master In Slave Out
#define MOSI 27 // Master Out Slave In
#define SS 18 // Slave Select
#define RST 14 // Reset pin
#define DIO0 26 // Interrupt pin
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
while (!Serial);
Serial.println("Initializing LoRa module...");
// Initialize LoRa module
if (!LoRa.begin(1250E6)) { // Set frequency to 1.25 GHz (within 1.2-1.3 GHz range)
Serial.println("LoRa initialization failed!");
while (1);
}
Serial.println("LoRa initialized successfully!");
}
void loop() {
// Send a test message
Serial.println("Sending message...");
LoRa.beginPacket();
LoRa.print("Hello, 1.2/1.3 GHz antenna!");
LoRa.endPacket();
delay(5000); // Wait 5 seconds before sending the next message
}
Note: Ensure the RF module supports the 1.2/1.3 GHz frequency range and is connected to the antenna via a compatible RF connector.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Weak signal strength:
- Cause: Obstructions or poor antenna placement.
- Solution: Reposition the antenna to a higher or more open location. Ensure there are no large metal objects nearby.
High VSWR:
- Cause: Impedance mismatch or damaged cable/connector.
- Solution: Verify impedance matching and inspect cables and connectors for damage. Replace if necessary.
No signal reception:
- Cause: Incorrect frequency or faulty connections.
- Solution: Confirm the operating frequency is within the 1.2 to 1.3 GHz range. Check all connections for proper attachment.
Intermittent signal loss:
- Cause: Environmental interference or loose connections.
- Solution: Identify and eliminate sources of interference. Secure all connections.
FAQs
Q: Can this antenna be used for GPS applications?
A: No, GPS typically operates at 1.575 GHz, which is outside the 1.2/1.3 GHz range.Q: Is this antenna suitable for outdoor use?
A: Yes, but ensure it is weatherproofed or installed in a protective enclosure.Q: What is the maximum range of this antenna?
A: The range depends on factors such as antenna gain, transmitter power, and environmental conditions. Typically, it can achieve several kilometers in open areas.Q: Can I use this antenna with a Wi-Fi router?
A: No, Wi-Fi operates at 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, which is outside the antenna's frequency range.