
How to Use PLUG: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with PLUG in Cirkit Designer
Design with PLUG in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A plug is a device that connects an electrical appliance to a power source, allowing electricity to flow into the appliance. It is an essential component in electrical systems, enabling the safe and efficient transfer of power. Plugs are commonly used in household appliances, industrial equipment, and portable devices. They come in various types and configurations to suit different power standards and regions.
Explore Projects Built with PLUG

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer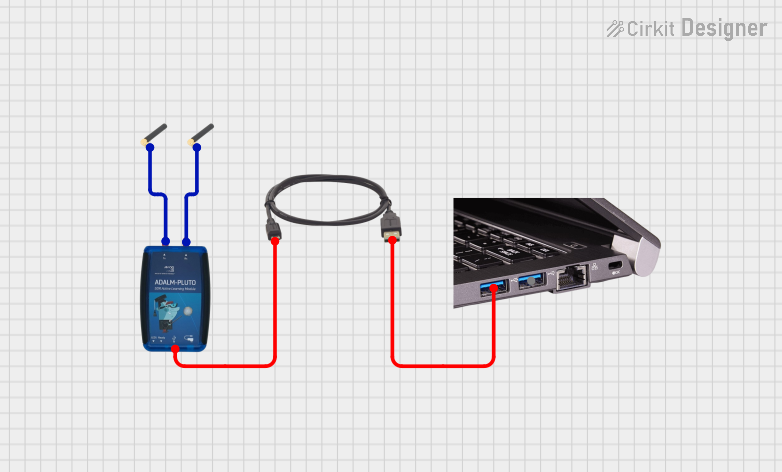
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer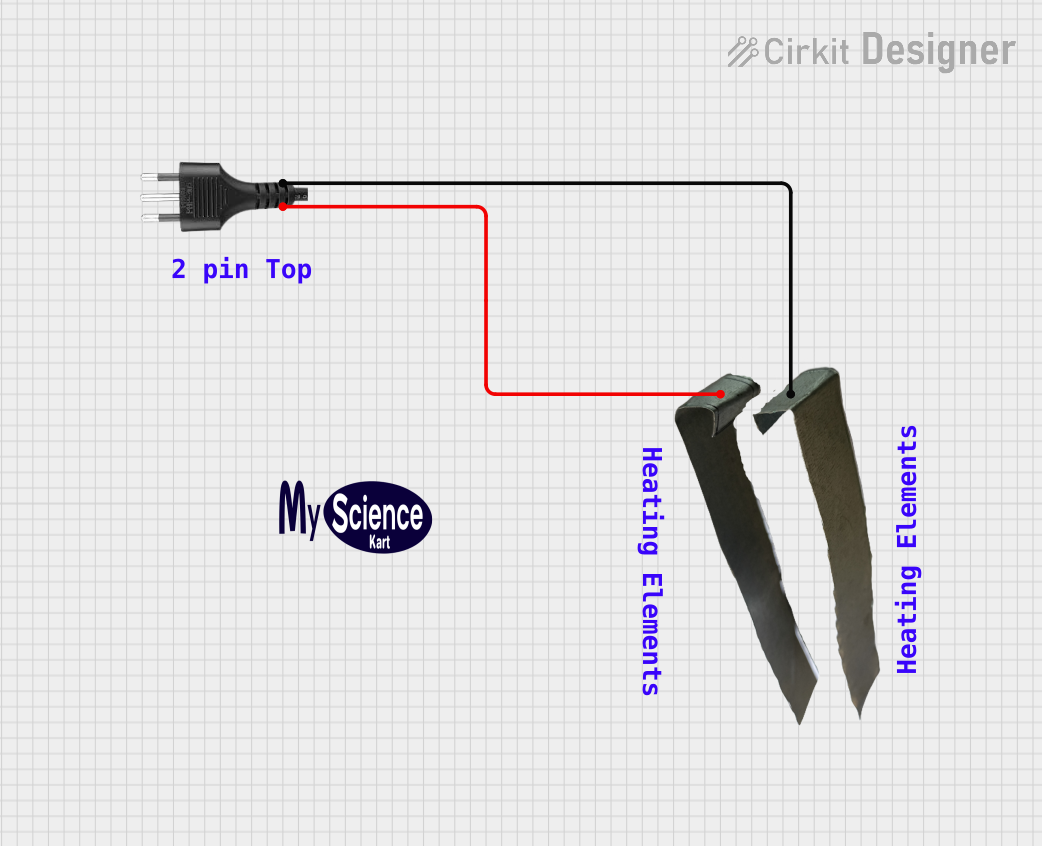
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PLUG

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering household appliances such as refrigerators, televisions, and lamps.
- Connecting industrial machinery to power outlets.
- Charging portable devices like laptops and smartphones.
- Temporary power connections for tools and equipment on construction sites.
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of a plug can vary depending on its type and intended use. Below are general specifications for a standard household plug:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 110V - 240V AC (varies by region) |
| Current Rating | 6A - 16A (depending on plug type) |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Material | Thermoplastic or thermoset for insulation |
| Contact Material | Brass or copper alloy |
| Safety Features | Grounding pin, insulated prongs |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration of a plug depends on its type. Below is an example of a standard three-pin plug:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Carries the current from the power source. |
| Neutral (N) | Completes the circuit back to the power source. |
| Ground (G) | Provides a safety path for fault currents. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Plug in a Circuit
- Inspect the Plug: Ensure the plug is in good condition, with no visible damage to the casing or pins.
- Connect to Appliance: Attach the plug to the appliance's power cord securely.
- Insert into Outlet: Insert the plug into a compatible power outlet, ensuring a snug fit.
- Power On: Turn on the appliance or device to begin operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Match Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the plug's voltage and current ratings match the appliance and power source.
- Use Grounded Plugs: For safety, always use plugs with a grounding pin when connecting high-power appliances.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the plug's current rating to prevent overheating or damage.
- Inspect Regularly: Check for wear and tear, such as frayed wires or loose connections, and replace damaged plugs immediately.
- Regional Compatibility: Use the correct plug type for the region to ensure compatibility with local power outlets.
Example: Connecting a Plug to an Arduino UNO
If you are using a plug to power an Arduino UNO via an external power adapter, follow these steps:
- Use a plug with a compatible DC power adapter.
- Connect the adapter's output to the Arduino's power jack.
- Ensure the adapter provides 7-12V DC, as required by the Arduino UNO.
// Example Arduino code to blink an LED
// Connect an LED to pin 13 with a resistor in series
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Plug Does Not Fit Outlet:
- Cause: Incorrect plug type for the region.
- Solution: Use a plug adapter or replace the plug with a compatible type.
Appliance Does Not Power On:
- Cause: Loose connection or damaged plug.
- Solution: Check the plug for damage and ensure it is securely connected.
Overheating Plug:
- Cause: Overloading or poor contact with the outlet.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the plug and ensure a proper fit in the outlet.
Sparking When Plugging In:
- Cause: Faulty outlet or plug.
- Solution: Inspect both the plug and outlet for damage and replace if necessary.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Always turn off the power source before inspecting or replacing a plug.
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and proper voltage levels.
- Replace damaged plugs with high-quality, certified replacements to ensure safety and reliability.