
How to Use ESP32S3-board: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
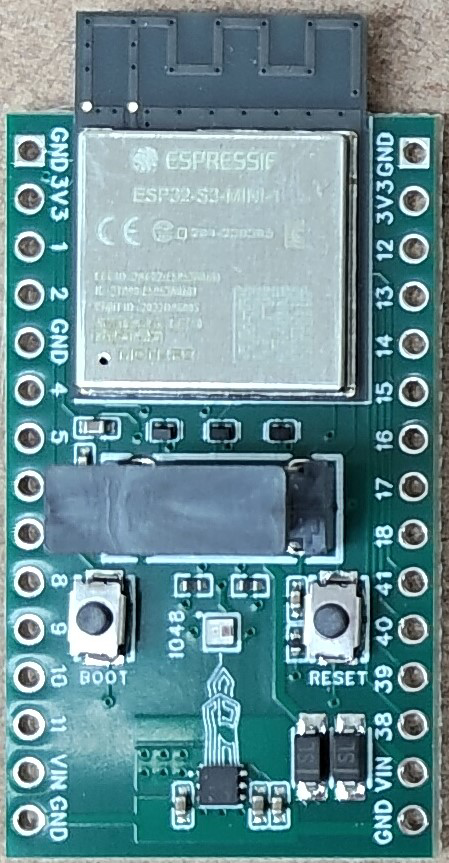

 Design with ESP32S3-board in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32S3-board in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32S3 board, manufactured by Custom, is a versatile and powerful microcontroller designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It features dual-core processing, integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, and a wide array of GPIO pins. This board is ideal for projects requiring wireless communication, edge computing, or advanced sensor integration. Its robust performance and support for various peripherals make it a popular choice for hobbyists, developers, and engineers alike.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32S3-board
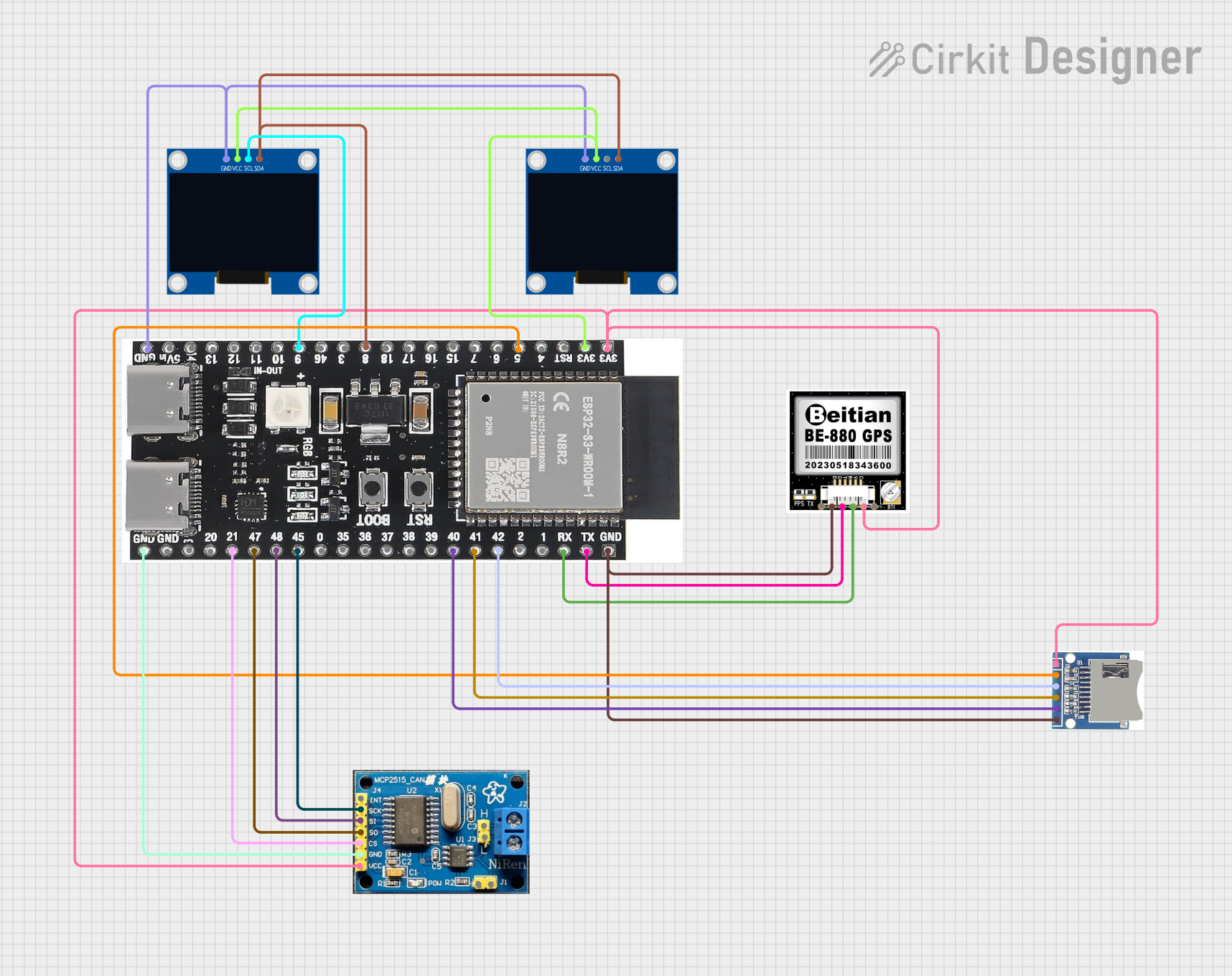
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer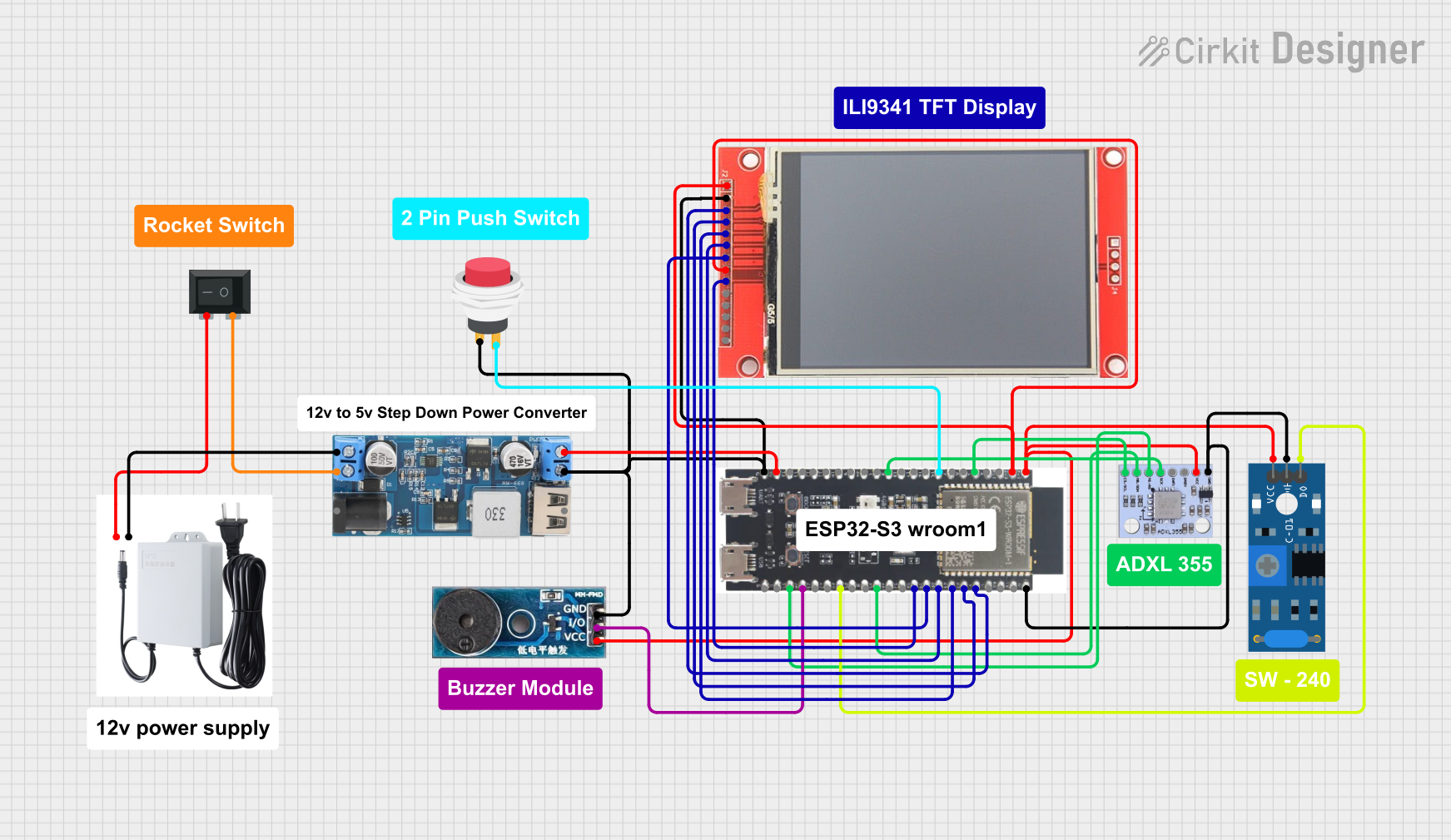
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32S3-board

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Smart home devices (e.g., smart lights, thermostats)
- Wearable technology
- Industrial IoT systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- Robotics and automation
- Edge AI and machine learning applications
Technical Specifications
The ESP32S3 board offers a rich set of features and capabilities. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Processor | Dual-core Xtensa® LX7, up to 240 MHz |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n (2.4 GHz), Bluetooth 5.0 LE |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (expandable, depending on the variant) |
| SRAM | 512 KB internal, with additional PSRAM support |
| GPIO Pins | 45 (configurable for digital I/O, ADC, DAC, PWM, etc.) |
| ADC Channels | 14 channels, 12-bit resolution |
| DAC Channels | 2 channels, 8-bit resolution |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, CAN, RMT, and USB OTG |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Power Supply | USB-C (5V input) or external 3.3V source |
| Dimensions | 50 mm x 25 mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32S3 board has a flexible pinout. Below is a table summarizing the key pins and their functions:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground pin |
| 2 | 3V3 | 3.3V power output |
| 3 | EN | Enable pin (active high) |
| 4 | GPIO0 | General-purpose I/O, used for boot mode selection |
| 5 | GPIO1-45 | Configurable GPIO pins for digital I/O, ADC, DAC, PWM, etc. |
| 6 | TXD0/RXD0 | UART0 transmit/receive pins (default serial communication) |
| 7 | SCL/SDA | I2C clock and data lines |
| 8 | MOSI/MISO/SCK | SPI interface pins |
| 9 | USB_DM/USB_DP | USB data lines for OTG functionality |
| 10 | VBUS | USB power input (5V) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32S3 Board in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the board to a USB-C cable for power and programming.
- Alternatively, supply 3.3V to the 3V3 pin and connect GND to the ground of your circuit.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF for development.
- Add the ESP32 board package to the Arduino IDE via the Board Manager.
- Select "ESP32S3" as the target board and the correct COM port.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins for connecting sensors, actuators, or other peripherals.
- Ensure the voltage levels of connected devices are compatible with the 3.3V logic of the ESP32S3.
Uploading Code:
- Write your code in the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF.
- Press the "Upload" button in the IDE to flash the code to the board.
- If required, hold the BOOT button during the upload process.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected devices operate at 3.3V logic levels to avoid damaging the board.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to prevent unexpected resets or malfunctions.
- GPIO Usage: Avoid using reserved pins (e.g., GPIO0, GPIO2) for general I/O, as they may interfere with boot modes.
- Heat Management: If running intensive tasks, consider adding a heatsink to manage heat dissipation.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of using the ESP32S3 to read a temperature sensor and send data via Wi-Fi:
#include <WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library
// Wi-Fi credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
// Pin configuration
const int tempSensorPin = 34; // GPIO34 for analog input
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(tempSensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
// Connect to Wi-Fi
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
}
void loop() {
// Read temperature sensor value
int sensorValue = analogRead(tempSensorPin);
float voltage = sensorValue * (3.3 / 4095.0); // Convert ADC value to voltage
float temperature = (voltage - 0.5) * 100.0; // Convert voltage to temperature
// Print temperature to Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
delay(2000); // Wait 2 seconds before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Board Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the USB-C cable supports data transfer (not just charging).
- Check if the correct COM port is selected in the IDE.
Code Upload Fails:
- Hold the BOOT button while uploading the code.
- Verify that the correct board and port are selected in the IDE.
Wi-Fi Connection Issues:
- Double-check the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network operates on the 2.4 GHz band (not 5 GHz).
Unstable Operation:
- Use a stable power source with sufficient current (at least 500 mA).
- Avoid connecting high-power peripherals directly to the GPIO pins.
FAQs
Q: Can the ESP32S3 board run on battery power?
A: Yes, the board can be powered by a 3.7V LiPo battery with a suitable voltage regulator.
Q: Does the ESP32S3 support over-the-air (OTA) updates?
A: Yes, the ESP32S3 supports OTA updates, allowing you to upload new firmware wirelessly.
Q: Can I use the ESP32S3 for machine learning applications?
A: Absolutely! The ESP32S3 has hardware acceleration for AI tasks and supports frameworks like TensorFlow Lite.
Q: Is the ESP32S3 compatible with Arduino libraries?
A: Yes, the ESP32S3 is fully compatible with most Arduino libraries, making it easy to integrate into existing projects.