
How to Use dc : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with dc in Cirkit Designer
Design with dc in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Direct Current (DC) motor is an electronic component that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. It operates on the basic principle that a current-carrying conductor is placed within a magnetic field, which causes it to experience a force and thus create motion. DC motors are widely used in various applications such as electric vehicles, industrial machinery, robotics, and consumer electronics due to their simplicity, reliability, and ease of control.
Explore Projects Built with dc
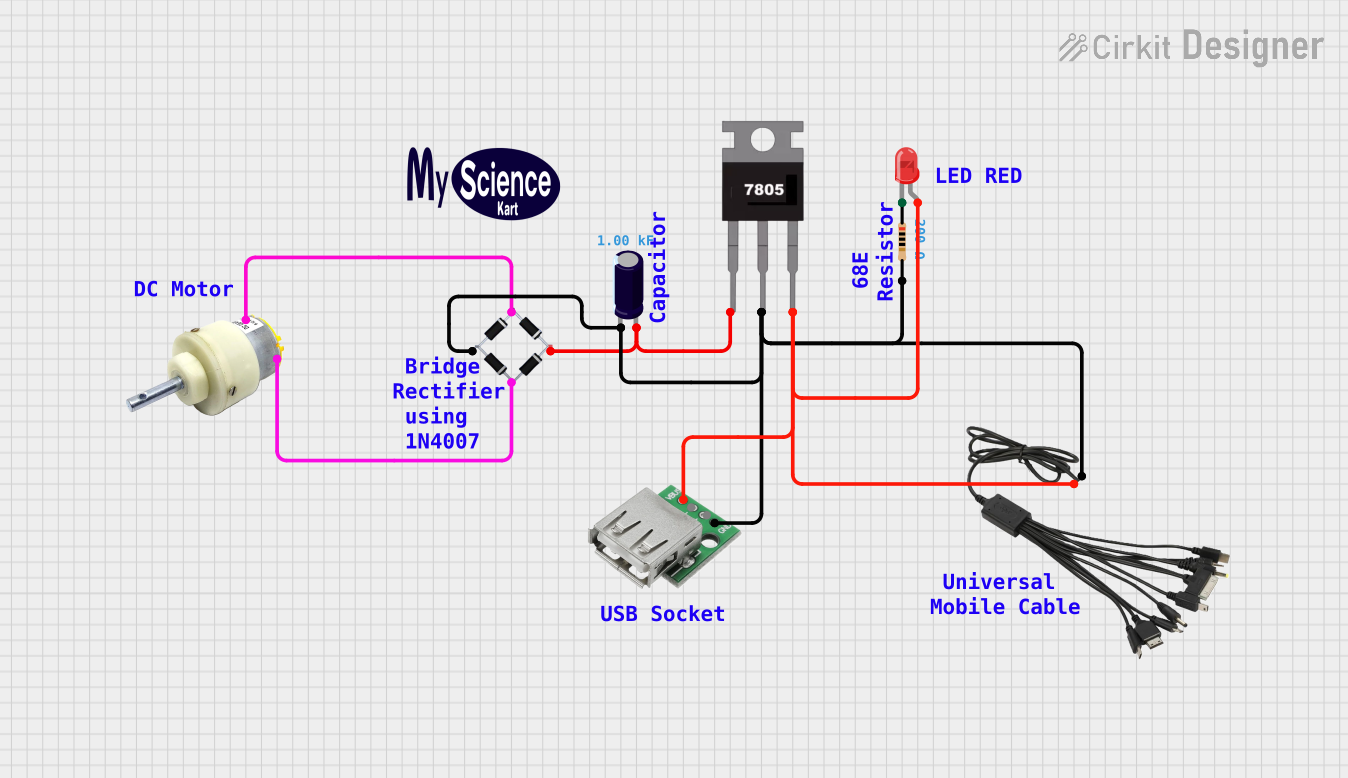
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer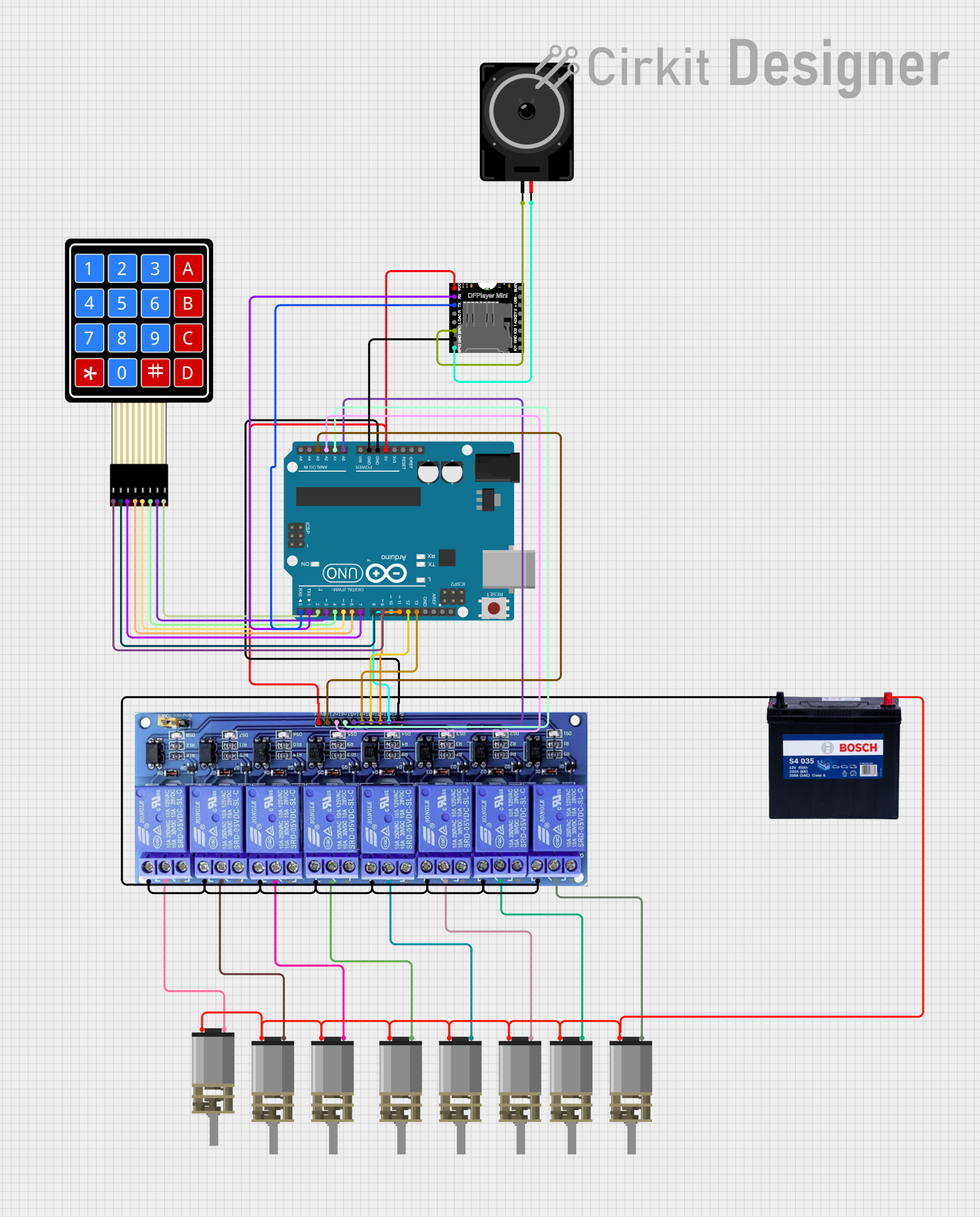
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with dc

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Actuation of robotic limbs and wheels.
- Consumer Electronics: Drives in computer disk drives, fans, and vibrators in mobile phones.
- Automotive: Fuel pump controllers, power windows, and seat adjusters.
- Industrial Control: Conveyor systems, hoists, and process control applications.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Range: Typically 1.5V to 300V DC
- Current Rating: Varies with size and model, from mA to hundreds of Amperes
- Power Ratings: From milliwatts to several kilowatts
- Speed: Typically from 1000 RPM to 15000 RPM for small motors
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive Supply (V+) | Connect to positive voltage |
| 2 | Negative Supply (GND) | Connect to ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply Connection: Connect the positive terminal of the DC motor to the positive voltage supply and the negative terminal to the ground.
- Speed Control: To control the speed of the DC motor, a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal can be applied to the positive terminal.
- Direction Control: To change the direction of the motor, reverse the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor terminals.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Rating: Do not exceed the voltage rating of the motor as it can cause overheating and damage.
- Current Draw: Ensure the power supply can handle the motor's current draw, especially during startup.
- Motor Driver: Use a motor driver or H-bridge to interface the motor with microcontrollers for better control and to protect the microcontroller from high current.
- Flyback Diode: Always use a flyback diode across the motor terminals to protect the circuit from voltage spikes when the motor is turned off.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Motor not spinning: Check if the power supply is connected correctly and if it provides sufficient voltage and current.
- Motor overheating: Ensure the motor is not overloaded and that it operates within its rated voltage and current.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Verify that all connections are secure and correct.
- Measure Voltage and Current: Use a multimeter to ensure the motor is receiving the correct voltage and current.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Look for signs of damage or wear on the motor that could impede its operation.
FAQs
Q: Can I control a DC motor using an Arduino? A: Yes, you can control a DC motor using an Arduino by using a motor driver and PWM signals.
Q: What is the purpose of a flyback diode? A: A flyback diode is used to protect the circuit from voltage spikes caused by the inductive load of the motor when it is turned off.
Q: How can I reverse the direction of a DC motor? A: You can reverse the direction by reversing the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor's terminals.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Example code to control a DC motor with an Arduino UNO
#include <Arduino.h>
const int motorPin = 3; // PWM pin connected to the DC motor
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motor pin as output
}
void loop() {
analogWrite(motorPin, 127); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(1000); // Run motor for 1 second
analogWrite(motorPin, 0); // Stop motor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Note: This example assumes the use of a motor driver or H-bridge connected to the motor and the Arduino. The analogWrite function sends a PWM signal to control the motor speed. Always ensure that the motor driver is compatible with the motor's voltage and current specifications.