
How to Use Pushbutton: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
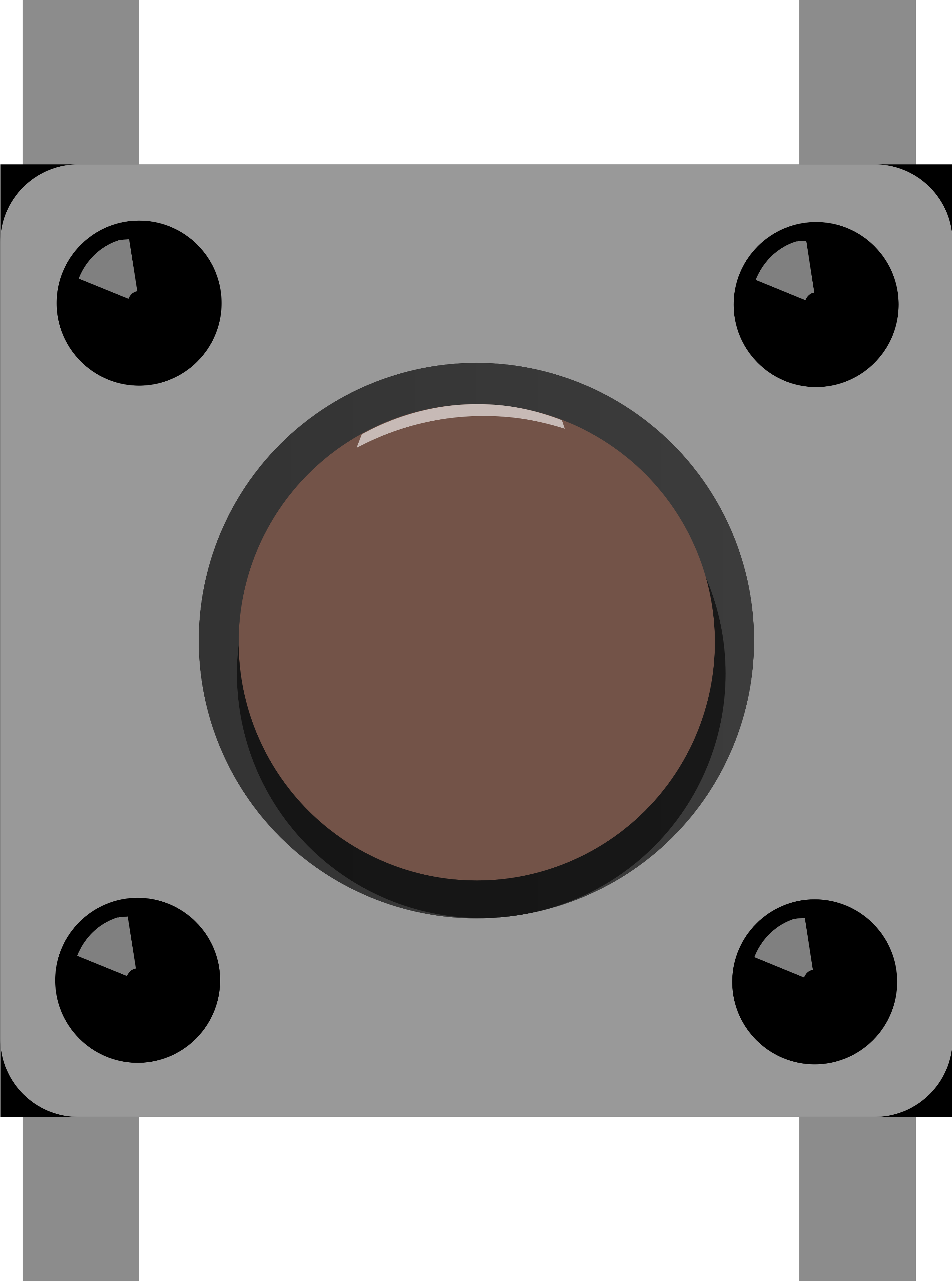

 Design with Pushbutton in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pushbutton in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A pushbutton is a momentary switch that completes a circuit when pressed and breaks the circuit when released. It is a simple yet essential component in electronics, commonly used for user input in devices such as calculators, remote controls, and microcontroller-based projects. Pushbuttons are available in various sizes and designs, making them versatile for a wide range of applications.
Explore Projects Built with Pushbutton

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer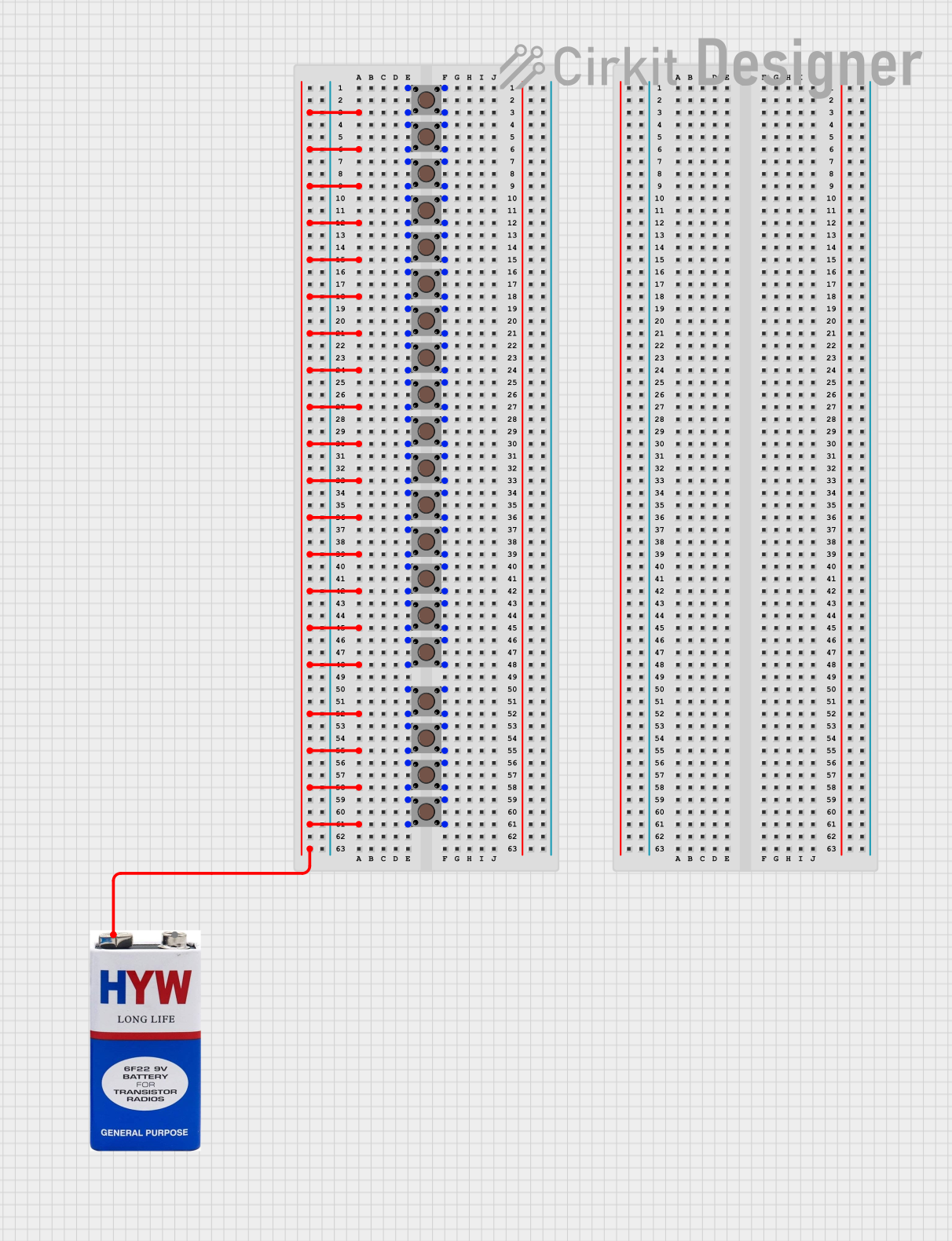
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer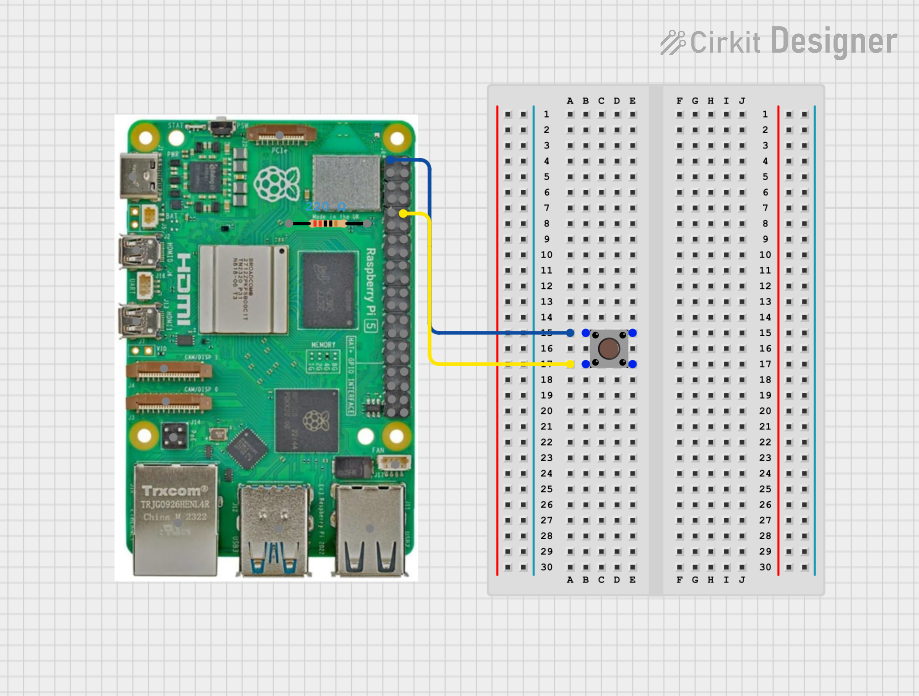
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer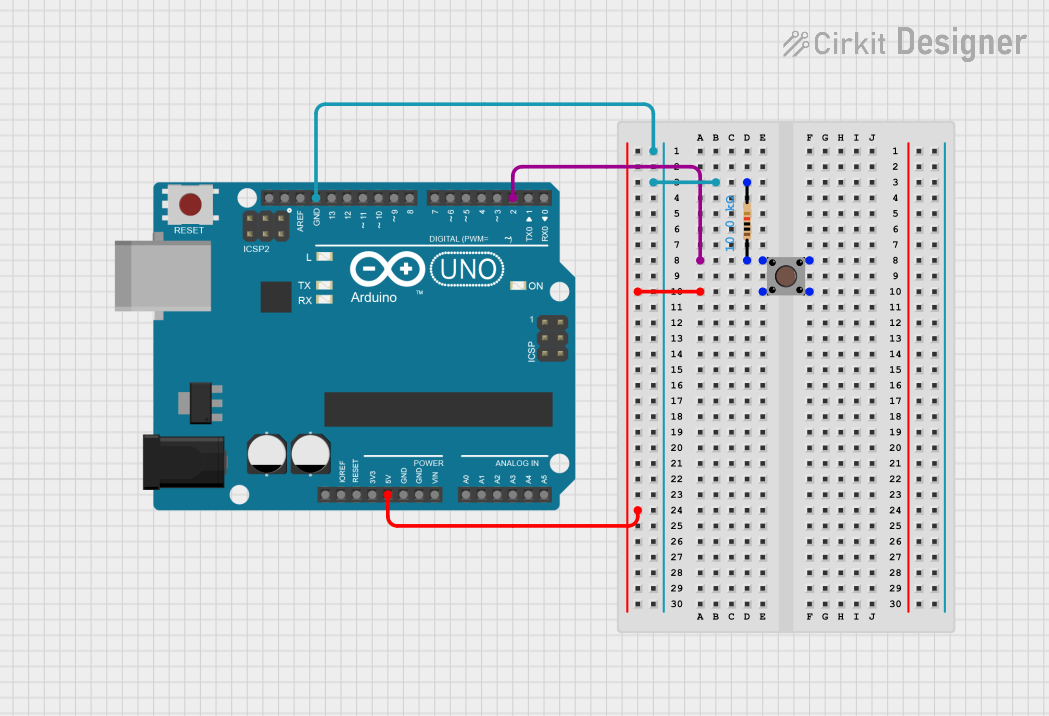
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pushbutton

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- User input for microcontroller projects (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- Reset or power buttons in electronic devices
- Control panels for industrial equipment
- Keyboards and gaming controllers
- Doorbells and alarm systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard pushbutton:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 12V (typical) |
| Maximum Current Rating | 50mA to 500mA (depending on type) |
| Contact Resistance | < 100 mΩ |
| Insulation Resistance | > 100 MΩ |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +70°C |
| Mechanical Lifespan | 100,000 to 1,000,000 presses |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
A standard 4-pin pushbutton typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| Pin 1 | Normally Open (NO) terminal |
| Pin 2 | Normally Open (NO) terminal (connected internally to Pin 1) |
| Pin 3 | Normally Open (NO) terminal |
| Pin 4 | Normally Open (NO) terminal (connected internally to Pin 3) |
Note: Pins 1 and 2 are internally connected, as are Pins 3 and 4. When the button is pressed, Pins 1/2 are connected to Pins 3/4, completing the circuit.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Pushbutton in a Circuit
- Identify the Pins: Use a multimeter to confirm the internal connections of the pushbutton. Pins 1 and 2 are connected, as are Pins 3 and 4.
- Connect to a Microcontroller or Circuit:
- Connect one side of the pushbutton (e.g., Pins 1/2) to a digital input pin of a microcontroller or to the positive voltage rail.
- Connect the other side (e.g., Pins 3/4) to ground through a pull-down resistor (typically 10kΩ) to ensure a stable LOW signal when the button is not pressed.
- Debounce the Button: Pushbuttons can produce noise or "bouncing" when pressed. Use either a hardware debounce circuit (e.g., a capacitor) or software debounce logic to ensure reliable operation.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect a pushbutton to an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Connect one side of the pushbutton (Pins 1/2) to Arduino digital pin 2.
- Connect the other side (Pins 3/4) to ground.
- Add a 10kΩ pull-down resistor between digital pin 2 and ground.
Arduino Code Example
// Pushbutton Example with Arduino UNO
// This code reads the state of a pushbutton and turns on an LED when pressed.
const int buttonPin = 2; // Pin connected to the pushbutton
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); // Set the button pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); // Read the button state
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
// If the button is pressed, turn on the LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
// If the button is not pressed, turn off the LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: Always implement hardware or software debouncing to avoid erratic behavior.
- Current Limiting: Ensure the current through the pushbutton does not exceed its maximum rating.
- Durability: For high-use applications, select a pushbutton with a higher mechanical lifespan.
- Mounting: Ensure the pushbutton is securely mounted to avoid accidental disconnections.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Button Not Responding:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure all connections are secure.
Button Produces Erratic Behavior:
- Cause: Button bouncing.
- Solution: Add a hardware debounce circuit (e.g., a capacitor) or implement software debouncing.
Button Stuck or Not Clicking:
- Cause: Mechanical wear or debris inside the button.
- Solution: Replace the pushbutton or clean it carefully if possible.
Microcontroller Not Detecting Button Press:
- Cause: Missing pull-down resistor or incorrect pin configuration.
- Solution: Add a pull-down resistor and verify the microcontroller pin setup.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a pushbutton without a pull-down resistor?
A: It is not recommended. Without a pull-down resistor, the input pin may float, causing unreliable readings.
Q: How do I debounce a pushbutton in software?
A: Use a delay or timing-based logic to ignore rapid state changes. For example, wait 50ms after detecting a button press before checking again.
Q: Can I use a pushbutton with a 5V circuit?
A: Yes, most pushbuttons are compatible with 5V circuits. Ensure the current does not exceed the button's rating.
Q: What is the difference between a pushbutton and a toggle switch?
A: A pushbutton is momentary (only active while pressed), while a toggle switch maintains its state until toggled again.