
How to Use fuse: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with fuse in Cirkit Designer
Design with fuse in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A fuse is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current. It operates by breaking the circuit when the current exceeds a predefined threshold, thereby preventing damage to components and reducing the risk of fire or electrical hazards. Fuses are essential in a wide range of applications, including household appliances, automotive systems, industrial equipment, and electronic devices.
Explore Projects Built with fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer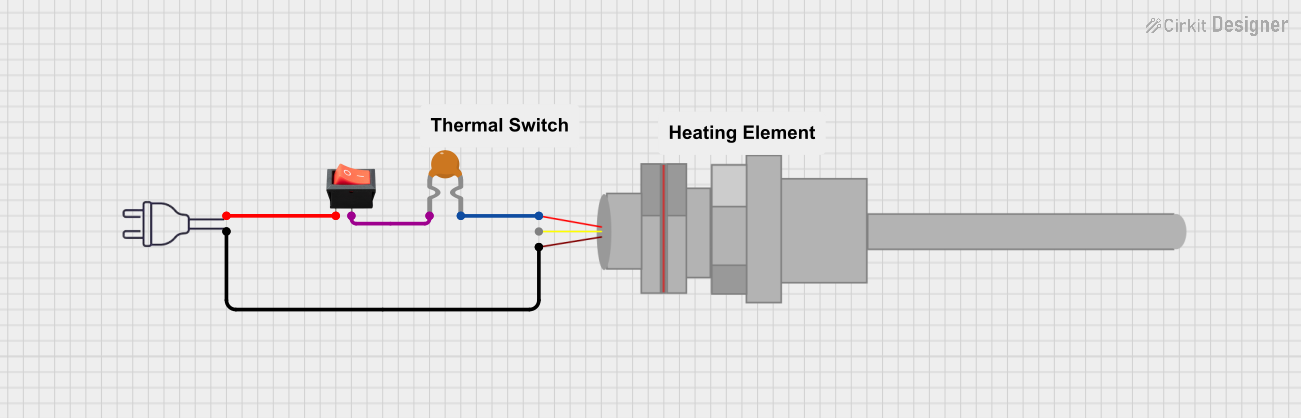
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer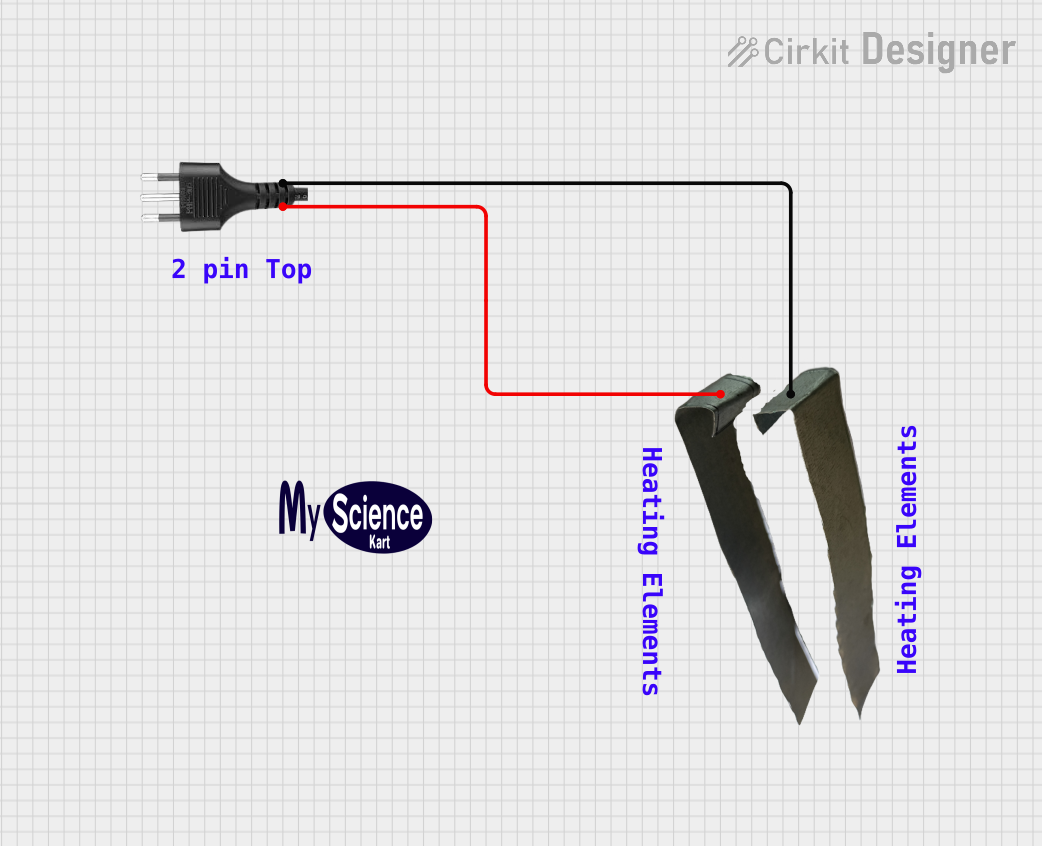
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer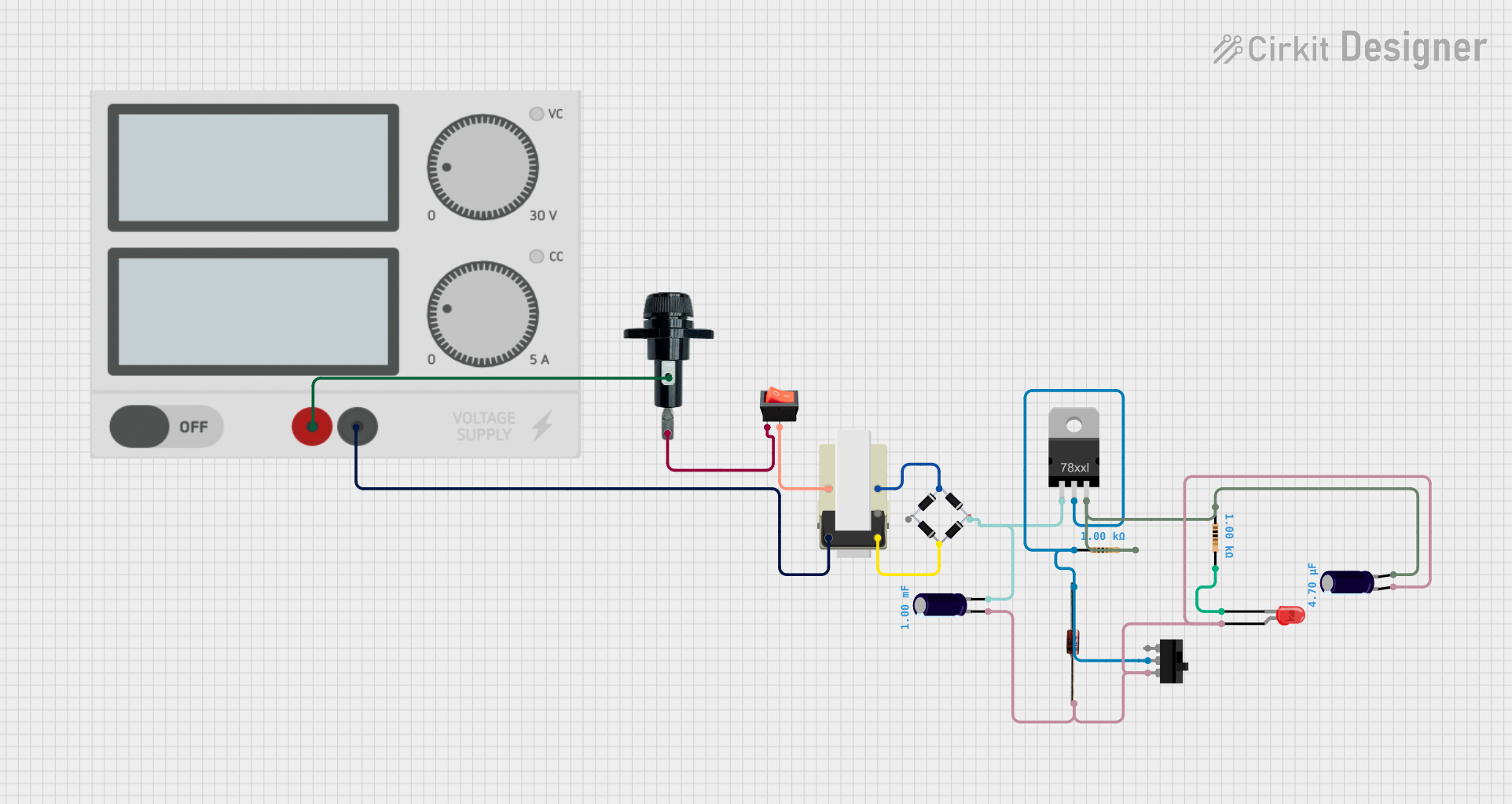
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Household Appliances: Protects devices like refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves.
- Automotive Systems: Safeguards electrical systems in vehicles, such as lighting and infotainment systems.
- Industrial Equipment: Ensures the safety of heavy machinery and control systems.
- Electronic Devices: Prevents damage to sensitive components in circuits, such as microcontrollers and sensors.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the fuse manufactured by 5A with part ID 230 VAC:
General Specifications
- Manufacturer: 5A
- Part ID: 230 VAC
- Type: Cartridge Fuse
- Rated Voltage: 230 VAC
- Rated Current: 5 A
- Breaking Capacity: 1000 A
- Response Time: Fast-acting
- Material: Ceramic body with metal end caps
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
- Mounting Type: Through-hole or clip-in
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Fuses typically do not have pins like integrated circuits but are instead connected via terminals or clips. Below is a table describing the connection points:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Input connection for the electrical circuit. |
| Terminal 2 | Output connection to the protected circuit. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Fuse in a Circuit
- Determine the Fuse Rating: Select a fuse with a current rating slightly higher than the normal operating current of your circuit but lower than the maximum current the circuit can handle.
- Insert the Fuse: Place the fuse in series with the circuit you want to protect. Ensure the fuse is securely mounted in a fuse holder or clip.
- Verify Connections: Double-check that the fuse is properly connected to the input and output terminals of the circuit.
- Power On the Circuit: Turn on the power supply and monitor the circuit for proper operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Correct Rating: Always use a fuse with the correct voltage and current rating for your application.
- Replacement: Replace a blown fuse with one of the same type and rating to maintain safety and functionality.
- Environment: Avoid exposing the fuse to extreme temperatures or moisture, as this can affect its performance.
- Testing: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the fuse if you suspect it has blown.
Example: Using a Fuse with an Arduino UNO
When connecting a fuse to protect an Arduino UNO, place the fuse in series with the power supply to the Arduino. For example, if the Arduino operates at 5V and draws a maximum current of 500 mA, use a fuse rated for 5V and 1 A.
// Example: Arduino UNO circuit with a fuse
// This code demonstrates a simple LED blink program.
// Ensure a fuse is connected in series with the 5V power supply to protect the Arduino.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output for the LED
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Fuse Blows Frequently:
- Cause: The fuse rating is too low for the circuit's normal operating current.
- Solution: Replace the fuse with one that has a slightly higher current rating.
Circuit Does Not Power On:
- Cause: The fuse is blown or not properly connected.
- Solution: Check the fuse for continuity using a multimeter and replace it if necessary.
Fuse Overheats:
- Cause: Poor contact between the fuse and its holder.
- Solution: Ensure the fuse is securely mounted and the terminals are clean.
Fuse Does Not Blow During Overcurrent:
- Cause: The fuse rating is too high for the circuit.
- Solution: Replace the fuse with one that has a lower current rating.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a higher-rated fuse to prevent frequent blowing?
A: No, using a higher-rated fuse can compromise the safety of your circuit. Always use a fuse with the correct rating.Q: How do I know if a fuse is blown?
A: Use a multimeter to check for continuity. A blown fuse will show an open circuit.Q: Can I replace a ceramic fuse with a glass fuse?
A: Only if the replacement fuse has the same voltage, current, and breaking capacity ratings.Q: What happens if I bypass a fuse?
A: Bypassing a fuse removes the circuit's protection, increasing the risk of damage or fire during overcurrent conditions. Always use a fuse for safety.