
How to Use STM32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
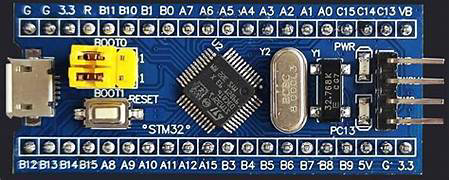
 Design with STM32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with STM32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The STM32 is a family of 32-bit microcontrollers developed by STMicroelectronics. These microcontrollers are based on the ARM Cortex-M architecture, offering a balance of high performance, low power consumption, and a rich set of peripherals. STM32 microcontrollers are widely used in embedded systems, including industrial automation, IoT devices, robotics, and consumer electronics.
Common applications of STM32 include:
- Motor control systems
- Sensor interfacing and data acquisition
- Communication protocols (e.g., UART, SPI, I2C, CAN, USB)
- Real-time operating systems (RTOS) and low-power applications
- Prototyping with development boards like the STM32 Nucleo or Discovery series
Explore Projects Built with STM32
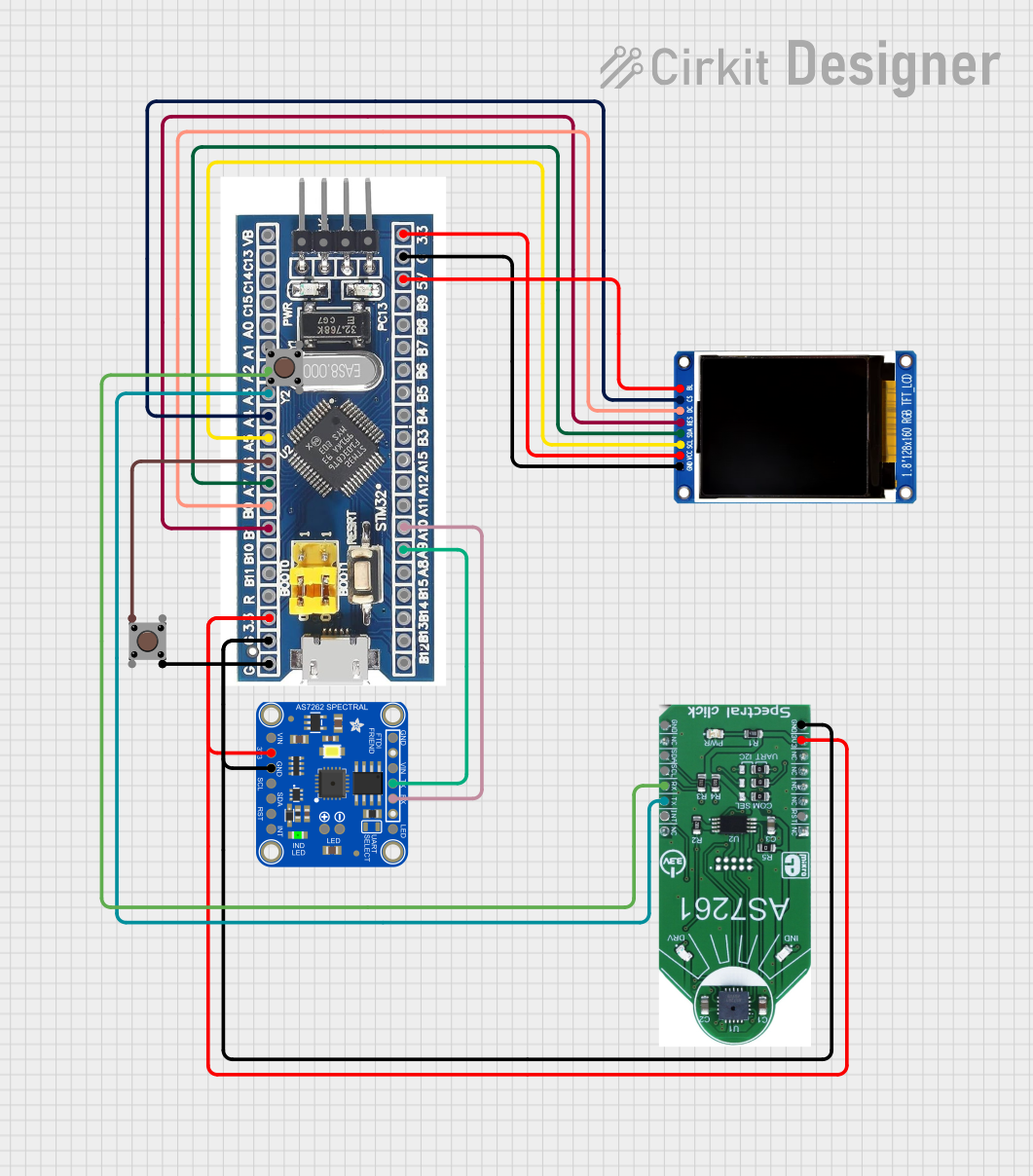
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer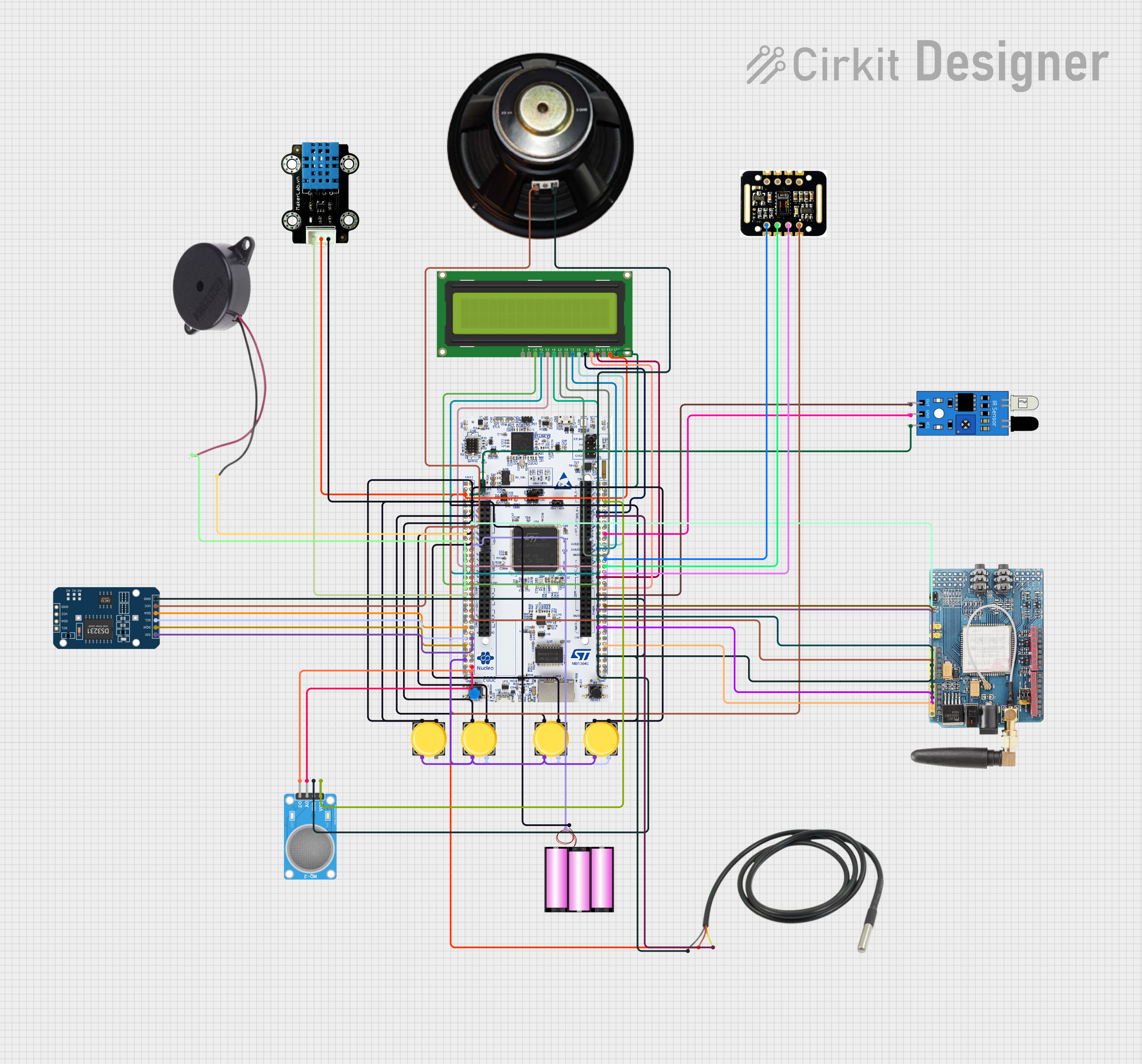
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer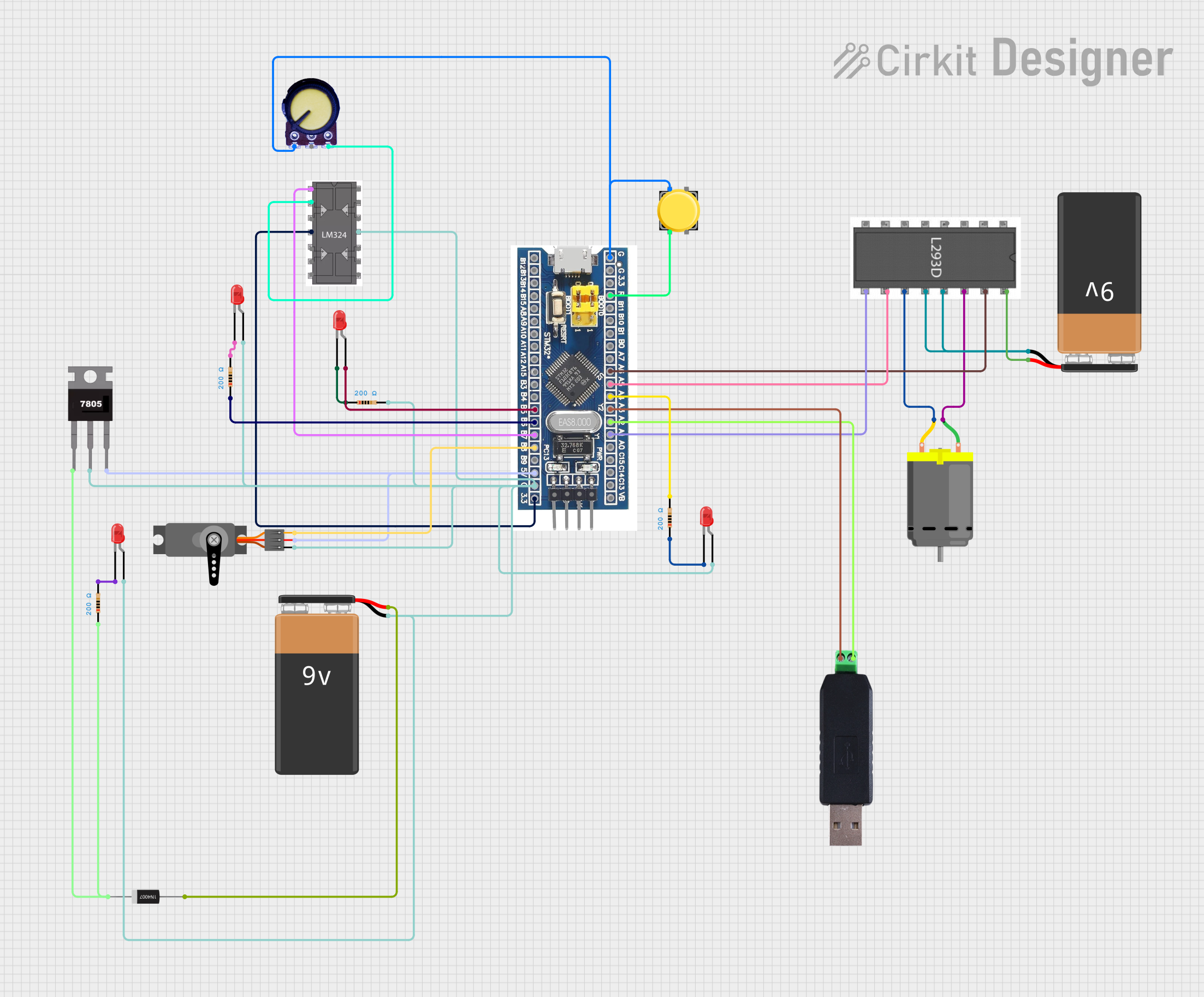
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with STM32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The STM32 family includes a wide range of microcontrollers, but the following specifications are typical for many models:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core | ARM Cortex-M0, M0+, M3, M4, or M7 (depending on the model) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 480 MHz (varies by model) |
| Flash Memory | 16 KB to 2 MB |
| SRAM | 4 KB to 1 MB |
| Operating Voltage | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| GPIO Pins | Up to 168 pins (depending on the package) |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C, CAN, USB, Ethernet, and more |
| Timers | General-purpose, advanced, and low-power timers |
| ADC/DAC | 12-bit or 16-bit ADC, and optional DAC |
| Power Modes | Sleep, Stop, and Standby modes for low-power operation |
| Package Options | LQFP, BGA, WLCSP, and others |
Pin Configuration Example (STM32F103C8T6)
Below is the pin configuration for the STM32F103C8T6, a popular model in the STM32 family:
| Pin Name | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PA0-PA15 | GPIO, ADC, Timer, etc. | General-purpose I/O pins with alternate functions |
| PB0-PB15 | GPIO, I2C, SPI, etc. | General-purpose I/O pins with alternate functions |
| PC13-PC15 | GPIO | General-purpose I/O pins |
| VDD | Power Supply | Positive power supply (3.3V typical) |
| VSS | Ground | Ground connection |
| NRST | Reset | Active-low reset pin |
| BOOT0 | Boot Mode Selection | Selects boot mode (e.g., Flash, SRAM, or System) |
Refer to the specific datasheet for your STM32 model for detailed pin mappings.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the STM32 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the microcontroller is powered with a stable voltage (typically 3.3V). Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) near the VDD and VSS pins to reduce noise.
- Clock Configuration: Connect an external crystal oscillator (e.g., 8 MHz) to the OSC_IN and OSC_OUT pins, or use the internal RC oscillator if available.
- Programming: Use an ST-Link programmer/debugger or a USB-to-serial adapter to upload firmware. The STM32 supports programming via SWD (Serial Wire Debug) or UART.
- Boot Mode Selection: Configure the BOOT0 pin to select the desired boot mode:
- BOOT0 = 0: Boot from Flash memory
- BOOT0 = 1: Boot from System memory (e.g., for firmware updates)
- Peripherals: Connect external devices (e.g., sensors, displays, communication modules) to the appropriate GPIO pins. Configure the pins in software for the desired function (e.g., input, output, alternate function).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected devices operate at compatible voltage levels (e.g., 3.3V logic).
- Debugging: Use the SWD interface for debugging and real-time monitoring of the microcontroller.
- Code Development: Use STM32CubeIDE or Keil uVision for firmware development. STM32CubeMX can help generate initialization code.
- Power Management: Utilize low-power modes (Sleep, Stop, Standby) to reduce power consumption in battery-powered applications.
Example Code: Blinking an LED with STM32 and Arduino IDE
The STM32 can be programmed using the Arduino IDE with the STM32duino core. Below is an example of blinking an LED connected to pin PA5:
// Include the Arduino framework for STM32
#include <Arduino.h>
// Define the LED pin (PA5 is typically the onboard LED on STM32 Nucleo boards)
#define LED_PIN PA5
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set PA5 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(500); // Wait for 500 milliseconds
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(500); // Wait for 500 milliseconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Microcontroller Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or wiring.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage and connections. Check for loose wires or shorts.
Cannot Upload Code
- Cause: Incorrect BOOT0 pin configuration or missing drivers.
- Solution: Ensure BOOT0 is set to the correct mode. Install the ST-Link or USB-to-serial drivers.
Peripherals Not Working
- Cause: Incorrect pin configuration or initialization in software.
- Solution: Double-check the pin assignments and ensure the peripheral is properly initialized in the code.
High Power Consumption
- Cause: Unused peripherals or improper power mode.
- Solution: Disable unused peripherals in software and use low-power modes when possible.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the STM32 with 5V devices?
- A: Most STM32 microcontrollers operate at 3.3V logic levels. Use level shifters or voltage dividers to interface with 5V devices.
Q: How do I reset the STM32?
- A: You can reset the STM32 by pulling the NRST pin low or using the software reset function in your code.
Q: What development tools are recommended for STM32?
- A: STM32CubeIDE, STM32CubeMX, Keil uVision, and IAR Embedded Workbench are popular tools for STM32 development.
Q: Can I program the STM32 without an external programmer?
- A: Yes, many STM32 models support programming via USB (DFU mode) or UART bootloader.
For further details, refer to the official STM32 datasheets and reference manuals provided by STMicroelectronics.