
How to Use OXY-LC Interface Board: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
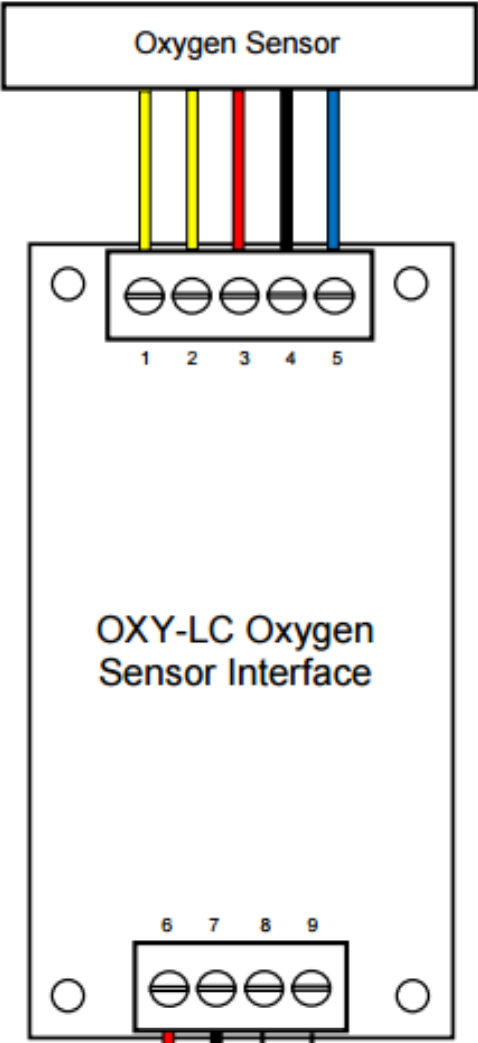
 Design with OXY-LC Interface Board in Cirkit Designer
Design with OXY-LC Interface Board in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The OXY-LC Interface Board (OXY-LC-485), manufactured by SST Sensing, is a specialized circuit board designed to interface with OXY-LC oxygen sensors. It facilitates seamless communication and data transfer between the sensor and external devices such as microcontrollers, PLCs, or industrial systems. The board supports RS-485 communication, making it suitable for robust and long-distance data transmission in industrial and environmental monitoring applications.
Explore Projects Built with OXY-LC Interface Board
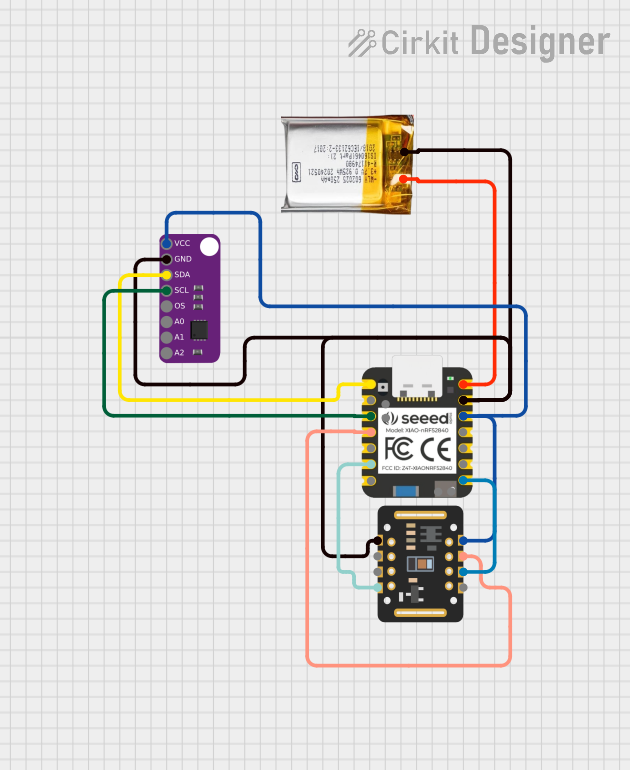
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer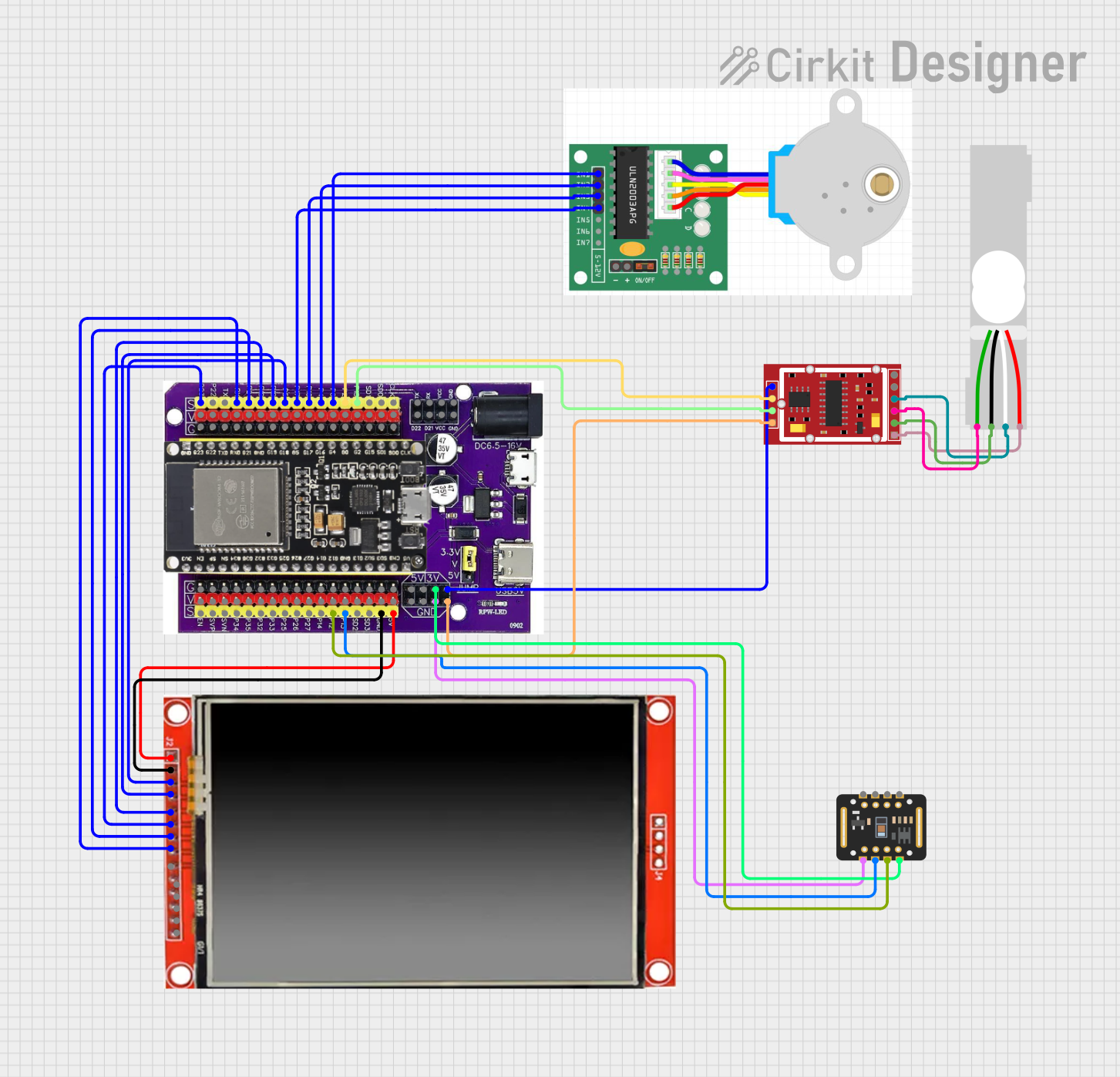
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer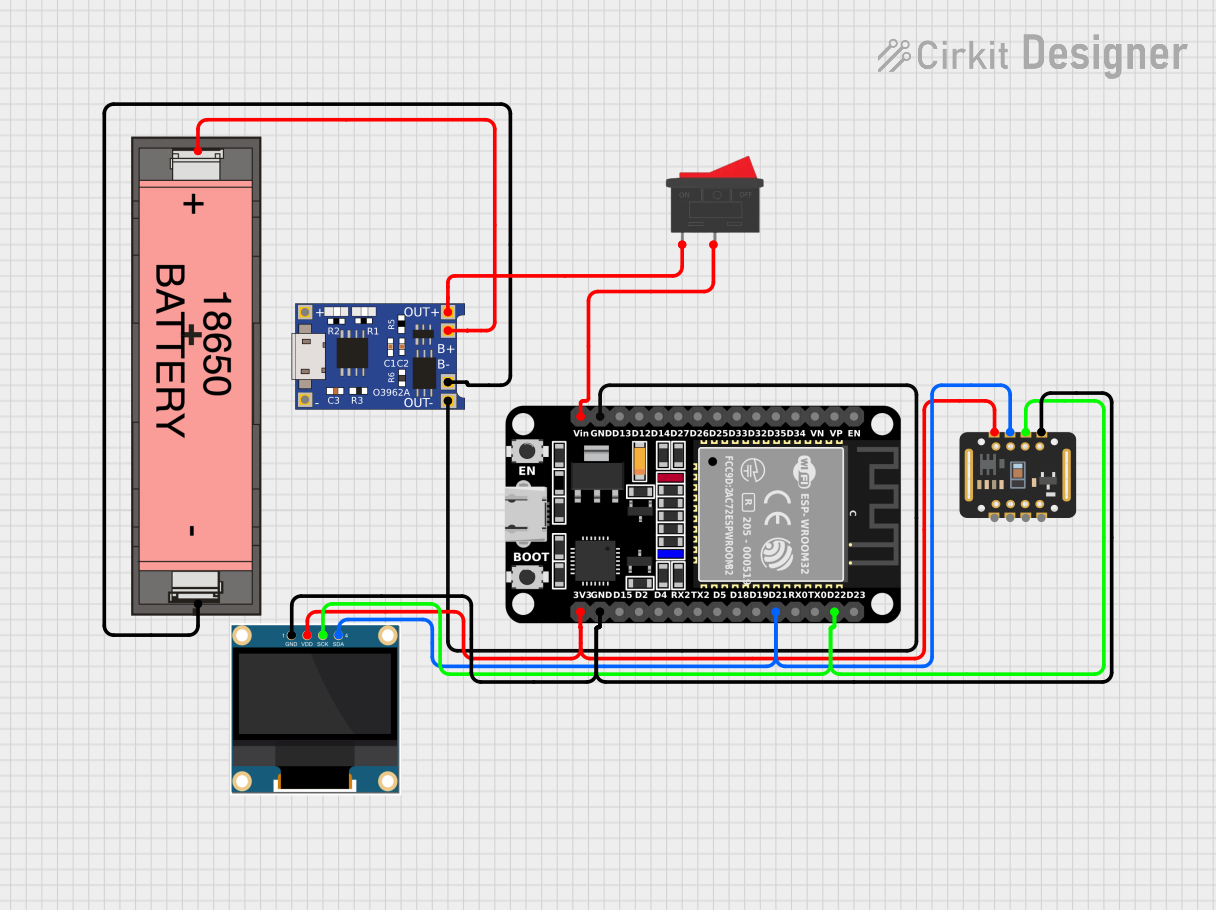
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with OXY-LC Interface Board

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial Process Control: Monitoring oxygen levels in manufacturing processes.
- Environmental Monitoring: Measuring oxygen concentration in air or water.
- Medical Equipment: Integration into devices requiring precise oxygen sensing.
- Research and Development: Prototyping and testing oxygen sensor-based systems.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 5V DC ± 5% |
| Communication Protocol | RS-485 |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +60°C |
| Power Consumption | < 1W |
| Dimensions | 50mm x 25mm x 10mm |
| Connector Type | 4-pin Molex for sensor connection |
| Baud Rate | Configurable (default: 9600 bps) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Sensor Connector (4-pin Molex)
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (5V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | TX+/A | RS-485 differential signal (positive) |
| 4 | TX-/B | RS-485 differential signal (negative) |
RS-485 Communication Interface
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A (TX+) | RS-485 differential signal (positive) |
| 2 | B (TX-) | RS-485 differential signal (negative) |
| 3 | GND | Ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a regulated 5V DC power supply to the VCC and GND pins of the interface board.
- Sensor Connection: Attach the OXY-LC sensor to the 4-pin Molex connector on the board.
- RS-485 Communication: Connect the A (TX+) and B (TX-) pins to the RS-485 bus of your microcontroller or PLC.
- Baud Rate Configuration: Ensure the baud rate of your microcontroller matches the default or configured baud rate of the interface board (default: 9600 bps).
- Data Reading: Use the RS-485 protocol to send commands and receive oxygen concentration data from the sensor.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Use a stable and noise-free 5V DC power source to avoid communication errors.
- Termination Resistor: For long RS-485 bus lines, add a 120-ohm termination resistor between A and B lines at both ends of the bus.
- Grounding: Ensure a common ground between the interface board and the connected device.
- Cable Length: RS-485 supports long cable runs, but keep the length within 1200 meters for reliable communication.
- Sensor Warm-Up: Allow the sensor to stabilize for a few seconds after powering up before taking measurements.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the OXY-LC Interface Board with an Arduino UNO using an RS-485 module.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RS-485 communication pins
#define RX_PIN 10 // Arduino pin connected to RS-485 RX
#define TX_PIN 11 // Arduino pin connected to RS-485 TX
// Create a SoftwareSerial object for RS-485 communication
SoftwareSerial rs485Serial(RX_PIN, TX_PIN);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize RS-485 communication
rs485Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("OXY-LC Interface Board Communication Started");
}
void loop() {
// Send a command to the OXY-LC sensor (example command: 0x01 0x03 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x85 0xDB)
byte command[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x85, 0xDB};
rs485Serial.write(command, sizeof(command));
// Wait for a response
delay(100);
// Check if data is available
if (rs485Serial.available()) {
Serial.print("Sensor Response: ");
while (rs485Serial.available()) {
byte response = rs485Serial.read();
Serial.print(response, HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
}
// Wait before sending the next command
delay(1000);
}
Notes:
- Replace the example command with the appropriate command for your specific application.
- Ensure the RS-485 module is properly connected to the Arduino UNO.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication with the Sensor
- Cause: Incorrect baud rate or wiring.
- Solution: Verify the baud rate and ensure proper connections between the interface board, RS-485 module, and microcontroller.
Unstable Readings
- Cause: Noisy power supply or improper grounding.
- Solution: Use a regulated power supply and ensure a common ground between devices.
Data Corruption on Long Cables
- Cause: Missing termination resistors.
- Solution: Add 120-ohm termination resistors at both ends of the RS-485 bus.
Sensor Not Responding
- Cause: Sensor not properly connected or damaged.
- Solution: Check the sensor connection and replace the sensor if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 3.3V microcontroller with the OXY-LC Interface Board?
A: Yes, but you will need a level shifter to convert the 3.3V logic to 5V for RS-485 communication.Q: What is the maximum cable length supported by RS-485?
A: RS-485 supports cable lengths up to 1200 meters, but ensure proper termination and shielding for long runs.Q: How do I change the baud rate of the interface board?
A: Refer to the OXY-LC Interface Board user manual for instructions on configuring the baud rate.Q: Can I connect multiple sensors to the same RS-485 bus?
A: Yes, RS-485 supports multi-drop communication. Assign unique addresses to each sensor.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the OXY-LC Interface Board effectively. For further assistance, consult the manufacturer's datasheet or technical support.