
How to Use đế ra chân và esp32 s3: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with đế ra chân và esp32 s3 in Cirkit Designer
Design with đế ra chân và esp32 s3 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The "Đế Ra Chân" (commonly referred to as a breakout board) is a versatile accessory designed to simplify the connection and usage of microcontrollers like the ESP32-S3. The ESP32-S3 is a powerful, low-power microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it ideal for IoT applications, smart devices, and wireless communication projects. When paired with a breakout board, the ESP32-S3 becomes easier to integrate into prototyping and development environments.
Explore Projects Built with đế ra chân và esp32 s3
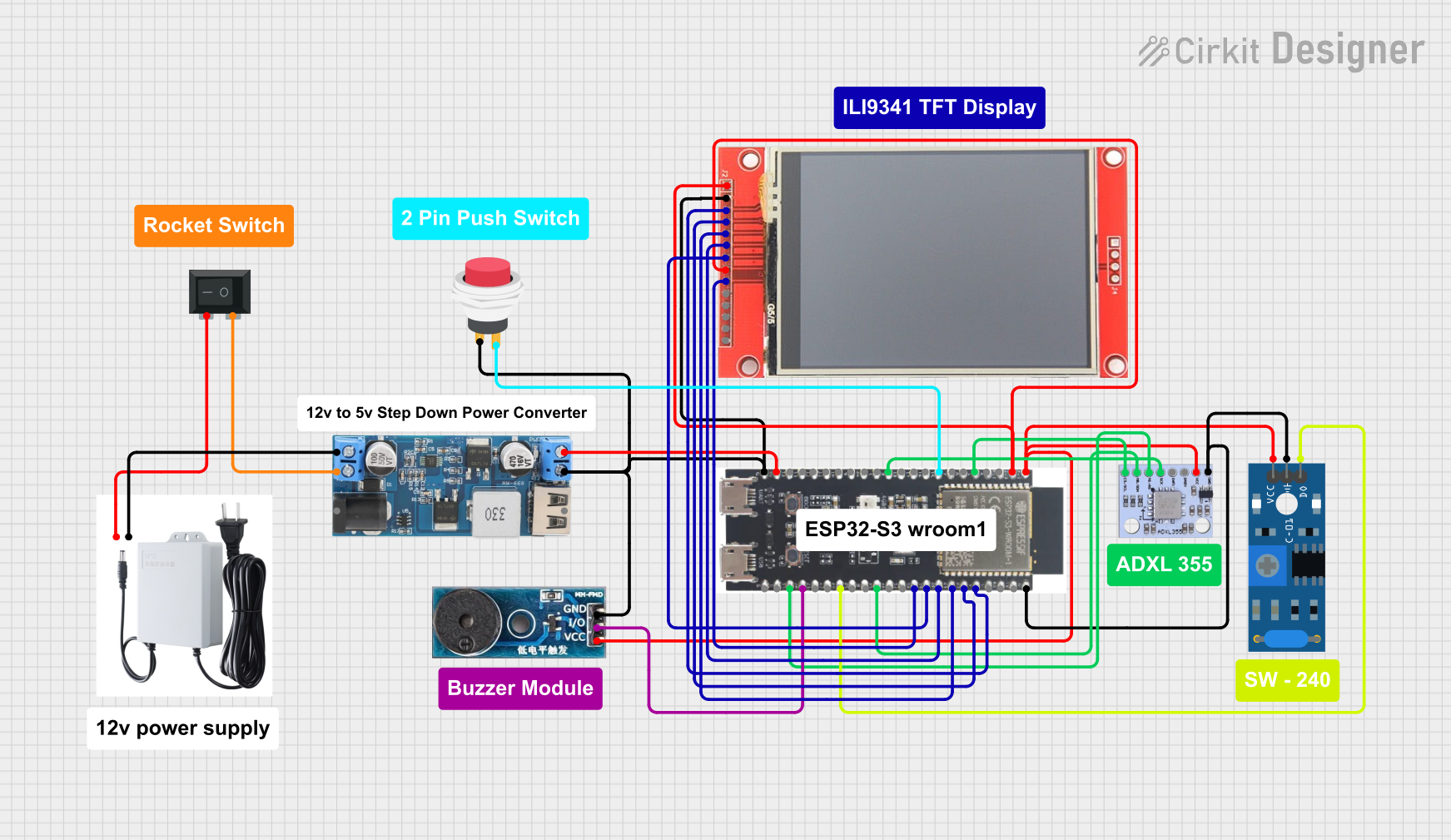
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer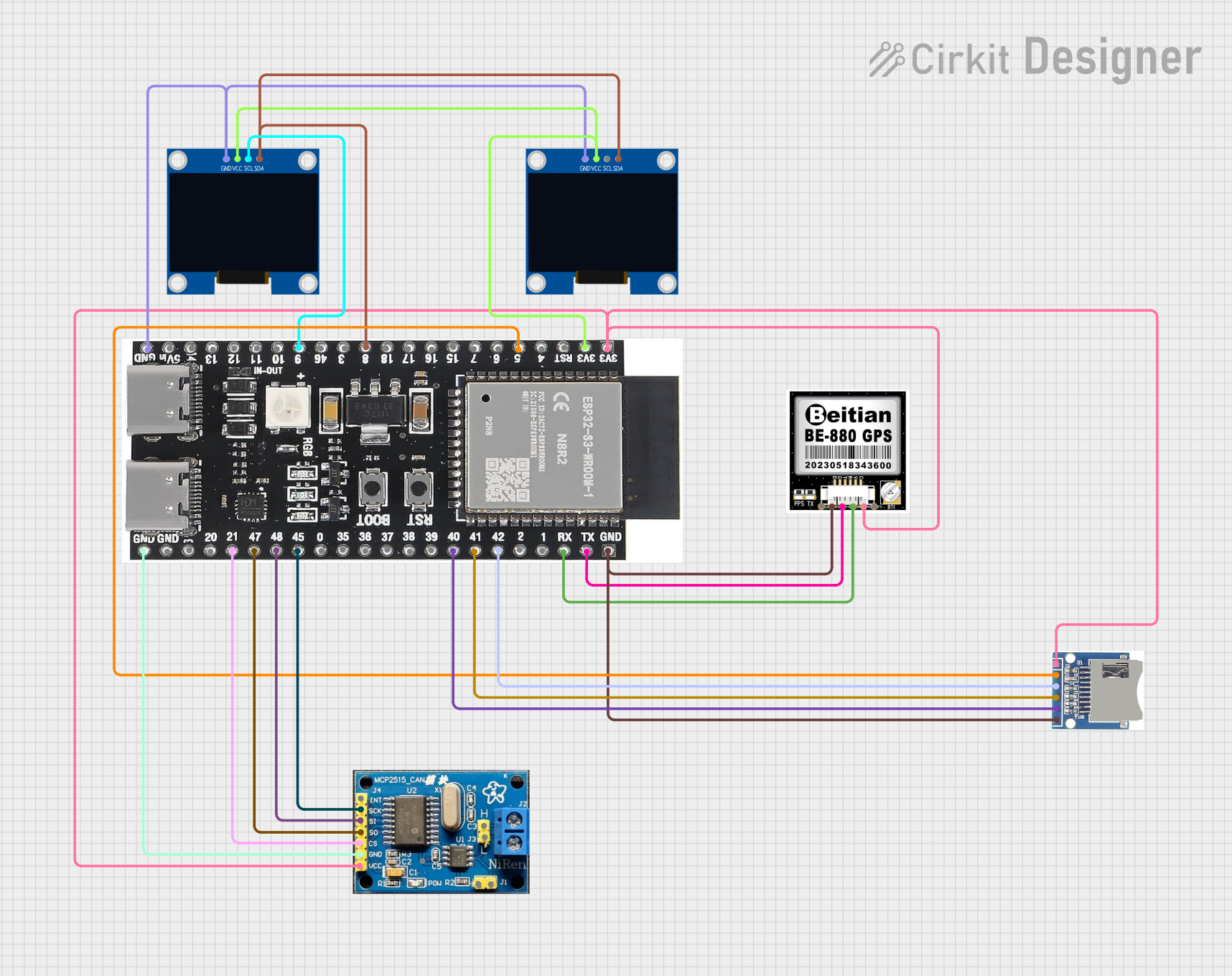
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer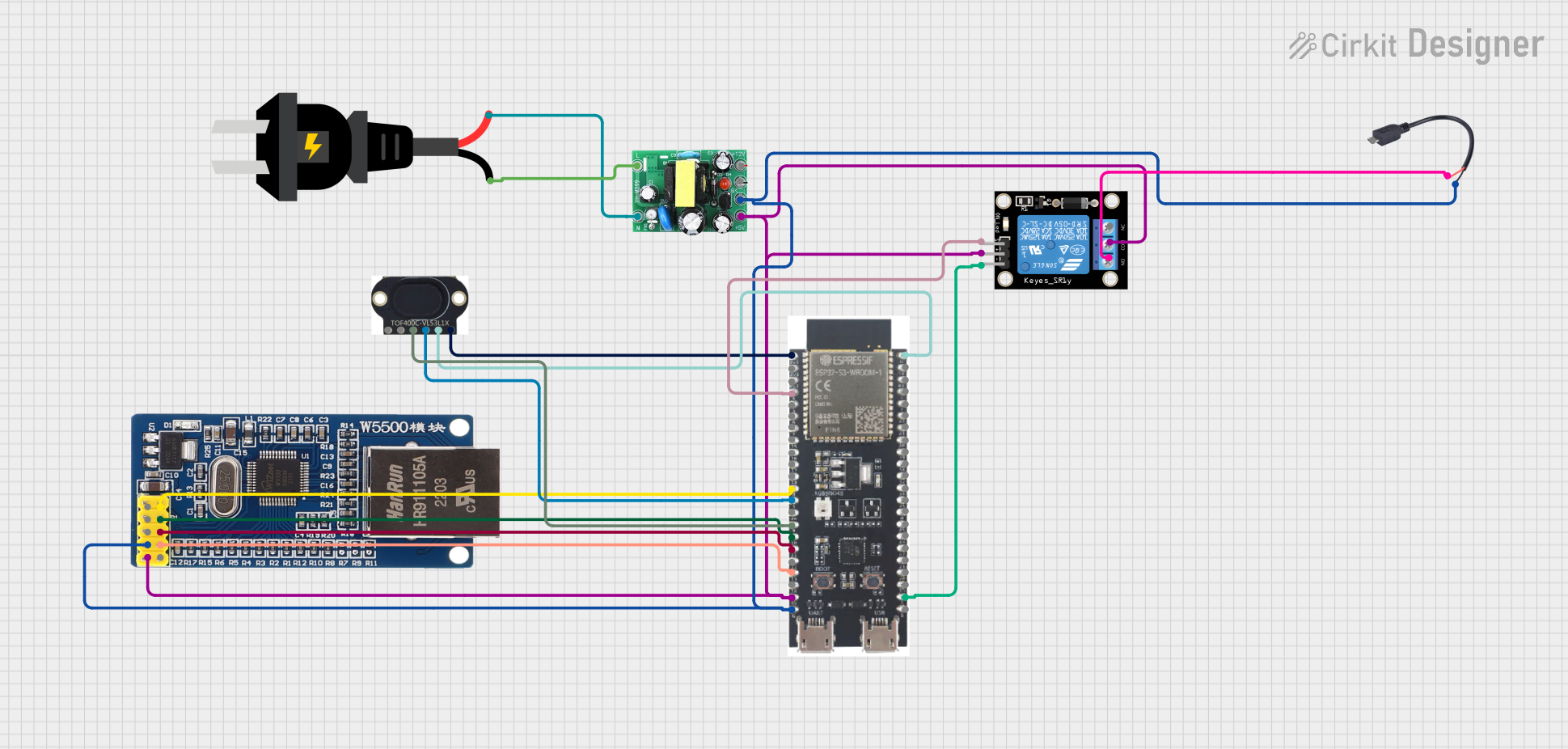
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with đế ra chân và esp32 s3

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Wireless communication systems (Wi-Fi and Bluetooth)
- Sensor data acquisition and processing
- Robotics and motor control
- Edge computing and AI/ML applications
Technical Specifications
ESP32-S3 Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-S3 (Xtensa® 32-bit LX7 dual-core) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (varies by model) |
| RAM | 512 KB SRAM + 8 MB PSRAM (optional) |
| Wi-Fi | 802.11 b/g/n (2.4 GHz) |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.0 LE |
| GPIO Pins | Up to 45 GPIO pins |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Power Supply | 5V via USB or 3.3V via VIN |
Đế Ra Chân (Breakout Board) Pin Configuration
The breakout board provides easy access to the ESP32-S3's pins. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Power input (5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| 3V3 | 3.3V power output |
| GPIO0 | General-purpose I/O, boot mode selection |
| GPIO1-45 | General-purpose I/O pins |
| TXD | UART Transmit |
| RXD | UART Receive |
| EN | Enable pin (reset ESP32-S3) |
| IOREF | Reference voltage for I/O |
| SDA | I2C Data |
| SCL | I2C Clock |
| SPI Pins | MOSI, MISO, SCK, CS |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the ESP32-S3:
- Connect the VIN pin to a 5V power source or use the USB port for power.
- Ensure the GND pin is connected to the ground of your circuit.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals.
- For I2C devices, connect SDA and SCL to the corresponding pins on the breakout board.
Programming the ESP32-S3:
- Use a USB cable to connect the breakout board to your computer.
- Install the ESP32 board package in the Arduino IDE or use the ESP-IDF framework.
Uploading Code:
- Select the correct board (e.g., "ESP32-S3 Dev Module") in the Arduino IDE.
- Press the "Upload" button to flash your code to the ESP32-S3.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected peripherals operate at 3.3V logic levels to avoid damaging the ESP32-S3.
- Boot Mode: To enter boot mode for flashing firmware, hold the BOOT button while pressing the EN (reset) button.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid unexpected resets or performance issues.
- Pin Multiplexing: Many GPIO pins have multiple functions (e.g., UART, I2C, SPI). Check the datasheet to avoid conflicts.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of using the ESP32-S3 to read data from a DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor:
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <DHT_U.h>
// Define the DHT sensor type and GPIO pin
#define DHTPIN 4 // Connect DHT data pin to GPIO4
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT11 sensor type
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
dht.begin(); // Initialize the DHT sensor
Serial.println("DHT11 Sensor Example with ESP32-S3");
}
void loop() {
// Read temperature and humidity values
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
// Check if the readings are valid
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
// Print the readings to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print("% Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println("°C");
delay(2000); // Wait 2 seconds before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
ESP32-S3 Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
- Install the correct USB-to-serial driver for your operating system.
Code Upload Fails:
- Check that the correct board and COM port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Hold the BOOT button while pressing the EN button to enter boot mode.
Peripherals Not Working:
- Verify the wiring and connections.
- Ensure the peripherals are compatible with 3.3V logic levels.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Debugging with Serial Monitor: Use
Serial.print()statements to debug your code and monitor the ESP32-S3's behavior. - Check Power Supply: Use a multimeter to ensure the ESP32-S3 is receiving the correct voltage.
- Update Firmware: If issues persist, try updating the ESP32-S3's firmware using the ESP-IDF or Arduino IDE.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the Đế Ra Chân and ESP32-S3 for a wide range of applications.