
How to Use Hybrid Inverter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
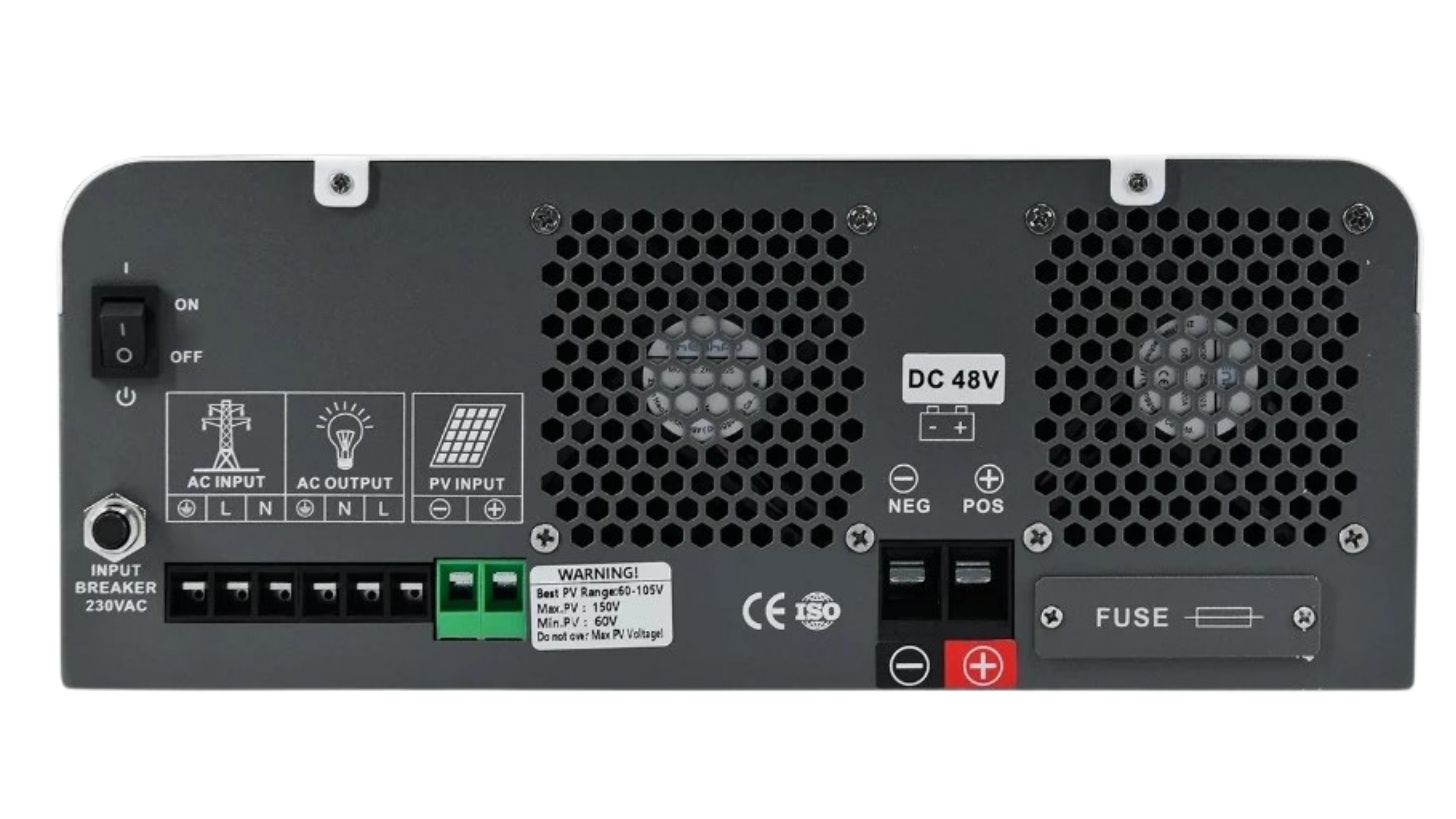

 Design with Hybrid Inverter in Cirkit Designer
Design with Hybrid Inverter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A hybrid inverter is a versatile electronic device that combines the functionalities of a solar inverter and a battery inverter. It is designed to manage energy from multiple sources, including solar panels, grid electricity, and battery storage systems. This integration allows for efficient energy optimization, enabling users to store excess solar energy for later use, reduce reliance on the grid, and ensure power availability during outages.
Explore Projects Built with Hybrid Inverter
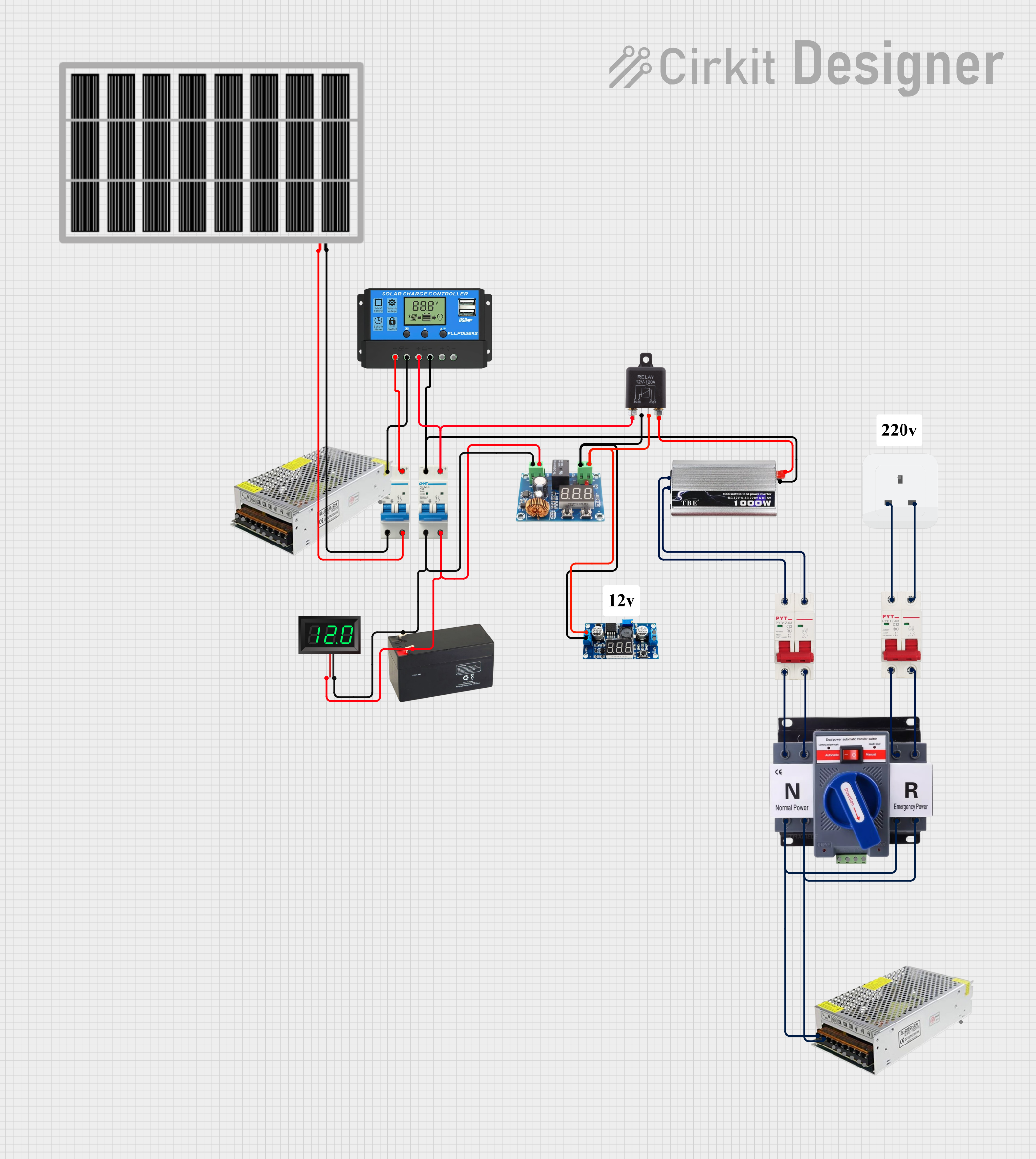
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer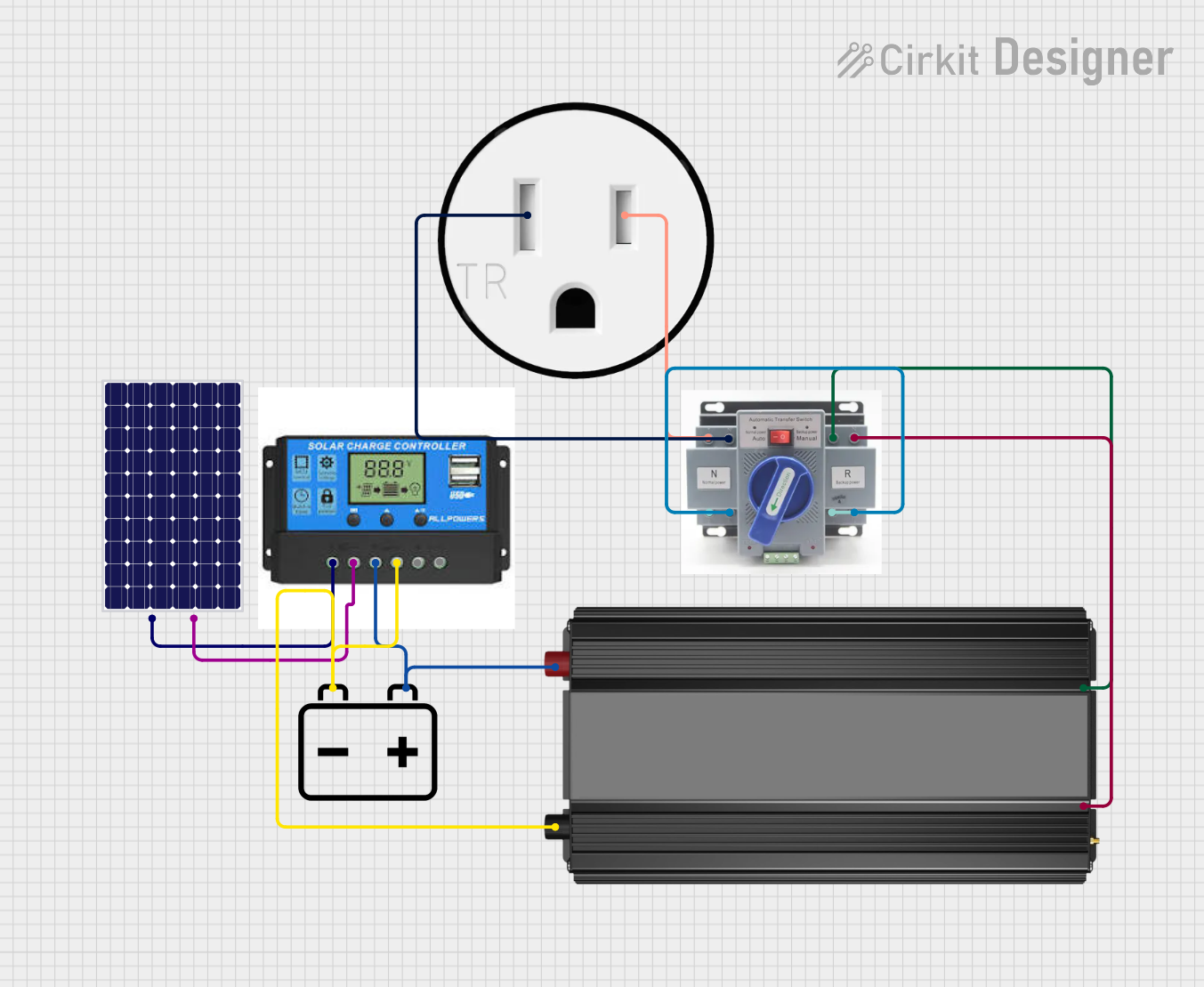
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer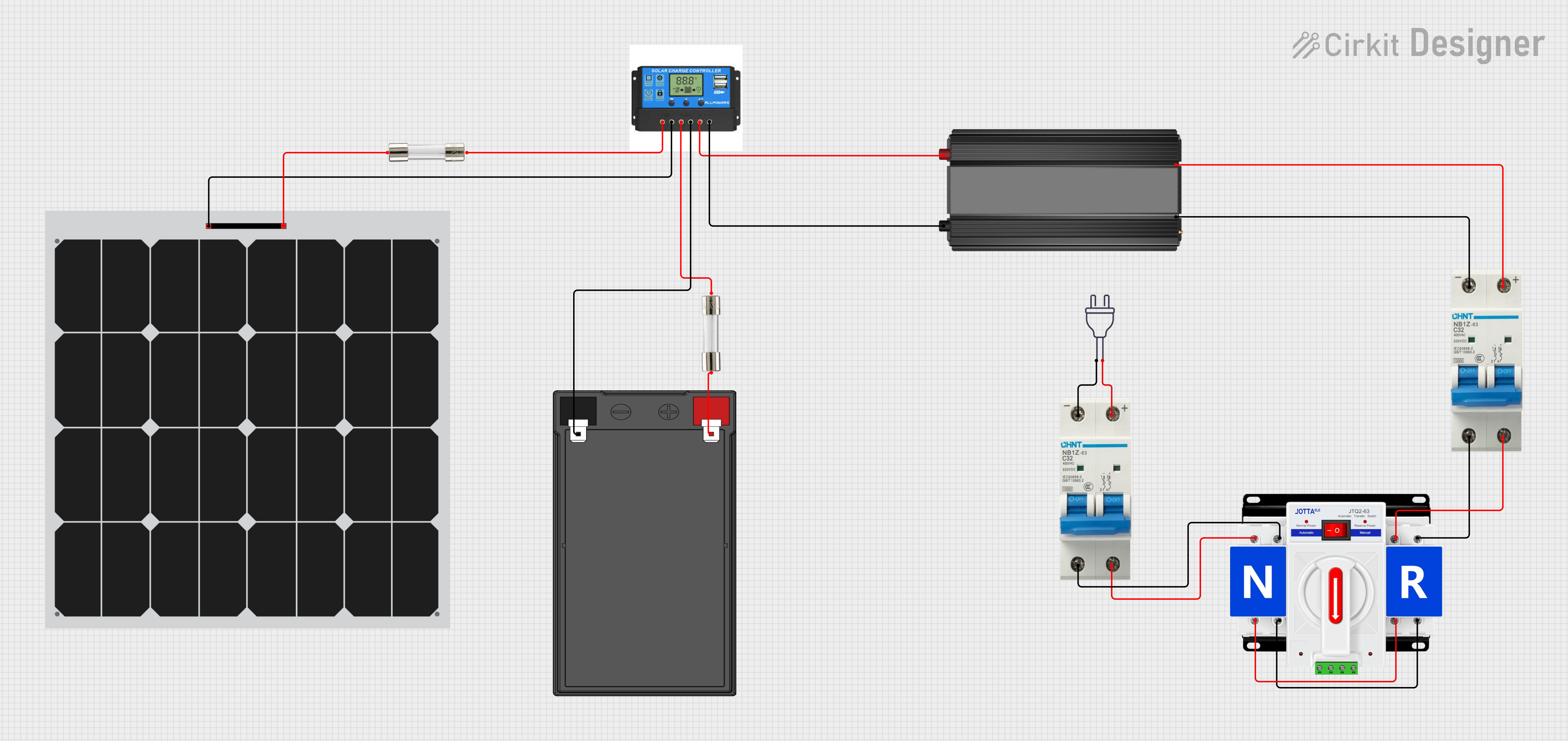
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Hybrid Inverter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential solar energy systems with battery storage
- Commercial and industrial renewable energy setups
- Off-grid and backup power systems
- Energy cost optimization through time-of-use (TOU) management
- Integration with smart home energy management systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage (DC) | 48V to 600V (varies by model) |
| Output Voltage (AC) | 120V/240V or 230V (single-phase) |
| Maximum Power Output | 3 kW to 10 kW (model-dependent) |
| Battery Compatibility | Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, or Gel |
| Efficiency | Up to 98% |
| Communication Interfaces | RS485, Wi-Fi, CAN, or Ethernet |
| Operating Temperature Range | -20°C to 60°C |
| Protection Features | Overload, short circuit, overvoltage |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PV+ | Positive terminal for solar panel input |
| PV- | Negative terminal for solar panel input |
| BAT+ | Positive terminal for battery connection |
| BAT- | Negative terminal for battery connection |
| AC IN | Input for grid power connection |
| AC OUT | Output for AC load connection |
| COM | Communication port for monitoring/control |
| GND | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Solar Panels: Attach the positive (PV+) and negative (PV-) terminals of the hybrid inverter to the corresponding terminals of the solar panel array.
- Connect the Battery: Link the battery's positive (BAT+) and negative (BAT-) terminals to the inverter. Ensure the battery type is compatible with the inverter.
- Connect to the Grid: If grid integration is required, connect the AC IN terminal to the grid power supply.
- Connect the Load: Attach the AC OUT terminal to the electrical load or distribution panel.
- Configure the System: Use the inverter's interface or communication port to set up parameters such as battery charging mode, grid priority, or time-of-use settings.
- Power On: Turn on the inverter and monitor its operation through the display or connected monitoring system.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure all connections are secure and follow the manufacturer's wiring diagram.
- Use appropriately rated cables and circuit breakers to prevent overheating or electrical hazards.
- Regularly monitor the system's performance using the communication interface or mobile app.
- Avoid overloading the inverter by ensuring the connected load does not exceed its rated capacity.
- Install the inverter in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
Arduino UNO Integration Example
While hybrid inverters are not typically controlled directly by an Arduino UNO, you can use the Arduino to monitor the inverter's status via its communication interface (e.g., RS485). Below is an example of how to read data from the inverter using an RS485 module:
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
// Create an instance of the ModbusMaster library
ModbusMaster node;
// Define the RS485 communication pins
#define RE_PIN 2 // Receiver Enable pin
#define DE_PIN 3 // Driver Enable pin
void preTransmission() {
digitalWrite(RE_PIN, HIGH); // Enable RS485 transmission
digitalWrite(DE_PIN, HIGH);
}
void postTransmission() {
digitalWrite(RE_PIN, LOW); // Disable RS485 transmission
digitalWrite(DE_PIN, LOW);
}
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Hybrid Inverter Monitoring");
// Initialize RS485 communication
pinMode(RE_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DE_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RE_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(DE_PIN, LOW);
// Configure Modbus communication
node.begin(1, Serial); // Set Modbus ID to 1
node.preTransmission(preTransmission);
node.postTransmission(postTransmission);
}
void loop() {
uint8_t result;
uint16_t data;
// Read a register (e.g., inverter status) from the hybrid inverter
result = node.readHoldingRegisters(0x0001, 1); // Replace 0x0001 with the desired register address
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
data = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
Serial.print("Inverter Status: ");
Serial.println(data);
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read data from inverter");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next read
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Inverter not powering on | Loose or incorrect wiring | Check all connections and wiring diagram |
| Low efficiency or power output | Dirty solar panels or shading | Clean panels and ensure proper placement |
| Battery not charging | Incorrect battery settings or fault | Verify battery type and settings |
| Communication failure with Arduino | Incorrect RS485 wiring or settings | Check wiring and ensure correct baud rate |
FAQs
Can I use a hybrid inverter without a battery?
Yes, most hybrid inverters can operate without a battery, directly supplying power from solar panels to the load or grid.What happens during a power outage?
If a battery is connected, the hybrid inverter will switch to battery power to supply the load. Without a battery, the inverter will shut down unless it has a backup power feature.How do I monitor the inverter remotely?
Use the built-in communication interface (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet) to connect the inverter to a monitoring app or web portal.What maintenance is required?
Periodically clean the inverter's exterior, check connections, and ensure proper ventilation. For battery systems, follow the manufacturer's maintenance guidelines.