
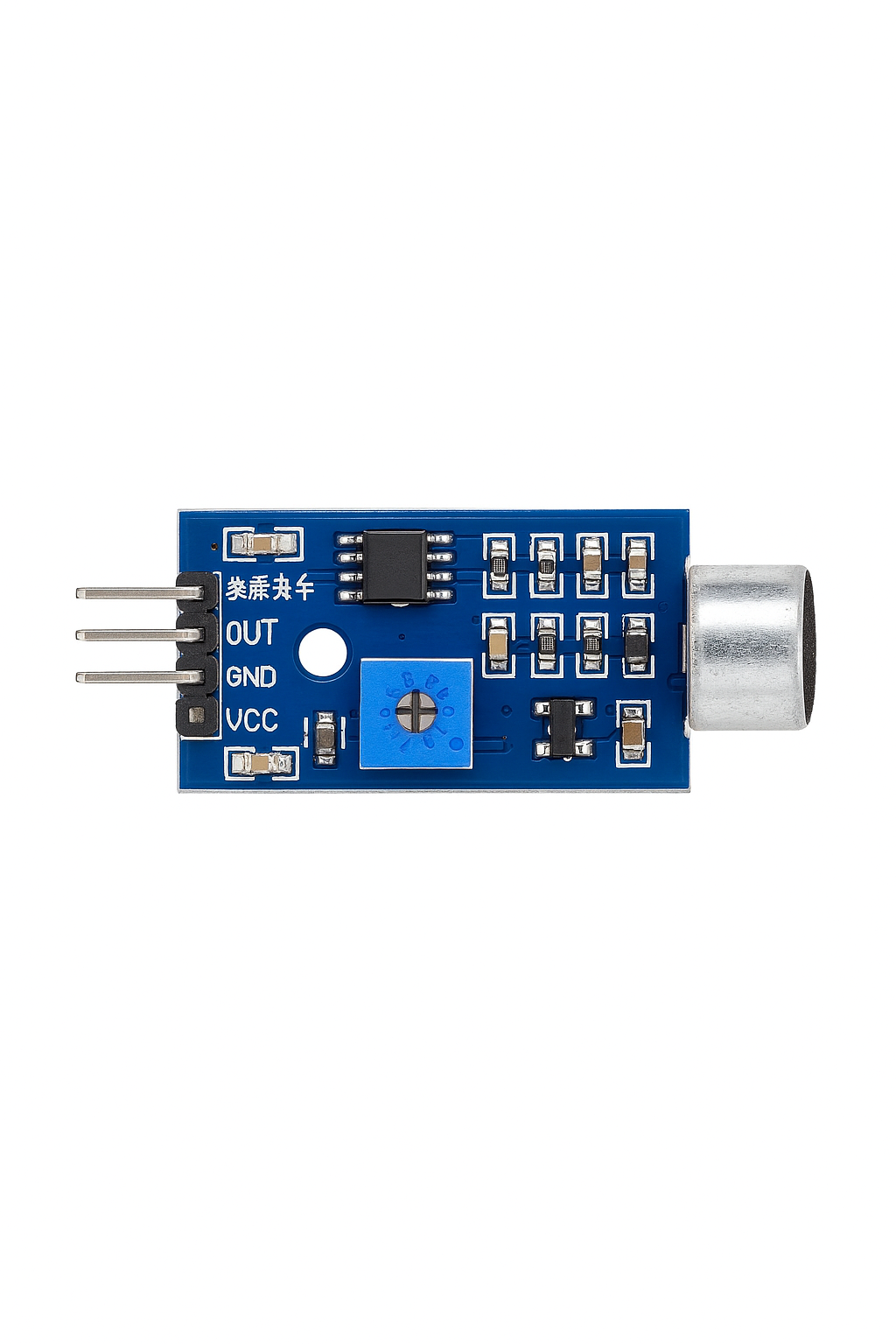
How to Use cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân in Cirkit Designer
Design with cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân (3-pin sound sensor) is a compact and versatile electronic component designed to detect sound levels and convert them into an electrical signal. Manufactured by S, this sensor is widely used in sound detection and response projects, such as voice-activated systems, sound level monitoring, and interactive audio-based applications.
Explore Projects Built with cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voice-activated devices
- Sound level monitoring systems
- Audio-reactive lighting
- Security systems with sound detection
- Robotics and interactive projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | S |
| Part ID | S |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Output Signal | Analog and Digital |
| Sensitivity Adjustment | Potentiometer (onboard) |
| Dimensions | ~32mm x 15mm x 8mm |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân has three pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 3 | OUT | Output pin. Provides an analog signal proportional to sound level or a digital |
| HIGH/LOW signal based on the threshold set by the potentiometer. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- Connect the Output:
- For analog sound level detection, connect the OUT pin to an analog input pin of your microcontroller.
- For digital sound detection, connect the OUT pin to a digital input pin.
- Adjust Sensitivity: Use the onboard potentiometer to set the desired sensitivity level. Turning the potentiometer clockwise increases sensitivity, while counterclockwise decreases it.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the cảm biến âm thanh 3 chân to an Arduino UNO:
| Sensor Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| OUT | A0 (for analog) or D2 (for digital) |
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following code demonstrates how to read both analog and digital signals from the sensor:
// Define pin connections
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to OUT
const int digitalPin = 2; // Digital pin connected to OUT
int analogValue = 0; // Variable to store analog reading
int digitalValue = 0; // Variable to store digital reading
void setup() {
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT); // Set digital pin as input
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read analog value from the sensor
analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
// Read digital value from the sensor
digitalValue = digitalRead(digitalPin);
// Print the values to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Analog Value: ");
Serial.print(analogValue);
Serial.print(" | Digital Value: ");
Serial.println(digitalValue);
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the sensor is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V to 5V).
- Noise Interference: Avoid placing the sensor near high-frequency noise sources to prevent false readings.
- Sensitivity Adjustment: Fine-tune the potentiometer to achieve the desired detection threshold for your application.
- Output Signal: Use appropriate pull-up or pull-down resistors if required for stable digital output.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Ensure the sensor is properly powered (check VCC and GND connections).
- Verify that the potentiometer is not set too low (increase sensitivity if needed).
Inconsistent Readings:
- Check for loose connections or poor soldering.
- Ensure the sensor is not exposed to excessive electrical noise.
Digital Output Always HIGH or LOW:
- Adjust the potentiometer to set an appropriate threshold.
- Verify that the sound level exceeds the detection threshold.
Analog Output Not Changing:
- Confirm that the analog pin on the microcontroller is functioning correctly.
- Test the sensor with a known sound source to verify its operation.
FAQs
Q: Can this sensor detect specific frequencies?
A: No, this sensor is designed to detect general sound levels and does not differentiate between specific frequencies.
Q: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the sensor operates within a voltage range of 3.3V to 5V, making it compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers like ESP32 or Raspberry Pi Pico.
Q: How do I increase the detection range?
A: You can increase the sensitivity by adjusting the onboard potentiometer. However, note that higher sensitivity may also increase noise interference.
Q: Is this sensor suitable for outdoor use?
A: The sensor is not weatherproof. For outdoor applications, ensure it is housed in a protective enclosure.