
How to Use BTS7960 High Current 43A H-Bridge Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
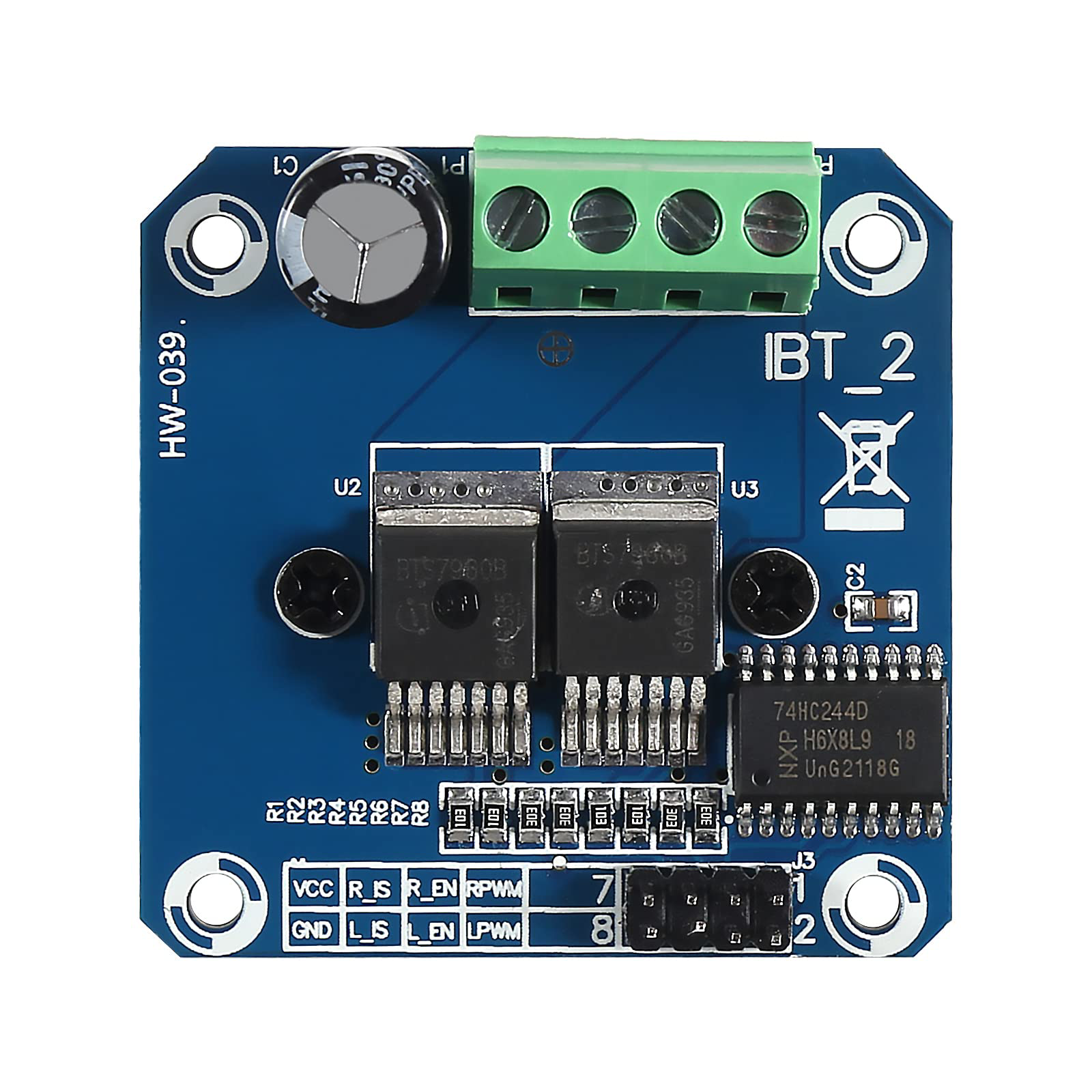
 Design with BTS7960 High Current 43A H-Bridge Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with BTS7960 High Current 43A H-Bridge Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BTS7960 is a robust and efficient motor driver module designed to control DC motors with high current requirements, supporting up to 43A. It features an H-Bridge configuration, enabling bidirectional motor control. This module is ideal for applications requiring precise motor control, such as robotics, electric vehicles, conveyor systems, and industrial automation.
The BTS7960 integrates overcurrent protection, overtemperature protection, and a high-power MOSFET design, ensuring reliable operation under demanding conditions. Its compatibility with microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and other development boards makes it a versatile choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with BTS7960 High Current 43A H-Bridge Motor Driver
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer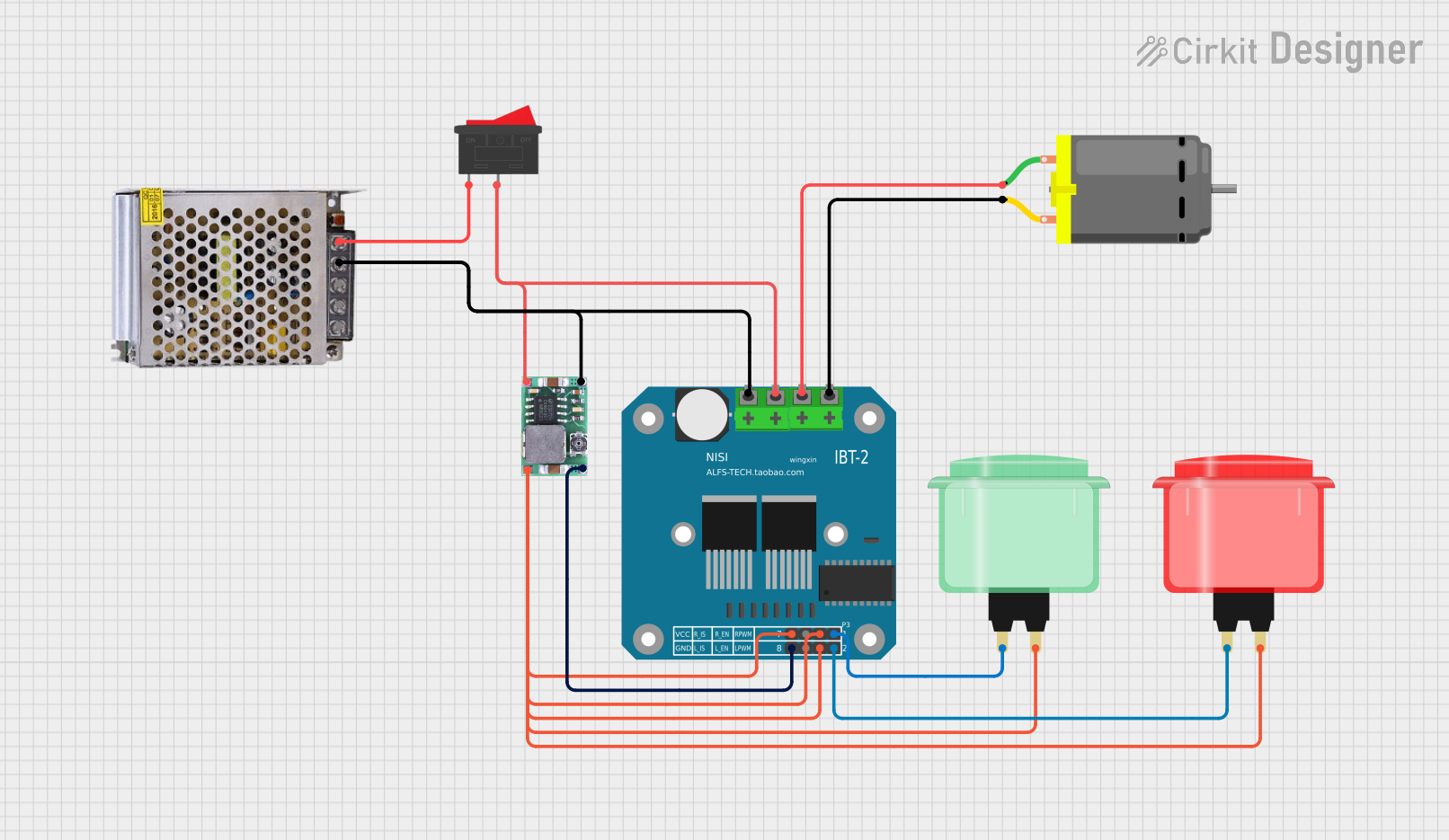
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer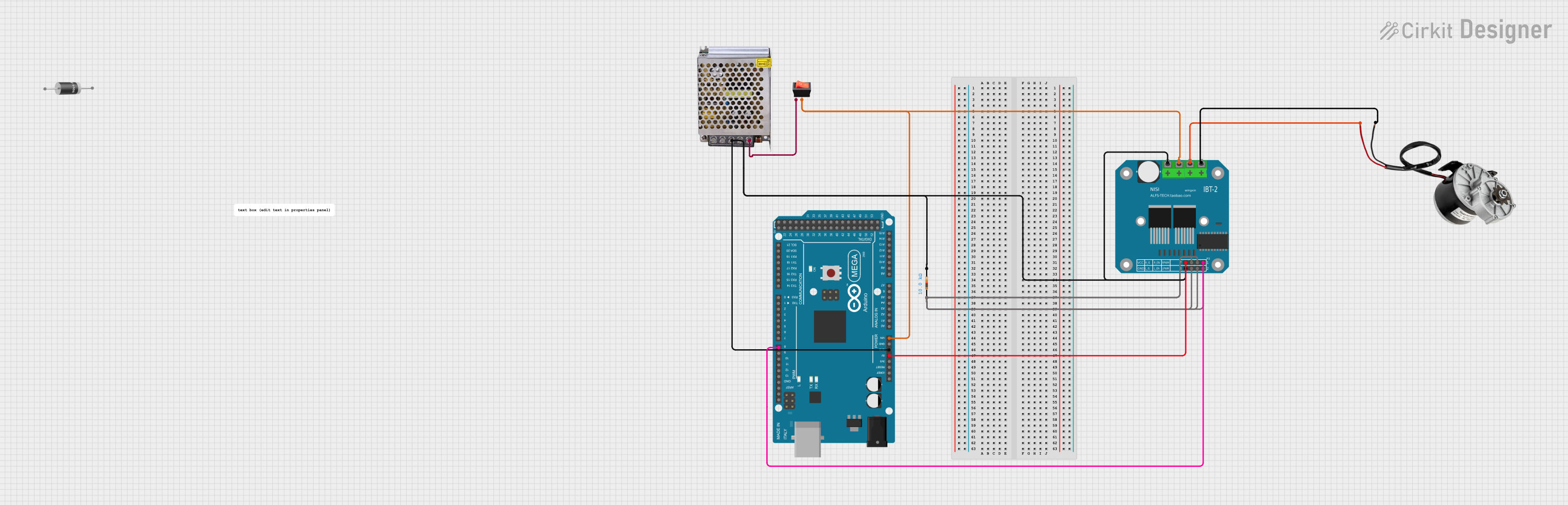
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer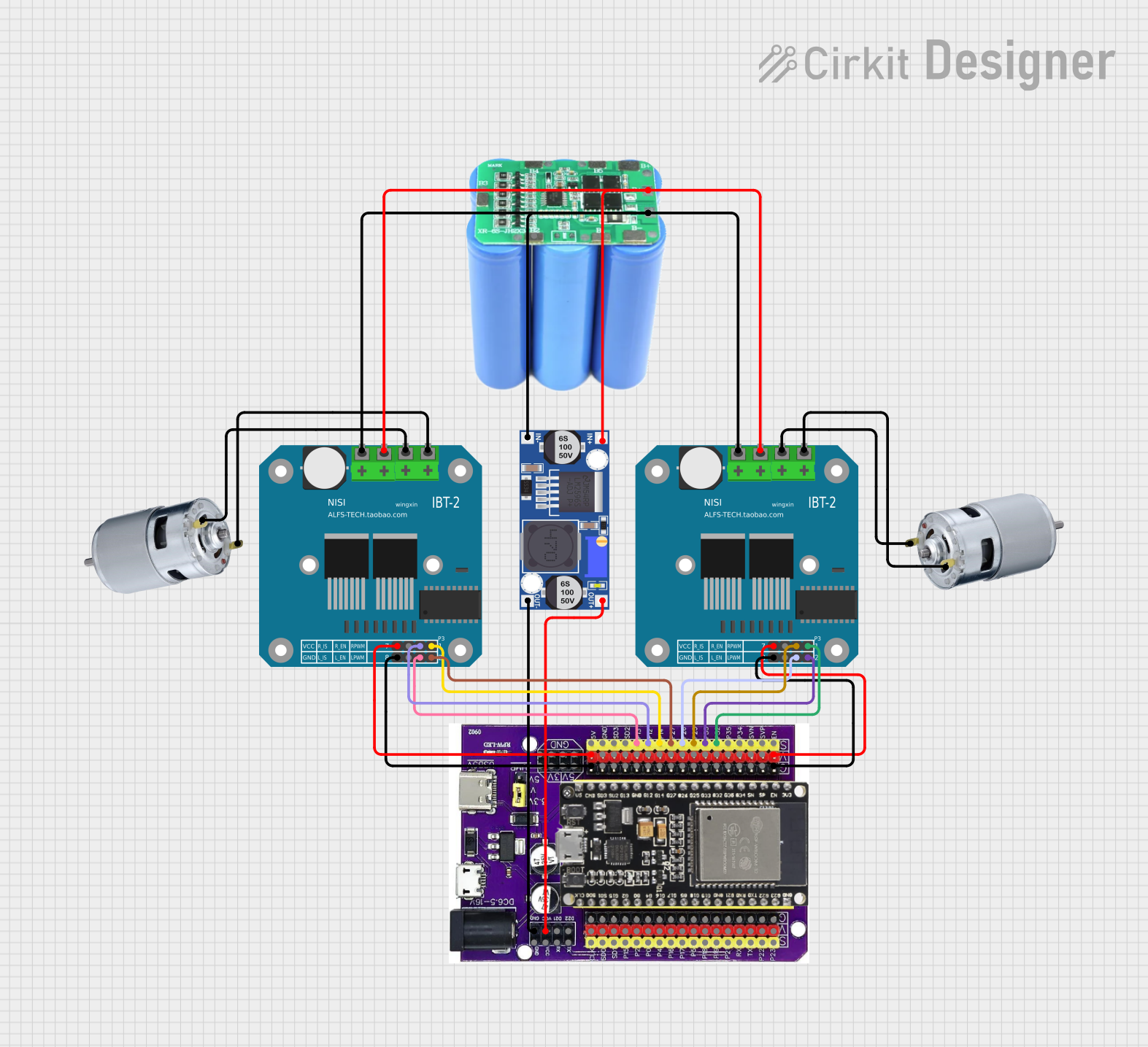
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BTS7960 High Current 43A H-Bridge Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Operating Voltage (Vcc): 5V (logic level)
- Motor Voltage (VM): 6V to 27V
- Maximum Continuous Current: 43A
- Control Logic Voltage: 3.3V or 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- PWM Frequency: Up to 25kHz
- Overcurrent Protection: Yes
- Overtemperature Protection: Yes
- Dimensions: 43mm x 45mm x 28mm (approx.)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BTS7960 module has multiple pins for power, control, and motor connections. Below is a detailed description:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power Input | 5V input for the logic circuit. Connect to the 5V pin of the microcontroller. |
| GND | Power Ground | Ground connection for the logic circuit. |
| IS | Output | Current sensing output. Provides feedback on motor current. |
| ENA | Input | Enable pin for motor A. High to enable motor A. |
| ENB | Input | Enable pin for motor B. High to enable motor B. |
| IN1 | Input | Control signal for motor direction (A). |
| IN2 | Input | Control signal for motor direction (B). |
| RPWM | PWM Input | PWM signal for motor speed control (A). |
| LPWM | PWM Input | PWM signal for motor speed control (B). |
| B+ | Power Input | Positive terminal for motor power supply (6V to 27V). |
| B- | Power Ground | Ground terminal for motor power supply. |
| M+ | Motor Output | Positive terminal for the motor connection. |
| M- | Motor Output | Negative terminal for the motor connection. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the BTS7960 in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the motor power supply (6V to 27V) to the
B+pin and ground to theB-pin. - Connect the logic power supply (5V) to the
VCCpin and ground to theGNDpin.
- Connect the motor power supply (6V to 27V) to the
Motor Connections:
- Connect the motor terminals to the
M+andM-pins.
- Connect the motor terminals to the
Control Connections:
- Connect the
ENAandENBpins to the microcontroller's GPIO pins to enable or disable the motor. - Use the
IN1andIN2pins to control the motor's direction. - Connect the
RPWMandLPWMpins to the microcontroller's PWM output pins for speed control.
- Connect the
Programming:
- Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) to send PWM signals and control the motor's speed and direction.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the motor's current rating does not exceed 43A to avoid damaging the module.
- Use a heat sink or cooling fan for prolonged high-current operation.
- Add a capacitor (e.g., 1000µF) across the motor power supply terminals to reduce voltage spikes.
- Avoid reversing the polarity of the power supply or motor connections.
- Use appropriate fuses or circuit breakers for additional protection.
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example code to control a DC motor using the BTS7960 and an Arduino UNO:
// Define control pins for the BTS7960
#define ENA 7 // Enable pin for motor A
#define ENB 8 // Enable pin for motor B
#define RPWM 9 // PWM pin for motor A
#define LPWM 10 // PWM pin for motor B
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LPWM, OUTPUT);
// Enable the motor driver
digitalWrite(ENA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ENB, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction
analogWrite(RPWM, 128); // Set speed (0-255)
analogWrite(LPWM, 0); // Stop the other direction
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction
analogWrite(RPWM, 0); // Stop one direction
analogWrite(LPWM, 128); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Running:
- Ensure the
ENAandENBpins are set to HIGH. - Verify the motor power supply voltage is within the specified range (6V to 27V).
- Check all connections for loose wires or incorrect polarity.
- Ensure the
Overheating:
- Use a heat sink or cooling fan to dissipate heat during high-current operation.
- Ensure the motor's current rating does not exceed 43A.
PWM Signal Not Working:
- Verify the PWM frequency is within the supported range (up to 25kHz).
- Check the microcontroller's PWM pin configuration and ensure it is functioning correctly.
Motor Running in the Wrong Direction:
- Swap the
IN1andIN2signals or reverse the motor connections (M+andM-).
- Swap the
FAQs
Can I use the BTS7960 with a 3.3V microcontroller? Yes, the BTS7960 is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
What is the maximum PWM frequency supported? The BTS7960 supports PWM frequencies up to 25kHz.
Do I need additional components for protection? While the BTS7960 has built-in protection, adding a capacitor across the motor power supply and a fuse can enhance safety and reliability.
Can I control two motors with one BTS7960 module? No, the BTS7960 is designed to control a single motor. For dual-motor control, use two separate modules.