
How to Use WEMOS D1 R1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with WEMOS D1 R1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with WEMOS D1 R1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The WEMOS D1 R1 is a microcontroller board based on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module, designed specifically for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It combines the power of the ESP8266 with the ease of use of an Arduino-like form factor, making it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced developers. The board features a USB interface for programming, multiple GPIO pins for connecting sensors and actuators, and built-in Wi-Fi capabilities for seamless wireless communication.
Explore Projects Built with WEMOS D1 R1
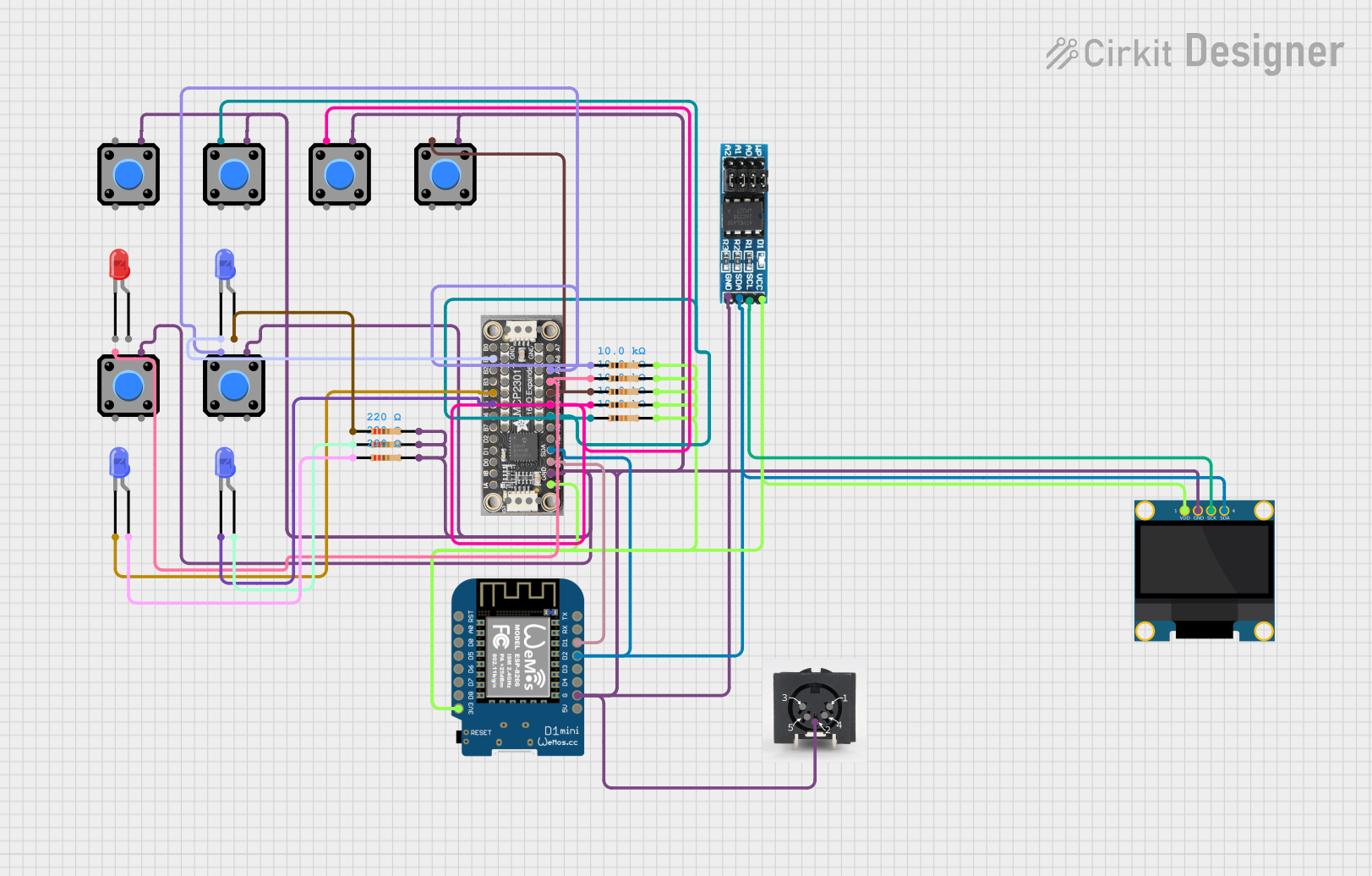
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer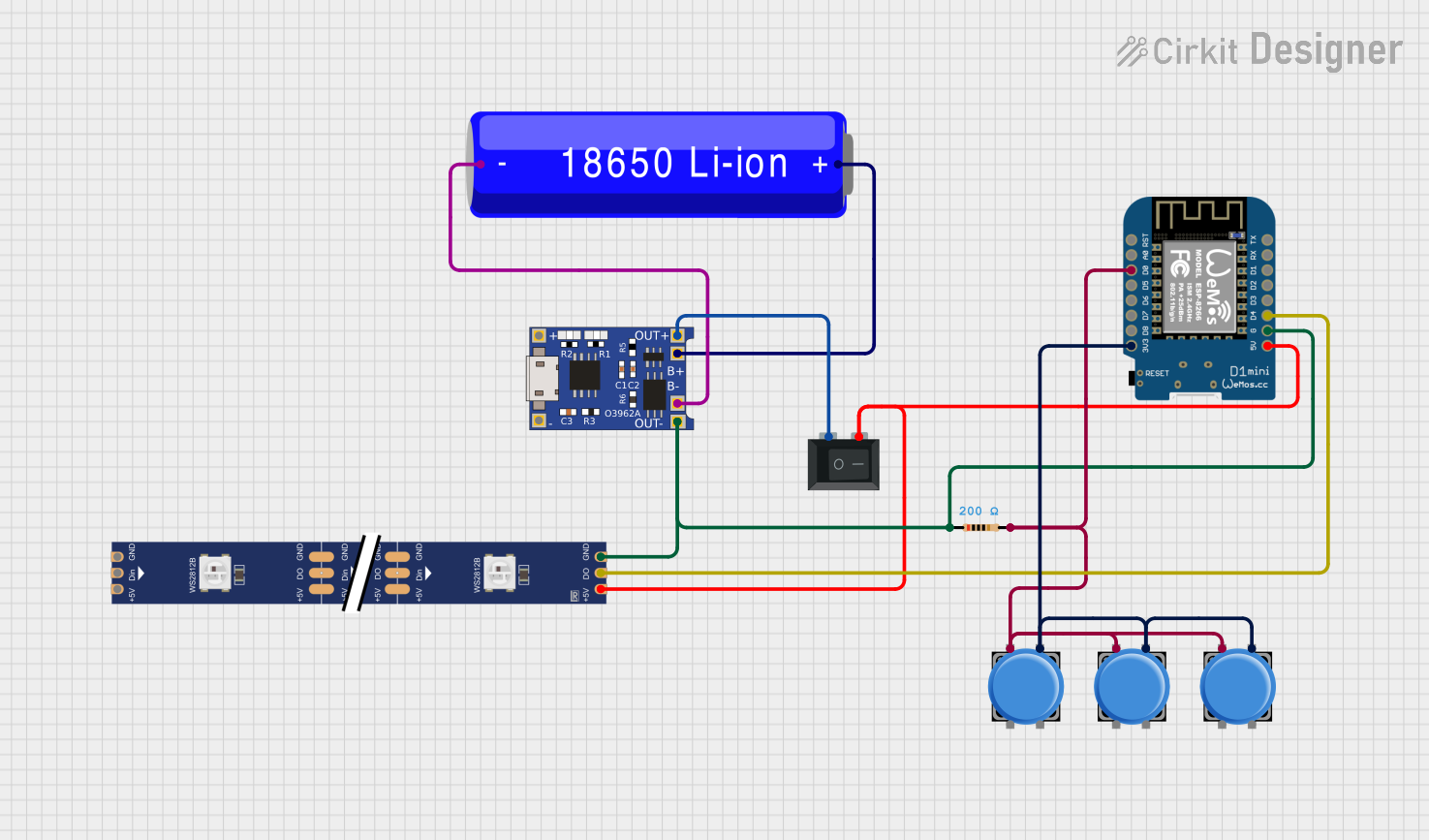
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer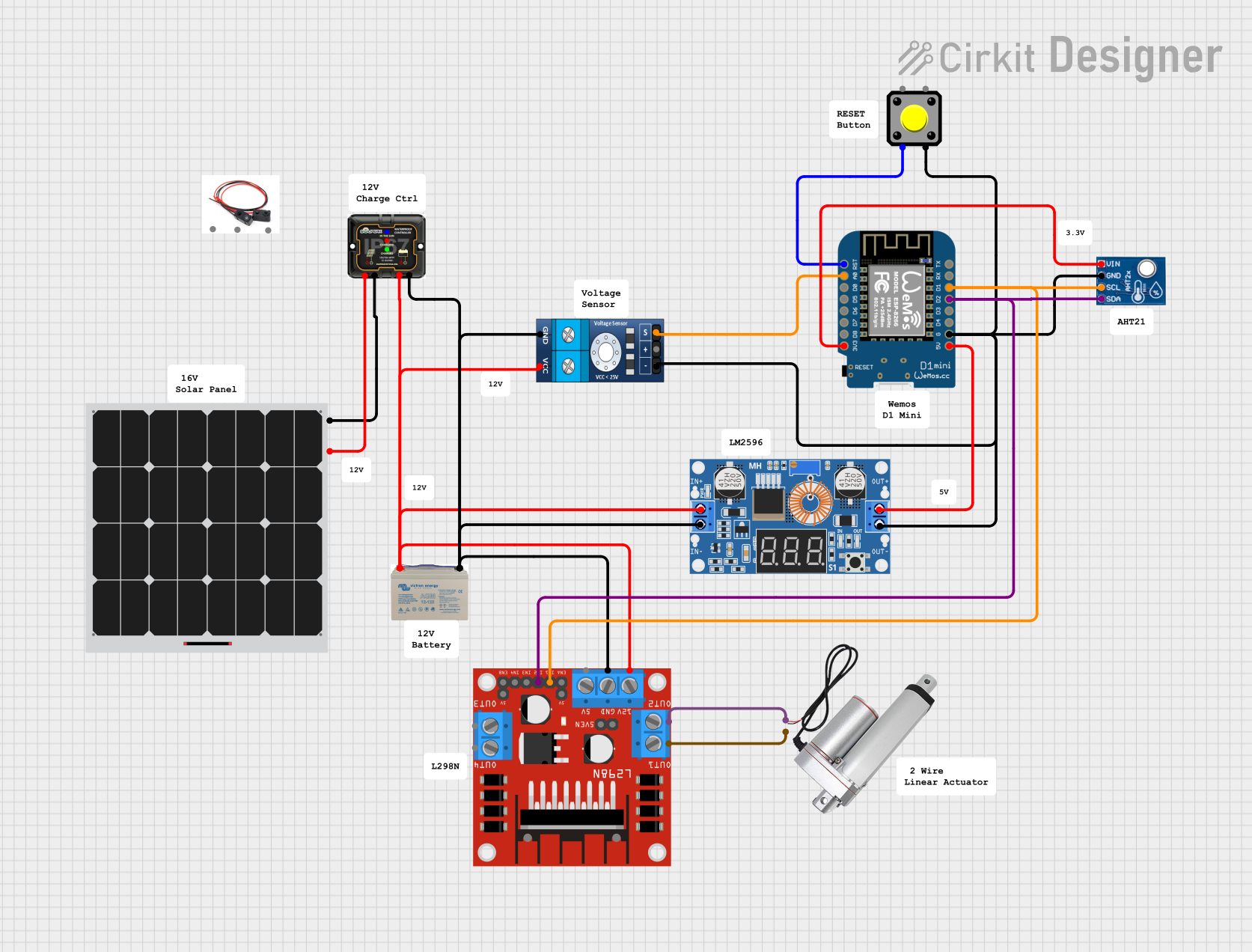
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer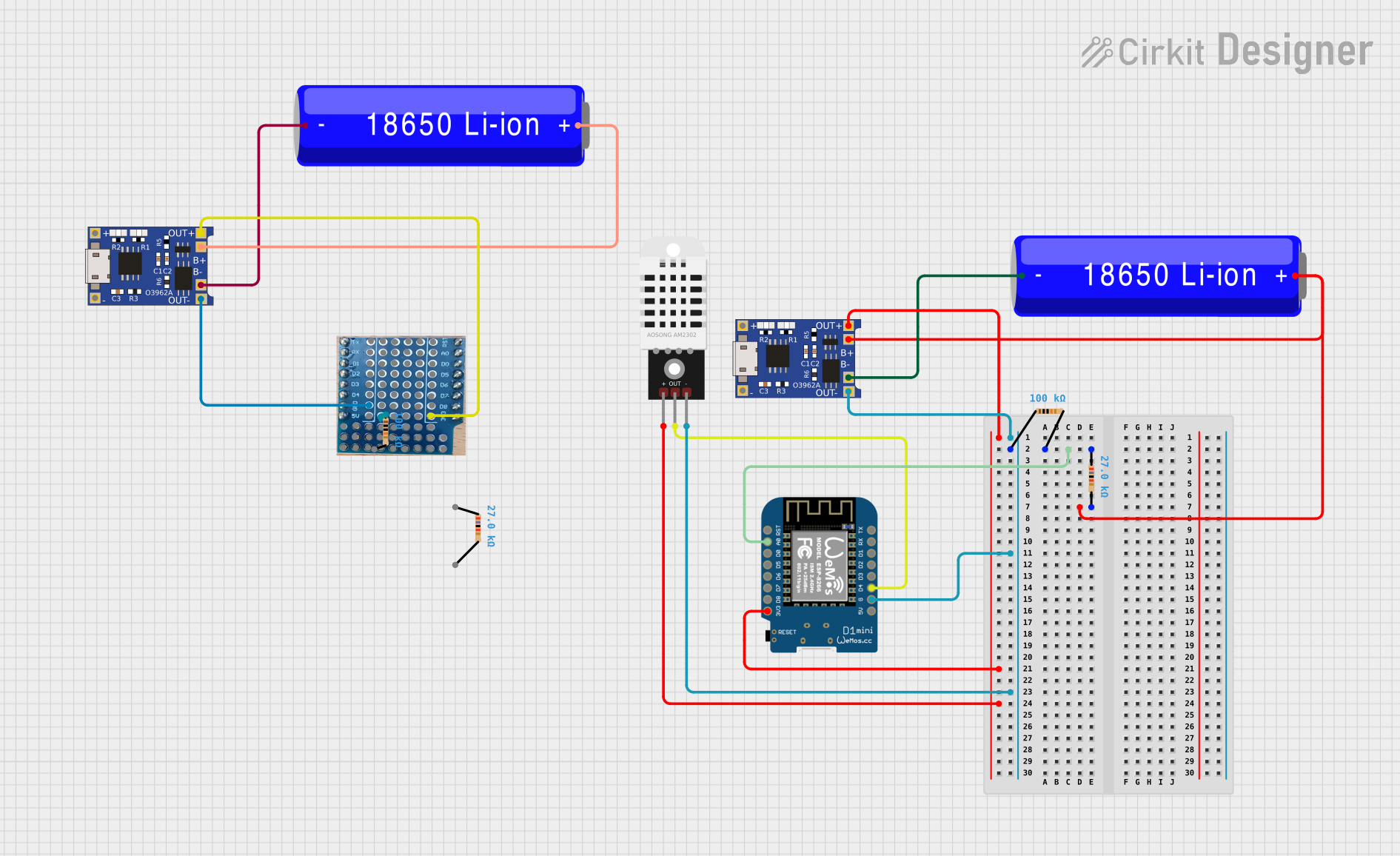
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with WEMOS D1 R1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- IoT-enabled devices
- Remote monitoring and control
- Prototyping smart devices
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP8266EX
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage: 7-12V (via barrel jack) or 5V (via USB)
- Digital I/O Pins: 11 (D0-D10)
- Analog Input Pins: 1 (A0, 10-bit resolution)
- Wi-Fi Standard: 802.11 b/g/n
- Flash Memory: 4MB
- Clock Speed: 80 MHz (can be overclocked to 160 MHz)
- USB Interface: Micro-USB
- Dimensions: 68.6mm x 53.4mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The WEMOS D1 R1 has a pinout similar to the Arduino UNO, but with some differences due to the ESP8266 architecture. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | D0 | GPIO16, can be used as a digital I/O pin |
| 2 | D1 | GPIO5, supports I2C (SCL) |
| 3 | D2 | GPIO4, supports I2C (SDA) |
| 4 | D3 | GPIO0, can be used as a digital I/O pin |
| 5 | D4 | GPIO2, can be used as a digital I/O pin |
| 6 | D5 | GPIO14, supports SPI (SCLK) |
| 7 | D6 | GPIO12, supports SPI (MISO) |
| 8 | D7 | GPIO13, supports SPI (MOSI) |
| 9 | D8 | GPIO15, supports SPI (SS) |
| 10 | A0 | Analog input, 0-3.3V, 10-bit resolution |
| 11 | G | Ground pin |
| 12 | 3V3 | 3.3V output for powering external components |
| 13 | 5V | 5V output (only available when powered via USB or barrel jack) |
| 14 | RST | Reset pin, used to restart the microcontroller |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the WEMOS D1 R1 in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Use a Micro-USB cable to power the board and upload code.
- Alternatively, supply 7-12V via the barrel jack or 5V directly to the 5V pin.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE and add the ESP8266 board package via the Board Manager.
- Select "WEMOS D1 R1" as the board type in the Tools menu.
- Connect the board to your computer via USB and upload your code.
Connecting Sensors and Actuators:
- Use the GPIO pins (D0-D8) for digital input/output.
- Use the A0 pin for analog input (ensure the input voltage does not exceed 3.3V).
- For I2C devices, connect to D1 (SCL) and D2 (SDA).
- For SPI devices, use D5 (SCLK), D6 (MISO), D7 (MOSI), and D8 (SS).
Wi-Fi Configuration:
- Use the ESP8266WiFi library to connect the board to a Wi-Fi network.
- The board can act as a client or an access point (AP).
Example Code: Connecting to Wi-Fi
Below is an example sketch to connect the WEMOS D1 R1 to a Wi-Fi network:
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID"; // Replace with your Wi-Fi network name
const char* password = "Your_Password"; // Replace with your Wi-Fi password
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Start the serial communication at 115200 baud
delay(10);
Serial.println("Connecting to Wi-Fi...");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // Start connecting to the Wi-Fi network
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500); // Wait for the connection to establish
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // Print the assigned IP address
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The GPIO pins operate at 3.3V. Avoid applying 5V directly to the pins to prevent damage.
- Power Supply: If using the barrel jack, ensure the input voltage is within the 7-12V range.
- Wi-Fi Signal Strength: Place the board in an area with a strong Wi-Fi signal for reliable communication.
- Heat Management: The ESP8266 can get warm during operation. Ensure proper ventilation if used in an enclosure.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Problem: The board is not detected by the Arduino IDE.
Solution:- Ensure the correct USB driver is installed (e.g., CH340 driver for some versions of the WEMOS D1 R1).
- Check that the correct board and port are selected in the Tools menu.
Problem: The board fails to connect to Wi-Fi.
Solution:- Double-check the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range and not using unsupported security protocols.
Problem: GPIO pins are not functioning as expected.
Solution:- Verify that the pins are not being used for multiple purposes (e.g., GPIO15 is also used for SPI SS).
- Check for proper wiring and connections.
Problem: The board resets unexpectedly.
Solution:- Ensure the power supply is stable and capable of providing sufficient current (at least 500mA).
- Avoid using long or thin wires for power connections.
FAQs
Can I use the WEMOS D1 R1 with 5V sensors?
Yes, but you will need a level shifter or voltage divider to step down the 5V signal to 3.3V.What is the maximum range of the Wi-Fi module?
The range depends on the environment but is typically around 30-50 meters indoors and up to 100 meters outdoors.Can the WEMOS D1 R1 be powered by batteries?
Yes, you can use a 7-12V battery connected to the barrel jack or a 3.7V LiPo battery with a step-up converter to 5V.Is the WEMOS D1 R1 compatible with Arduino libraries?
Yes, most Arduino libraries are compatible, but some may require modifications for the ESP8266 architecture.