
How to Use ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
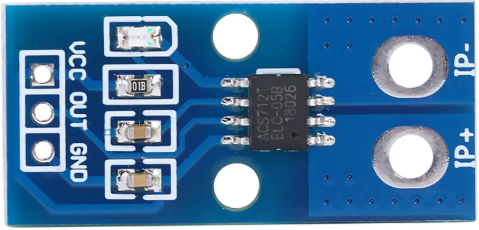
 Design with ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor is a non-invasive current sensor designed to measure both AC and DC currents up to 50A. It utilizes Hall effect technology to provide an analog output voltage that is proportional to the current being measured. This sensor is highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, including power monitoring, motor control, battery management systems, and overcurrent protection.
Explore Projects Built with ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor
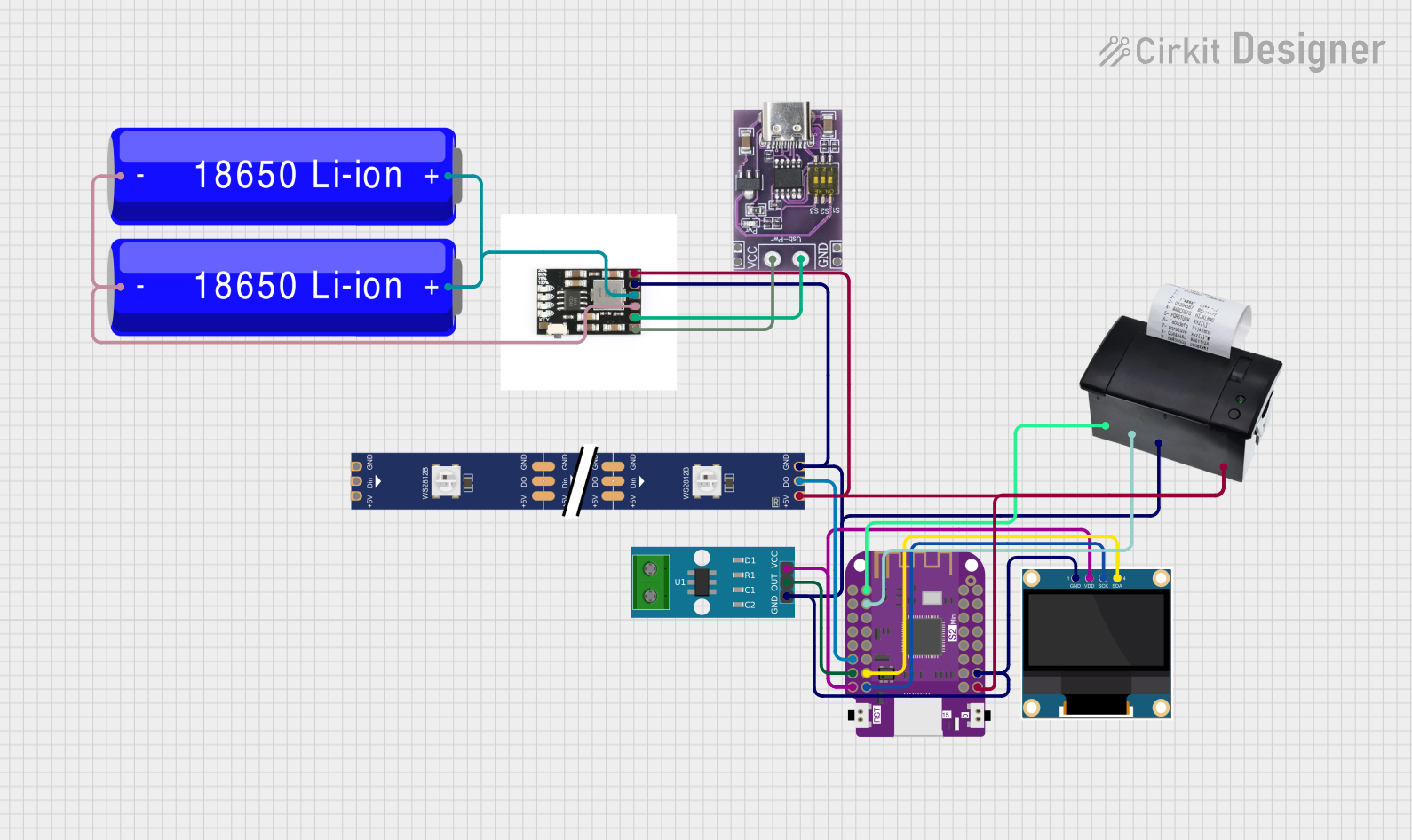
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer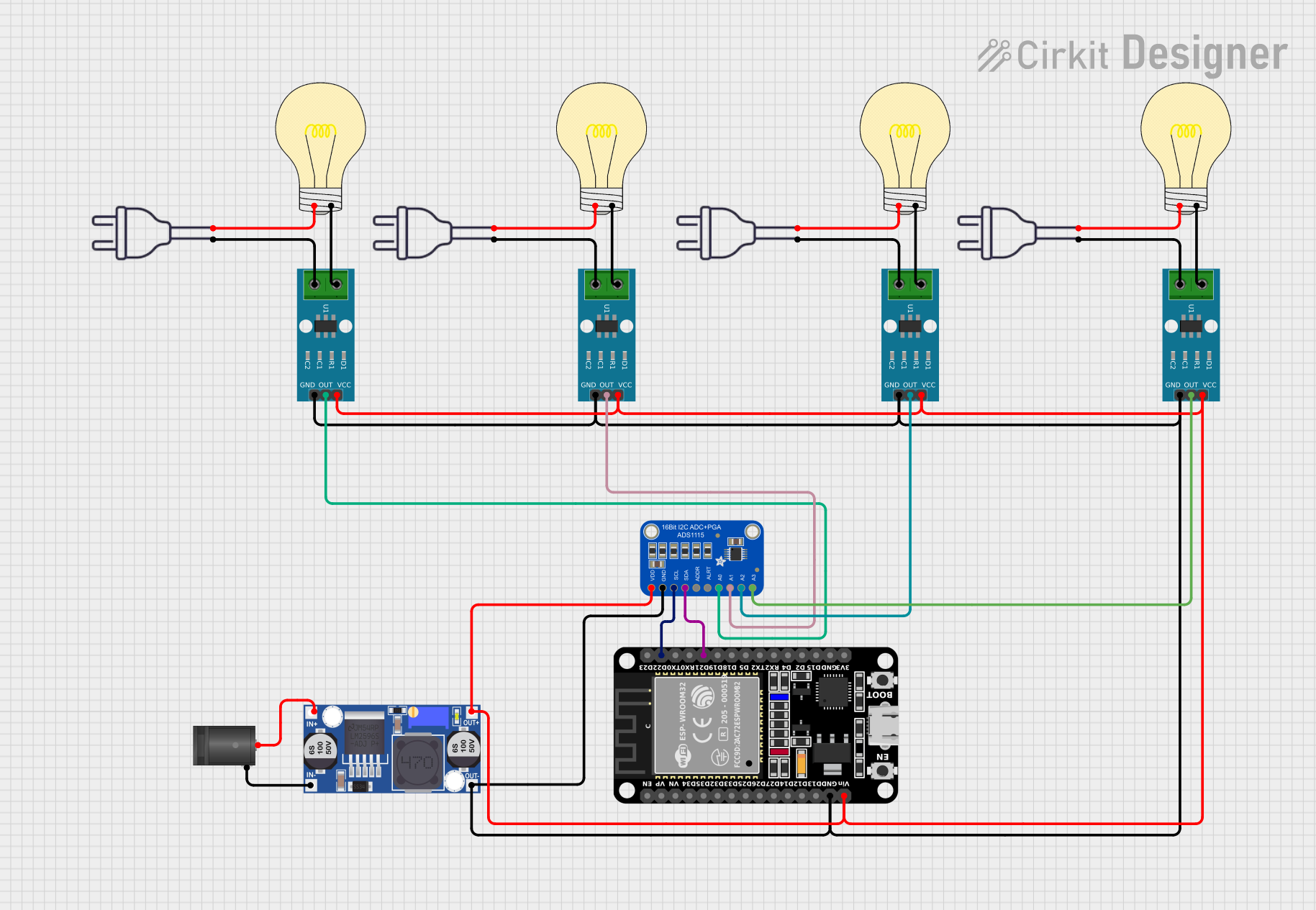
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer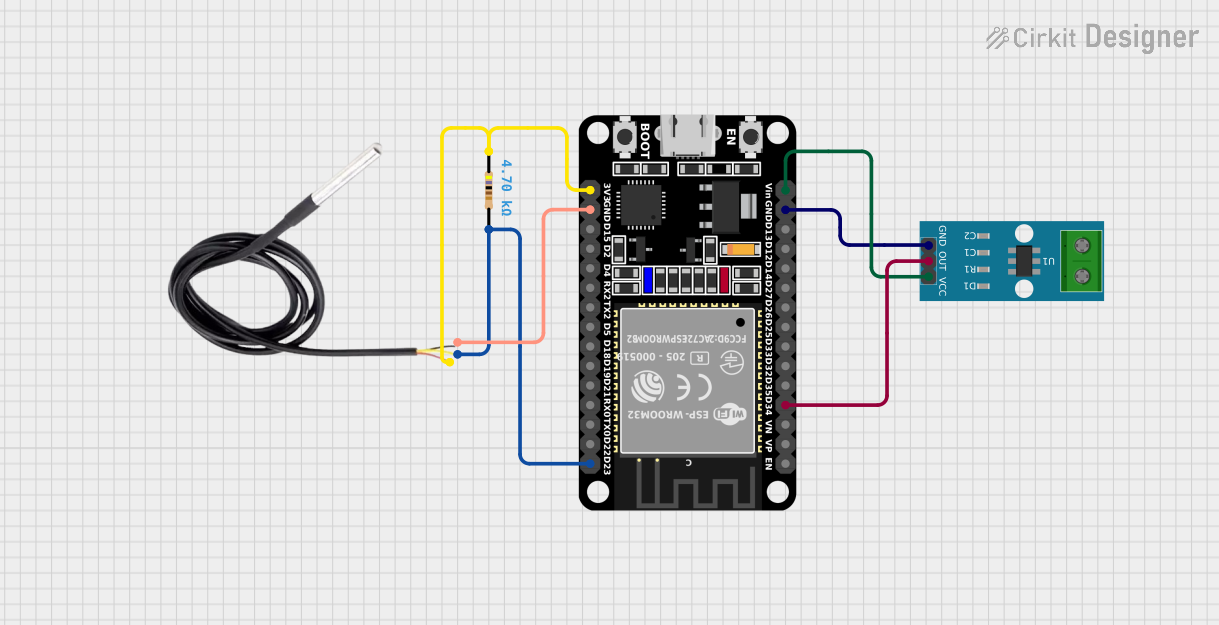
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer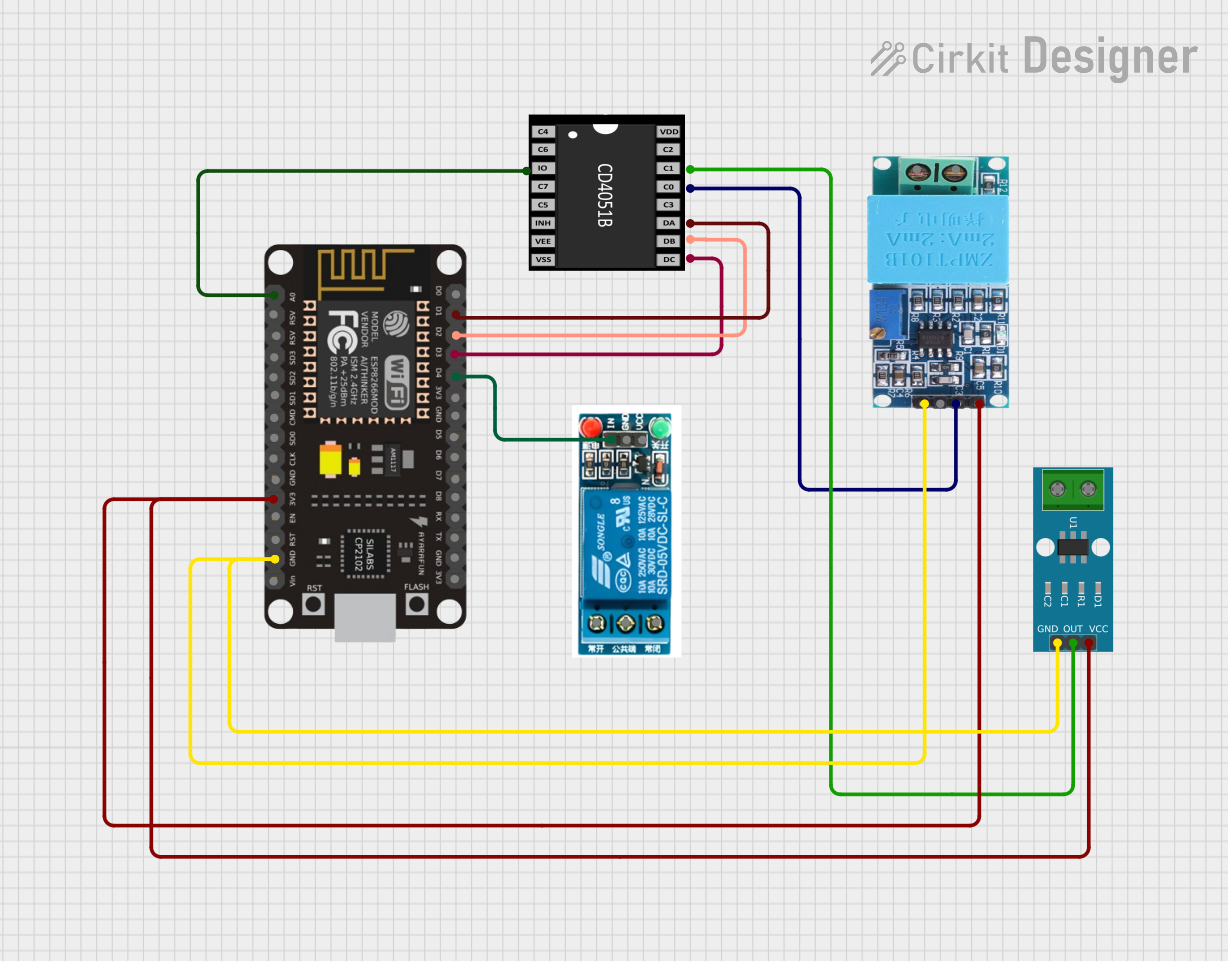
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power monitoring in industrial and residential systems
- Motor current sensing in robotics and automation
- Battery management systems for electric vehicles
- Overcurrent protection in power supplies
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar inverters)
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the ACS724 50A Hall Current Sensor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Generic |
| Part ID | ACS724 50A |
| Current Sensing Range | ±50A |
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Output Voltage Range | 0.5V to 4.5V |
| Sensitivity | 40mV/A |
| Bandwidth | 120 kHz |
| Response Time | 5 µs |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C |
| Isolation Voltage | 2.1 kV RMS |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ACS724 50A sensor has a simple pinout, as shown in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Power supply input (4.5V to 5.5V). Connect to the 5V pin of your microcontroller. |
| 2 | OUT | Analog output voltage proportional to the sensed current. |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection. Connect to the ground of your circuit. |
| 4 | IP+ | Current input terminal (positive). Connect to the high side of the current path. |
| 5 | IP- | Current input terminal (negative). Connect to the low side of the current path. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ACS724 50A in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the Vcc pin to a 5V power supply and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect the Current Path:
- Pass the current-carrying conductor through the IP+ and IP- terminals of the sensor.
- Ensure the current direction matches the sensor's orientation for accurate readings.
- Read the Output Voltage:
- The OUT pin provides an analog voltage proportional to the sensed current.
- Use an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) on a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) to read the output voltage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: The sensor's output voltage at 0A is typically 2.5V. Use this as a reference point for calibration.
- Filtering: Add a capacitor (e.g., 1 µF) between the OUT pin and GND to reduce noise in the output signal.
- Current Range: Ensure the current being measured does not exceed ±50A to avoid damaging the sensor.
- Isolation: The sensor provides electrical isolation between the current path and the output signal, making it safe for high-voltage applications.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following code demonstrates how to interface the ACS724 50A sensor with an Arduino UNO to measure current:
// Define the analog pin connected to the ACS724 OUT pin
const int sensorPin = A0;
// Define the sensor's sensitivity (40mV/A for ACS724 50A)
const float sensitivity = 0.04; // Sensitivity in V/A
// Define the reference voltage at 0A (typically 2.5V)
const float zeroCurrentVoltage = 2.5;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage (assuming 5V reference)
float sensorVoltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Calculate the current in Amperes
float current = (sensorVoltage - zeroCurrentVoltage) / sensitivity;
// Print the current to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Notes on the Code
- Ensure the Arduino's reference voltage is set to 5V for accurate ADC readings.
- The
zeroCurrentVoltagevalue may vary slightly between sensors. Measure the output voltage at 0A and adjust this value accordingly.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage or Incorrect Readings
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, especially the Vcc, GND, and OUT pins.
High Noise in Output Signal
- Cause: Electrical noise or lack of filtering.
- Solution: Add a capacitor (e.g., 1 µF) between the OUT pin and GND to filter noise.
Output Voltage Does Not Match Expected Values
- Cause: Calibration error or incorrect sensitivity value.
- Solution: Verify the
zeroCurrentVoltageandsensitivityvalues. Recalibrate if necessary.
Sensor Overheating
- Cause: Current exceeds the ±50A limit.
- Solution: Ensure the current being measured is within the sensor's specified range.
FAQs
Q: Can the ACS724 50A measure both AC and DC currents?
A: Yes, the sensor can measure both AC and DC currents up to ±50A.
Q: What is the typical output voltage at 0A?
A: The typical output voltage at 0A is 2.5V, but this may vary slightly between sensors.
Q: Is the sensor safe for high-voltage applications?
A: Yes, the ACS724 provides electrical isolation up to 2.1 kV RMS, making it suitable for high-voltage applications.
Q: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: The sensor requires a 5V power supply, but the output voltage can be read by a 3.3V ADC if the voltage levels are compatible. Use a voltage divider if necessary.
Q: How do I improve the accuracy of the sensor?
A: Calibrate the sensor by measuring the output voltage at 0A and adjusting the zeroCurrentVoltage value in your code. Additionally, use proper filtering to reduce noise.