
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use Comment: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Comment in Cirkit Designer
Design with Comment in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- A comment is a non-executable line in the code or schematic that provides explanations or notes for clarity. It is used to help users understand the purpose or function of the surrounding code or circuit.
- Common applications include:
- Documenting the functionality of code or circuit components.
- Providing instructions or reminders for future modifications.
- Enhancing collaboration by making the code or schematic more readable for others.
Explore Projects Built with Comment
Raspberry Pi 5-Based Project with Custom Comments
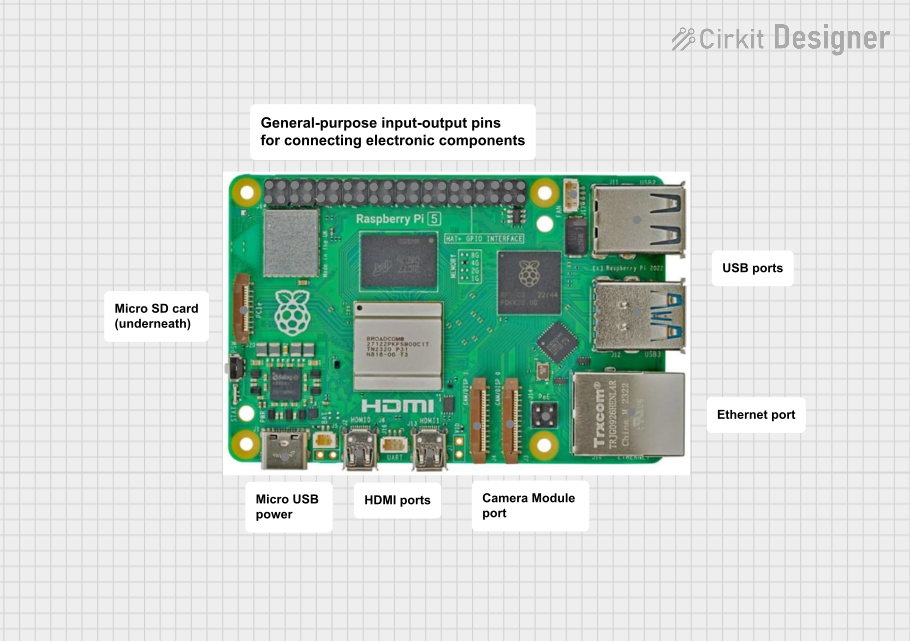
The circuit consists of a Raspberry Pi 5 with no additional electrical connections or code, suggesting it is either a placeholder for future development or a standalone component without any external interfacing in this configuration.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino Mega-Controlled Robotic Vehicle with RF Communication and Sensor Integration

This circuit is designed for advanced motion control and environmental sensing, featuring motor control with feedback, distance measurement, and wireless communication. It is powered by renewable energy sources, making it suitable for autonomous, remote, or outdoor applications. The lack of embedded code indicates that the control logic for the system's operation is not yet implemented.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino-Controlled Robotic Vehicle with RF Communication and Ultrasonic Sensing

This circuit is designed for a robotic or automated system with motor control, power management, and sensory data collection. It features microcontroller-based control with Arduino UNO and Nano, motor drivers for actuation, and a mix of ultrasonic and LIDAR sensors for environmental sensing. Additionally, it includes RF communication and image capture capabilities, with power supplied by a solar panel and managed by a charge controller and BMS.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerNFC-Enabled Access Control System with Real-Time Clock and OLED Display
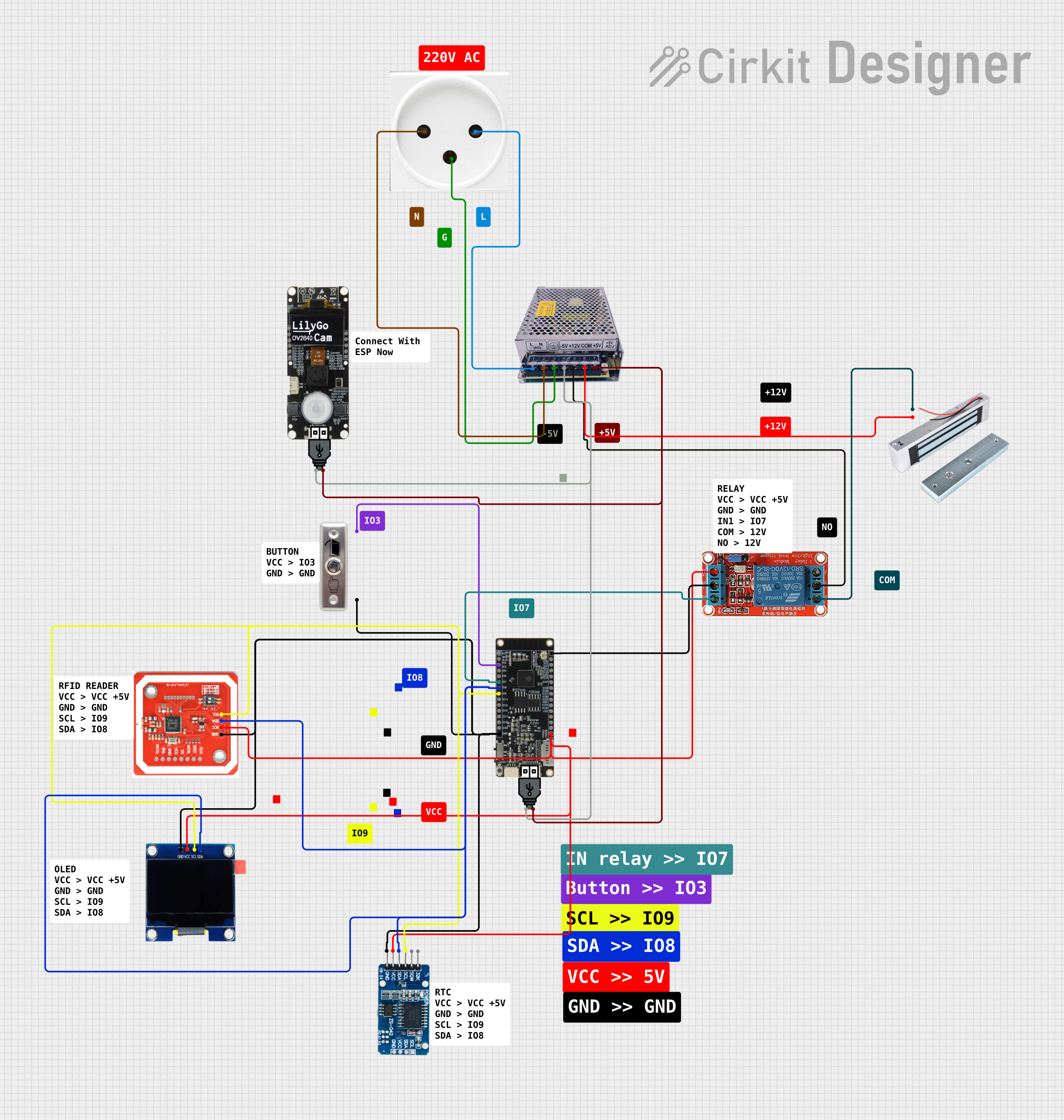
This circuit is designed as an access control system with time-tracking capabilities. It uses an NFC/RFID reader for authentication, a real-time clock for time-stamping events, and an OLED display for user interface, all controlled by a T8_S3 microcontroller. A relay module actuates a magnetic lock, and a button switch provides additional user input, with a switching power supply delivering the necessary voltages.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Comment

Raspberry Pi 5-Based Project with Custom Comments
The circuit consists of a Raspberry Pi 5 with no additional electrical connections or code, suggesting it is either a placeholder for future development or a standalone component without any external interfacing in this configuration.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino Mega-Controlled Robotic Vehicle with RF Communication and Sensor Integration
This circuit is designed for advanced motion control and environmental sensing, featuring motor control with feedback, distance measurement, and wireless communication. It is powered by renewable energy sources, making it suitable for autonomous, remote, or outdoor applications. The lack of embedded code indicates that the control logic for the system's operation is not yet implemented.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino-Controlled Robotic Vehicle with RF Communication and Ultrasonic Sensing
This circuit is designed for a robotic or automated system with motor control, power management, and sensory data collection. It features microcontroller-based control with Arduino UNO and Nano, motor drivers for actuation, and a mix of ultrasonic and LIDAR sensors for environmental sensing. Additionally, it includes RF communication and image capture capabilities, with power supplied by a solar panel and managed by a charge controller and BMS.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
NFC-Enabled Access Control System with Real-Time Clock and OLED Display
This circuit is designed as an access control system with time-tracking capabilities. It uses an NFC/RFID reader for authentication, a real-time clock for time-stamping events, and an OLED display for user interface, all controlled by a T8_S3 microcontroller. A relay module actuates a magnetic lock, and a button switch provides additional user input, with a switching power supply delivering the necessary voltages.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Comments are not physical components but are integral to programming and schematic design. They vary based on the programming language or design tool being used. Below are examples of how comments are implemented in different contexts:
Programming Languages
| Language | Comment Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C/C++ | // Single-line |
For single-line comments. |
/* Multi-line */ |
For multi-line comments. | |
| Python | # Single-line |
Python supports only single-line comments. |
| JavaScript | // Single-line |
For single-line comments. |
/* Multi-line */ |
For multi-line comments. | |
| HTML | <!-- Comment --> |
Used to comment out sections in HTML files. |
Schematic Design
| Design Tool | Comment Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EAGLE | Text annotations | Used to label or explain circuit elements. |
| KiCad | Text fields | Add notes or labels to schematics. |
| LTspice | .comment directive |
Used to add notes in simulation files. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use Comments in Code
Single-line Comments:
- Use single-line comments to explain a specific line or block of code.
- Example in Python:
# This is a single-line comment explaining the next line of code print("Hello, World!") # This prints a greeting message
Multi-line Comments:
- Use multi-line comments for detailed explanations or documentation.
- Example in C:
/* This is a multi-line comment. It can span multiple lines and is useful for providing detailed explanations. */ int x = 10; // Initialize variable x
Best Practices:
- Keep comments concise and relevant.
- Avoid over-commenting; focus on complex or non-obvious parts of the code.
- Use proper grammar and spelling for clarity.
How to Use Comments in Schematics
Adding Annotations:
- Use the text tool in your schematic design software to add comments near components or connections.
- Example in KiCad:
- Select the "Text" tool and click on the schematic to place a comment.
- Type your note, such as "This resistor limits current to the LED."
Best Practices:
- Place comments close to the components they describe.
- Use consistent formatting and font size for readability.
- Avoid cluttering the schematic with excessive comments.
Example: Using Comments with Arduino UNO
Here is an example of using comments in an Arduino sketch:
// This program blinks an LED connected to pin 13
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Code or Circuit is Not Working as Expected:
- Cause: Comments are not executed, so they do not affect functionality. However, unclear or incorrect comments can lead to misunderstandings.
- Solution: Review and update comments to ensure they accurately describe the code or circuit.
Comments are Cluttering the Code or Schematic:
- Cause: Overuse of comments or poor formatting.
- Solution: Remove unnecessary comments and focus on explaining complex or non-obvious parts.
Inconsistent Comment Style:
- Cause: Different team members use varying formats or styles.
- Solution: Establish a commenting standard for your project and ensure all contributors follow it.
FAQs
Q: Are comments necessary in every project?
- A: While not mandatory, comments are highly recommended for improving code readability and maintainability, especially in collaborative projects.
Q: Can comments slow down my program?
- A: No, comments are ignored by the compiler or interpreter and do not affect program performance.
Q: How do I decide what to comment?
- A: Focus on explaining complex logic, assumptions, or non-obvious decisions. Avoid commenting on trivial or self-explanatory code.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively use comments to enhance the clarity and maintainability of your code or schematics.