
How to Use Servo: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Servo in Cirkit Designer
Design with Servo in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Saavox 1262mg Servo is a high-performance rotary actuator designed for precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration. It integrates a motor, a position feedback sensor, and control circuitry into a compact unit. This servo is widely used in robotics, automation systems, RC vehicles, and other applications requiring accurate motion control.
Explore Projects Built with Servo
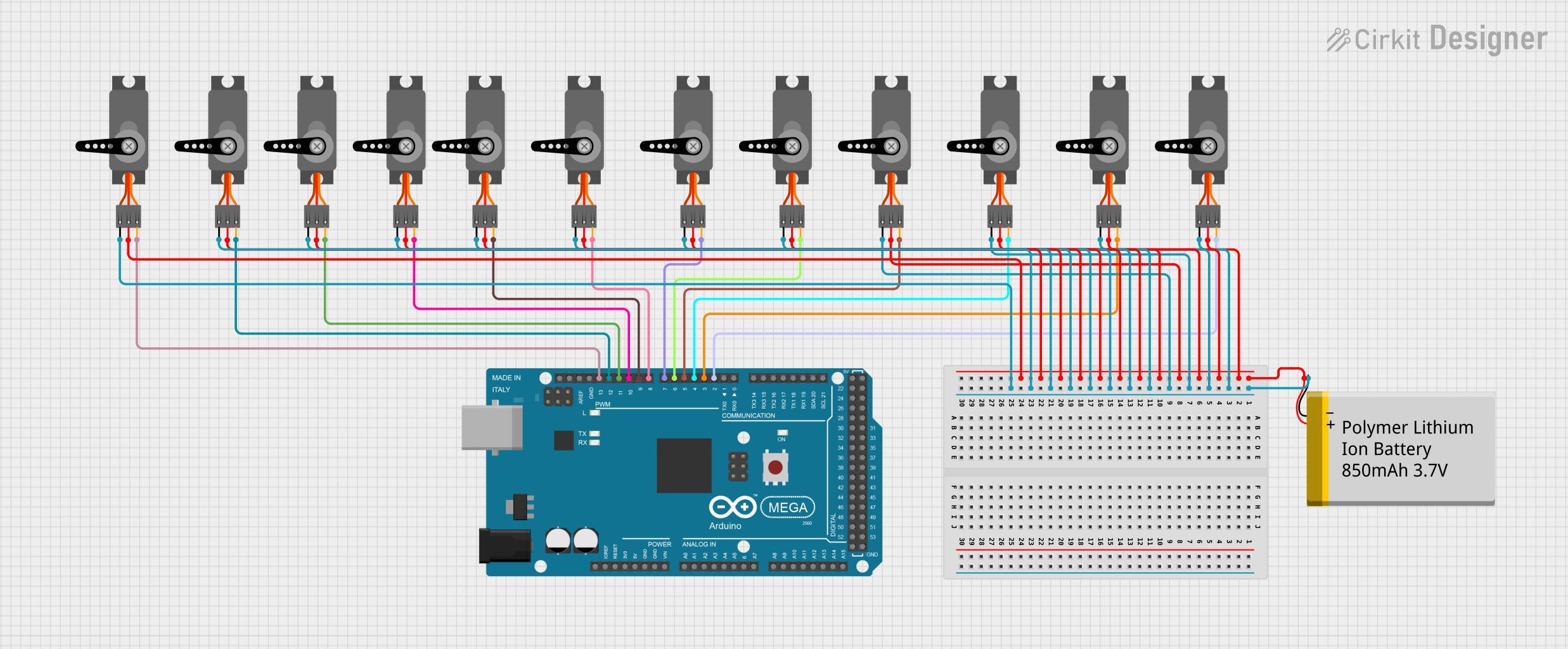
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer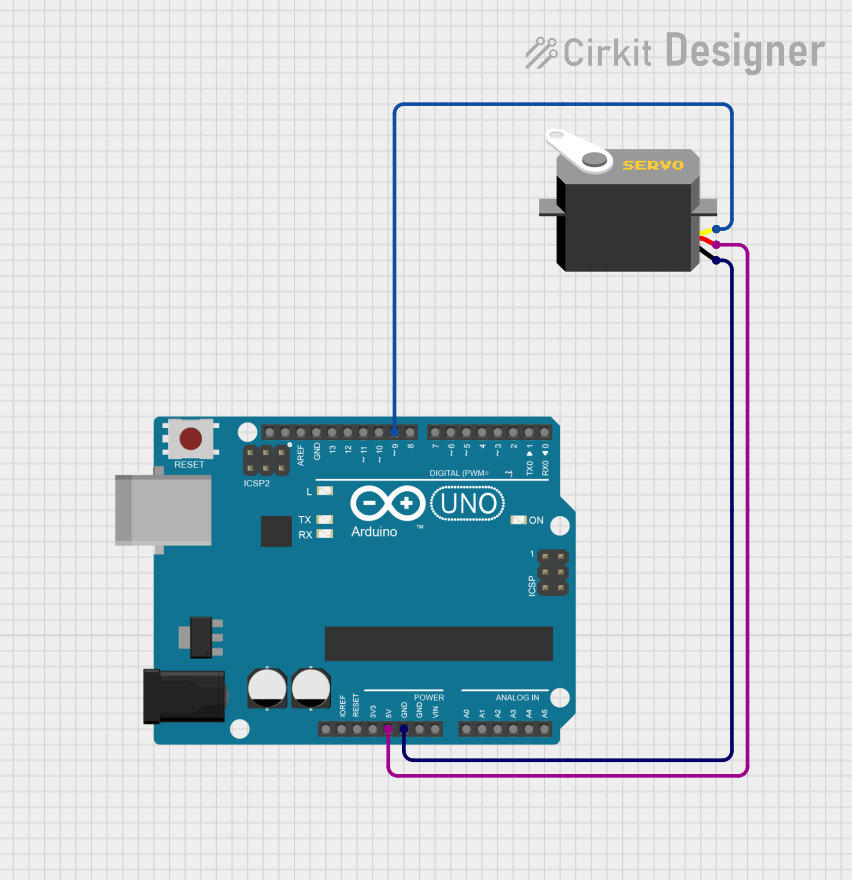
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer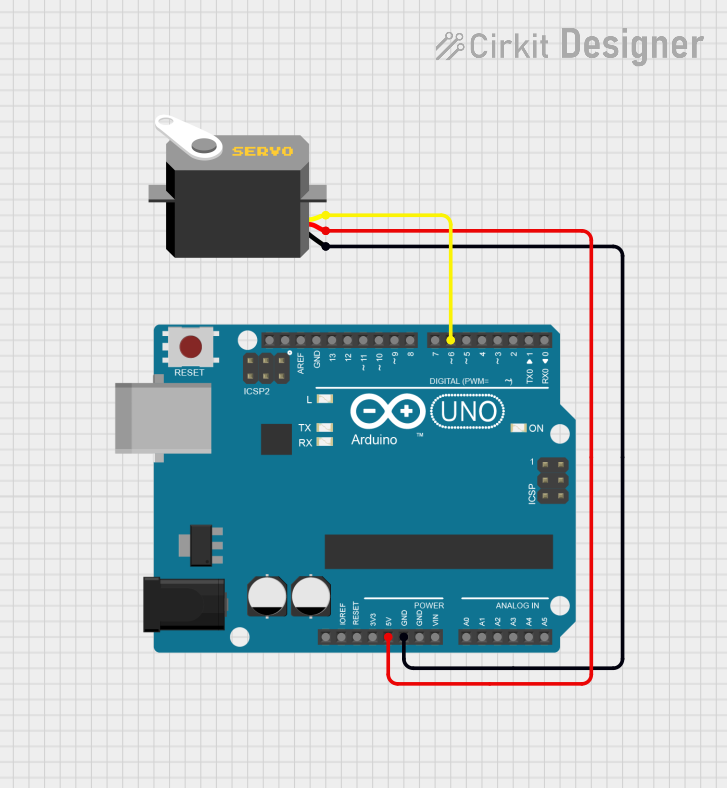
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer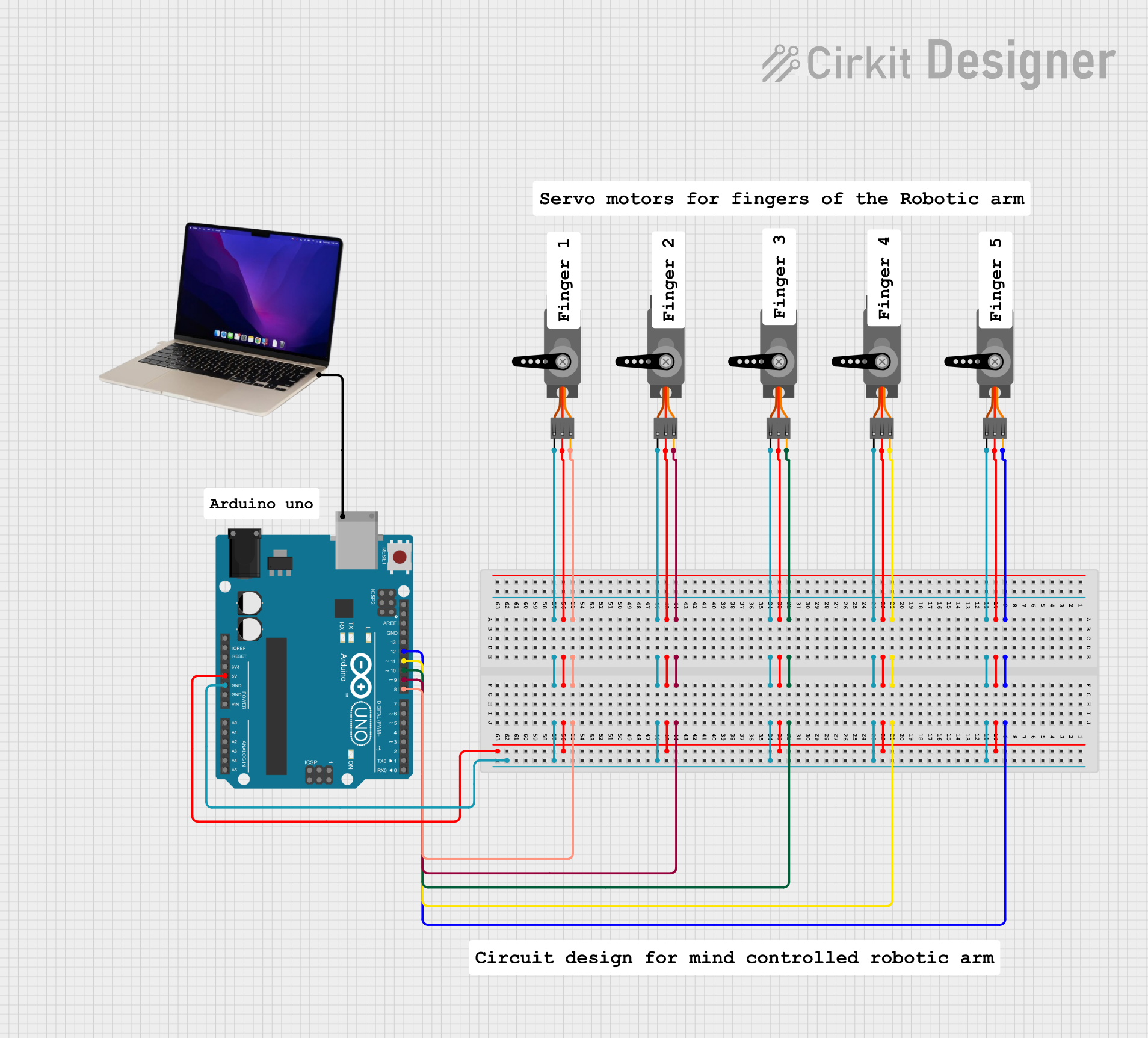
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Servo

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics (e.g., robotic arms, humanoid robots)
- RC vehicles (e.g., cars, planes, boats)
- Automation systems
- Camera gimbals and pan-tilt mechanisms
- Industrial machinery requiring precise positioning
Technical Specifications
The Saavox 1262mg Servo is engineered for reliability and precision. Below are its key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Saavox |
| Part ID | 1262mg |
| Operating Voltage | 4.8V to 6.6V |
| Stall Torque (6.0V) | 12 kg·cm (166.7 oz·in) |
| Operating Speed (6.0V) | 0.15 sec/60° |
| Gear Material | Metal |
| Motor Type | Coreless |
| Control Signal | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) |
| Weight | 55g |
| Dimensions | 40.5mm x 20mm x 38mm |
Pin Configuration
The Saavox 1262mg Servo has a standard 3-pin connector for power, ground, and signal. Below is the pinout:
| Pin Number | Wire Color | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brown | Ground (GND) | Connect to the ground of the power supply or microcontroller. |
| 2 | Red | Power (VCC) | Connect to a 4.8V-6.6V power source. |
| 3 | Orange | Signal (PWM) | Receives the PWM signal for position control. |
Usage Instructions
The Saavox 1262mg Servo is straightforward to use in a variety of circuits. Below are the steps and best practices for integrating it into your project.
Connecting the Servo
- Power Supply: Ensure the servo is powered by a stable 4.8V to 6.6V source. A dedicated power supply is recommended to avoid voltage drops.
- Ground Connection: Connect the brown wire to the ground of your power supply and microcontroller.
- Signal Input: Connect the orange wire to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
Controlling the Servo with Arduino UNO
The servo can be controlled using the Arduino Servo library. Below is an example code snippet to rotate the servo to specific angles:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo myServo; // Create a Servo object
void setup() {
myServo.attach(9); // Attach the servo to pin 9 on the Arduino
}
void loop() {
myServo.write(0); // Move the servo to 0 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(90); // Move the servo to 90 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(180); // Move the servo to 180 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Best Practices
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the stall torque rating to prevent damage to the motor or gears.
- Stable Power Supply: Use a capacitor across the power lines to reduce noise and voltage fluctuations.
- PWM Signal: Ensure the PWM signal has a frequency of 50Hz (20ms period) for optimal performance.
- Mechanical Limits: Avoid forcing the servo beyond its physical rotation limits (typically 0° to 180°).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Servo Not Moving
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements.
Servo Jittering
- Cause: Noisy power supply or unstable PWM signal.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 100µF) across the power lines and verify the PWM signal quality.
Overheating
- Cause: Prolonged operation at stall torque or excessive load.
- Solution: Reduce the load or avoid operating the servo at stall torque for extended periods.
Limited Range of Motion
- Cause: Incorrect PWM signal or mechanical obstruction.
- Solution: Verify the PWM signal range (typically 1ms to 2ms pulse width) and check for physical obstructions.
FAQs
Q: Can I power the servo directly from the Arduino UNO?
A: It is not recommended, as the Arduino's 5V pin may not provide sufficient current. Use an external power supply.
Q: What is the maximum rotation angle of the Saavox 1262mg Servo?
A: The servo typically rotates between 0° and 180°, but this may vary slightly depending on the PWM signal.
Q: Can I use the servo with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but ensure the PWM signal is 3.3V compatible and the servo is powered by a 4.8V-6.6V supply.
Q: How do I extend the servo's lifespan?
A: Avoid overloading, use a stable power supply, and operate the servo within its specified limits.
This concludes the documentation for the Saavox 1262mg Servo. For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or contact Saavox support.