
How to Use Leitungsschutzschalter 1 pol.: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Leitungsschutzschalter 1 pol. in Cirkit Designer
Design with Leitungsschutzschalter 1 pol. in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Leitungsschutzschalter 1 pol. (Hager MBS 116 B16) is a single-pole circuit breaker designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. Manufactured by Hager, this component ensures the safety and reliability of electrical systems by automatically interrupting the current flow when abnormal conditions are detected. It is widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations.
Explore Projects Built with Leitungsschutzschalter 1 pol.
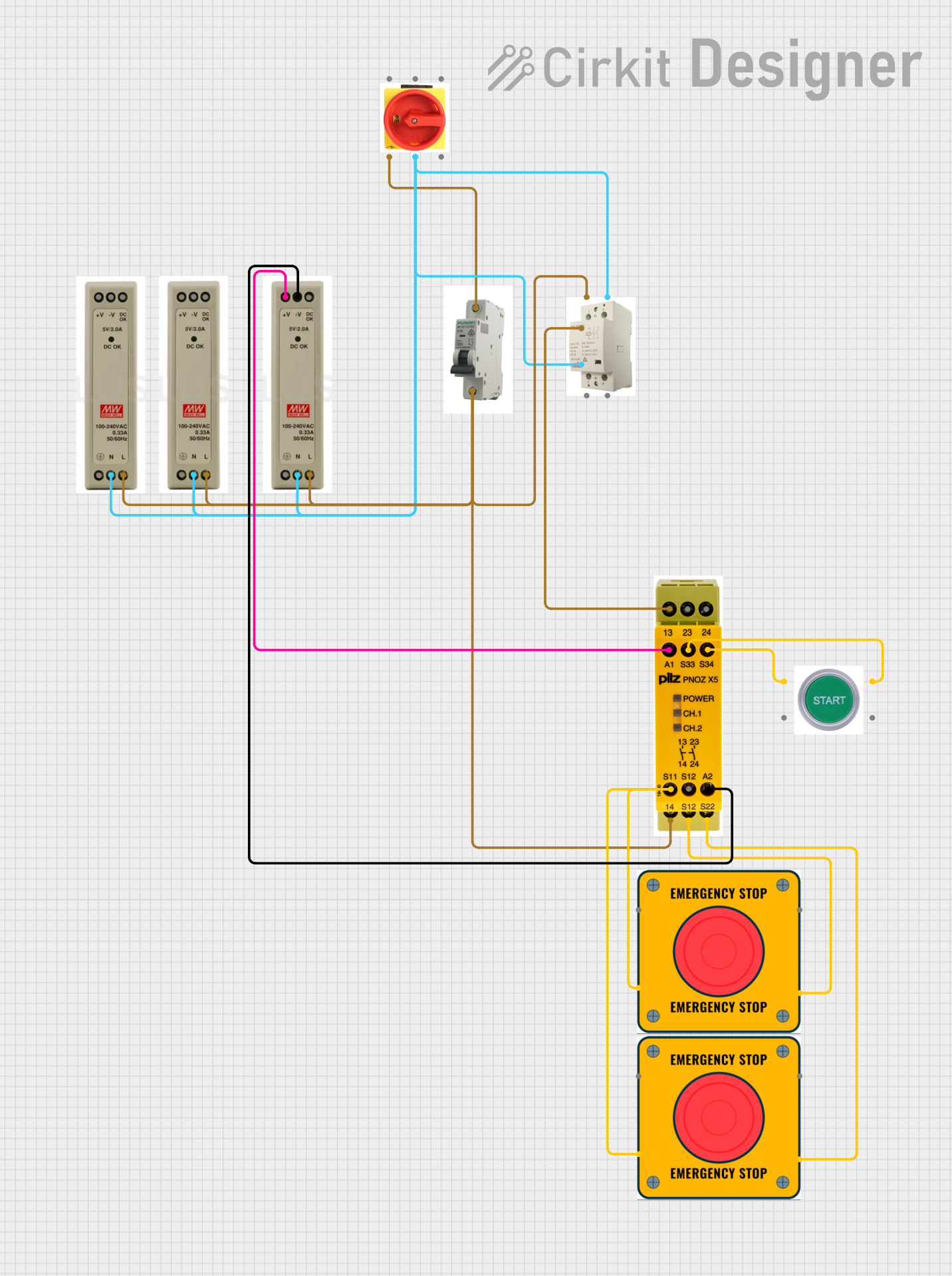
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer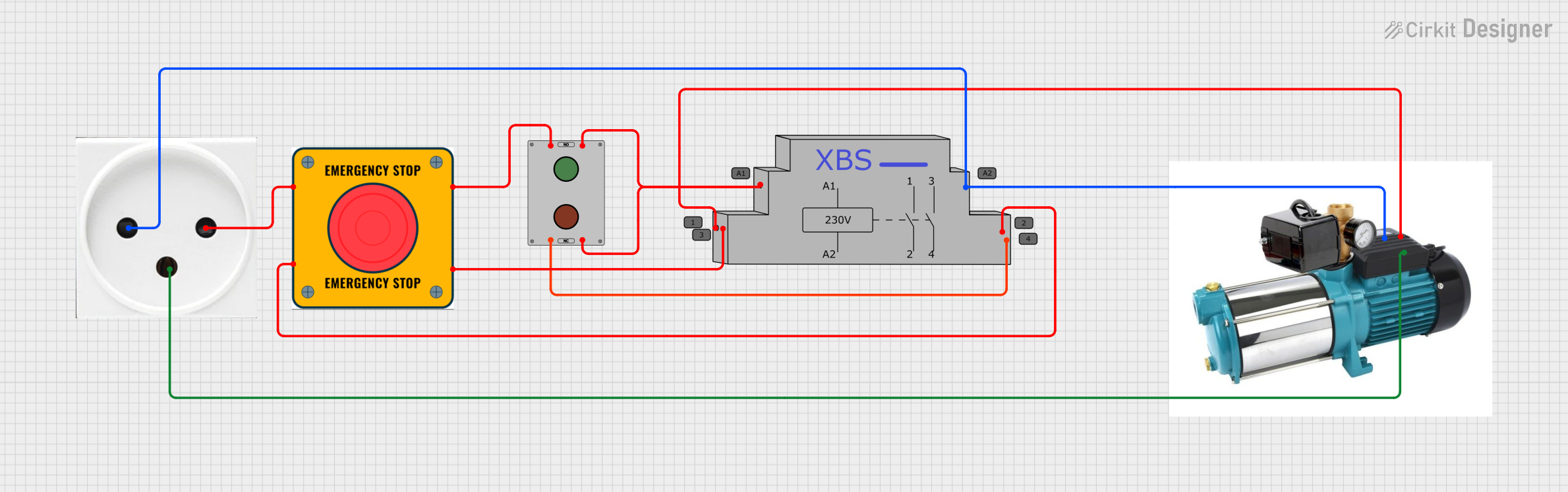
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Leitungsschutzschalter 1 pol.

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Protection of lighting circuits, power outlets, and small appliances.
- Prevention of electrical fires caused by overloads or short circuits.
- Use in distribution boards for residential and commercial buildings.
- Suitable for circuits with a nominal current of up to 16A.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Hager MBS 116 B16 circuit breaker:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Hager |
| Part Number | MBS 116 B16 |
| Type | Single-pole circuit breaker |
| Rated Current (In) | 16A |
| Tripping Curve | B (suitable for low inrush currents) |
| Rated Voltage (Un) | 230/400V AC |
| Breaking Capacity (Icn) | 6 kA |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Mounting Type | DIN rail (35mm) |
| Number of Poles | 1 |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +55°C |
| Standards Compliance | IEC/EN 60898-1 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Hager MBS 116 B16 has a simple terminal configuration for input and output connections:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Line (Input) | Connects to the incoming power supply. |
| Load (Output) | Connects to the protected circuit/load. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Mounting the Circuit Breaker:
- Install the circuit breaker on a standard 35mm DIN rail in the distribution board.
- Ensure the breaker is securely clipped onto the rail.
Wiring:
- Connect the incoming power supply to the Line (Input) terminal.
- Connect the protected circuit or load to the Load (Output) terminal.
- Tighten the terminal screws to ensure a secure connection.
Operation:
- Switch the breaker to the "ON" position to allow current flow.
- In case of an overload or short circuit, the breaker will trip to the "OFF" position automatically.
Resetting After a Trip:
- Identify and resolve the cause of the overload or short circuit.
- Switch the breaker back to the "ON" position to restore power.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the circuit breaker is rated appropriately for the circuit's current and voltage.
- Do not exceed the rated current of 16A to avoid nuisance tripping.
- Regularly inspect the breaker for signs of wear or damage.
- Always turn off the main power supply before installing or servicing the breaker.
- Use proper tools and follow local electrical codes during installation.
Arduino Integration
While the Hager MBS 116 B16 is not directly compatible with Arduino, it can be used in conjunction with an Arduino-based monitoring system. For example, you can use a current sensor (e.g., ACS712) to monitor the load current and trigger an alert if the breaker trips.
Here is an example Arduino code snippet for monitoring current:
// Include necessary libraries
#include <Wire.h>
// Define the analog pin connected to the current sensor
const int currentSensorPin = A0;
// Define the threshold current in amperes
const float currentThreshold = 16.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(currentSensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the current sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(currentSensorPin);
// Convert the sensor value to current (example conversion factor)
float current = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0) * 30.0;
// Print the current value to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
// Check if the current exceeds the threshold
if (current > currentThreshold) {
Serial.println("Warning: Current exceeds threshold! Check the circuit.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: The above code assumes the use of an ACS712 current sensor. Adjust the conversion factor based on your specific sensor model.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Breaker Trips Frequently:
- Cause: Overload or short circuit in the connected circuit.
- Solution: Check the connected devices for faults or reduce the load on the circuit.
Breaker Does Not Trip During Overload:
- Cause: Faulty breaker or incorrect installation.
- Solution: Replace the breaker or verify the wiring and connections.
Difficulty in Resetting the Breaker:
- Cause: Persistent fault in the circuit or damaged breaker.
- Solution: Inspect the circuit for faults and resolve them before resetting.
Loose Connections:
- Cause: Improper tightening of terminal screws.
- Solution: Ensure all connections are secure and properly tightened.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage levels in the circuit.
- Inspect the breaker for physical damage or signs of overheating.
- If the breaker trips repeatedly, consult a licensed electrician to diagnose the issue.
- Always follow safety precautions when working with electrical components.
By following this documentation, users can effectively install, operate, and troubleshoot the Hager MBS 116 B16 circuit breaker, ensuring the safety and reliability of their electrical systems.