
How to Use GND: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with GND in Cirkit Designer
Design with GND in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ground (GND) is a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured. It serves as a common return path for electric current and is essential for the proper functioning of electronic circuits. GND is typically represented by a symbol resembling a series of horizontal lines that taper downward. It is a fundamental concept in electronics, ensuring stability and safety in circuit design.
Explore Projects Built with GND
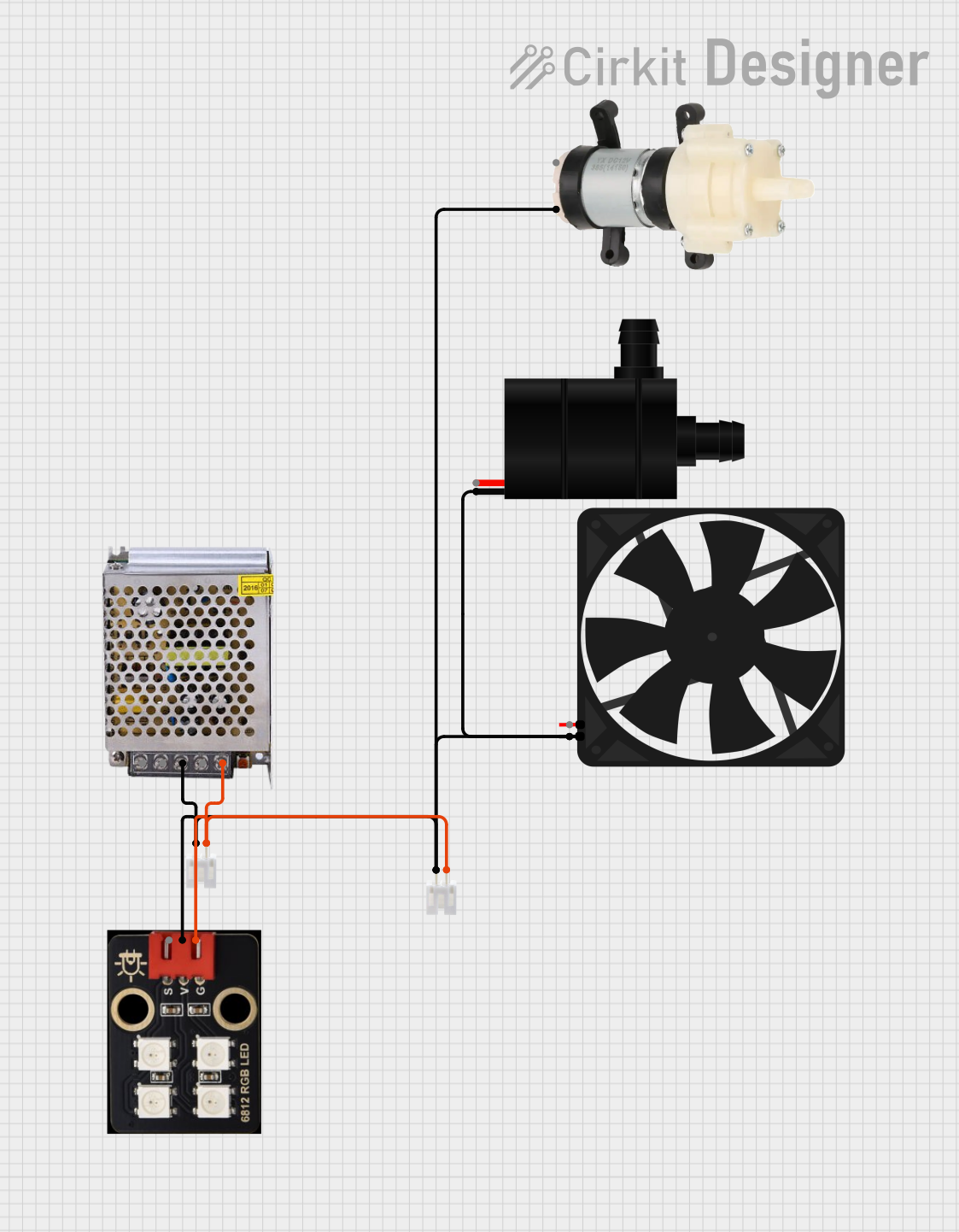
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer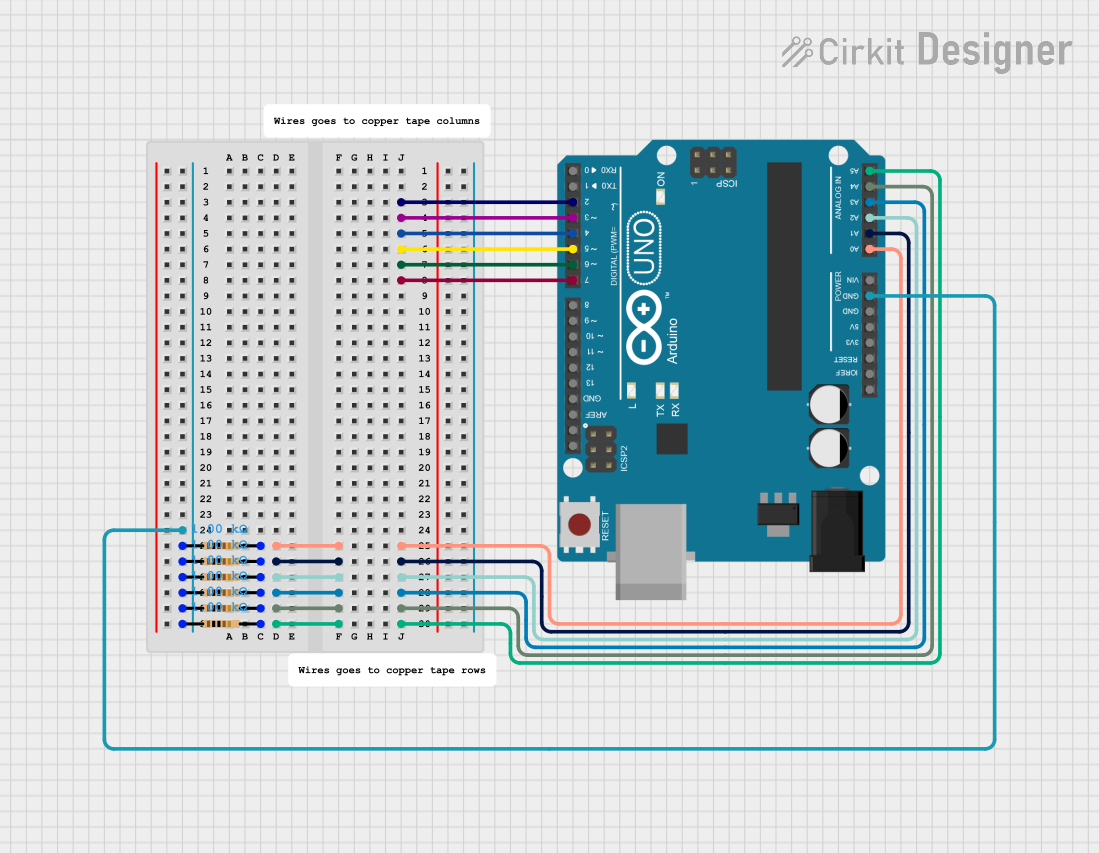
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GND

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voltage Reference: Provides a stable reference point for measuring voltages in a circuit.
- Current Return Path: Acts as the return path for electric current in a closed circuit.
- Signal Integrity: Helps maintain signal stability and reduces noise in communication systems.
- Safety: Protects users and components by providing a path for fault currents in case of short circuits.
Technical Specifications
While GND itself is not an active component, its implementation in a circuit is critical. Below are some key considerations:
General Characteristics
- Voltage Level: 0V (reference point for all other voltages in the circuit)
- Current Capacity: Depends on the circuit design and the thickness of the ground trace or wire.
- Impedance: Should be as low as possible to ensure minimal voltage drop and noise.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
GND is often represented as a pin or terminal in various electronic components and connectors. Below is an example of how GND is used in common devices:
| Device | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Microcontroller | GND | Ground pin for power and signal reference. |
| Power Supply | GND | Common return path for current. |
| Sensors | GND | Reference point for sensor operation. |
| Connectors (e.g., USB) | GND | Ground connection for power and data integrity. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use GND in a Circuit
- Connect All GND Points: Ensure that all components in the circuit share a common ground connection. This prevents potential differences that could disrupt circuit operation.
- Minimize Ground Loops: Avoid creating multiple ground paths that form loops, as these can introduce noise and interference.
- Use a Ground Plane: In PCB design, use a dedicated ground plane to reduce impedance and improve signal integrity.
- Connect to Earth Ground (if applicable): For safety, connect the circuit's ground to earth ground in high-power or sensitive applications.
Example: Connecting GND to an Arduino UNO
When using an Arduino UNO, GND is essential for proper operation. Below is an example of connecting a sensor to the Arduino:
// Example: Connecting a sensor to Arduino UNO with GND
// This code reads an analog value from a sensor and prints it to the Serial Monitor.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Sensor connected to analog pin A0
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor reading
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Note: Ensure the sensor's GND pin is connected to the Arduino's GND pin to establish a common reference point.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Wire Thickness: Use appropriately thick wires for GND connections in high-current circuits to prevent overheating and voltage drops.
- Star Grounding: In complex circuits, use a star grounding technique where all ground connections converge at a single point to reduce noise.
- Avoid Floating Grounds: Ensure that all components have a proper ground connection to avoid erratic behavior.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Floating Ground: Components behave erratically or fail to operate.
- Solution: Check all GND connections and ensure they are properly connected.
- Ground Loops: Noise or interference in the circuit.
- Solution: Redesign the circuit to eliminate multiple ground paths forming loops.
- Voltage Drop Across GND: Unexpected voltage differences between GND points.
- Solution: Use a thicker ground trace or wire to reduce impedance.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect multiple GND points in a circuit?
A: Yes, all GND points should be connected to ensure a common reference. However, avoid creating ground loops.
Q: What happens if GND is not connected in a circuit?
A: The circuit may not function correctly, as there will be no reference point for voltages or a return path for current.
Q: How do I identify the GND pin on a component?
A: The GND pin is usually labeled as "GND" or marked with a ground symbol. Refer to the component's datasheet for details.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure proper use of GND in your electronic projects, leading to stable and reliable circuit performance.