
How to Use Humidity YL-69: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
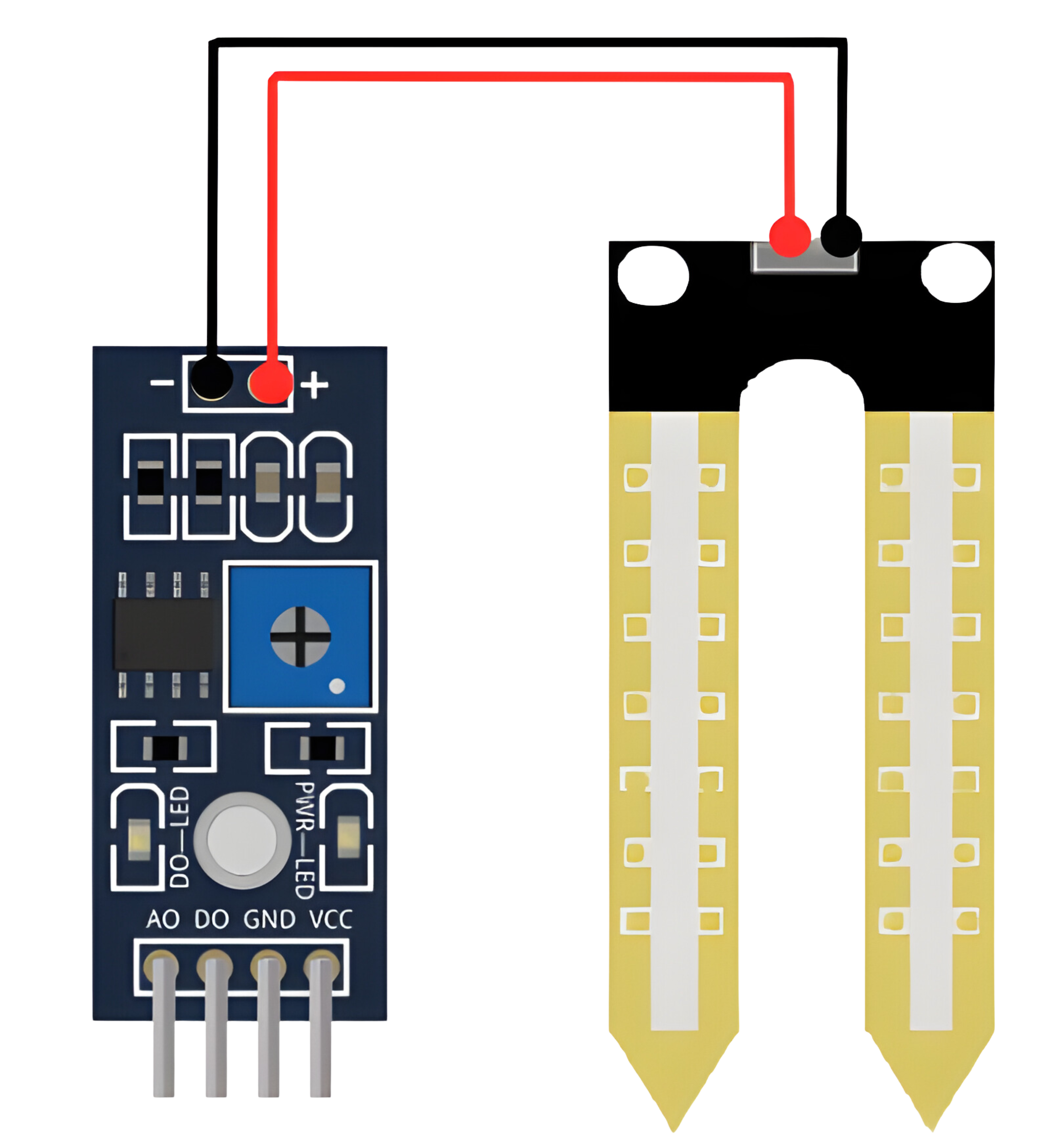
 Design with Humidity YL-69 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Humidity YL-69 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Humidity YL-69 sensor, also known as the Soil Humidity Sensor, is an electronic device designed to measure the relative humidity in soil or similar environments. It is commonly used in gardening projects, irrigation systems, and environmental monitoring to ensure optimal moisture levels for plant growth or to conserve water by automating watering schedules.
Explore Projects Built with Humidity YL-69
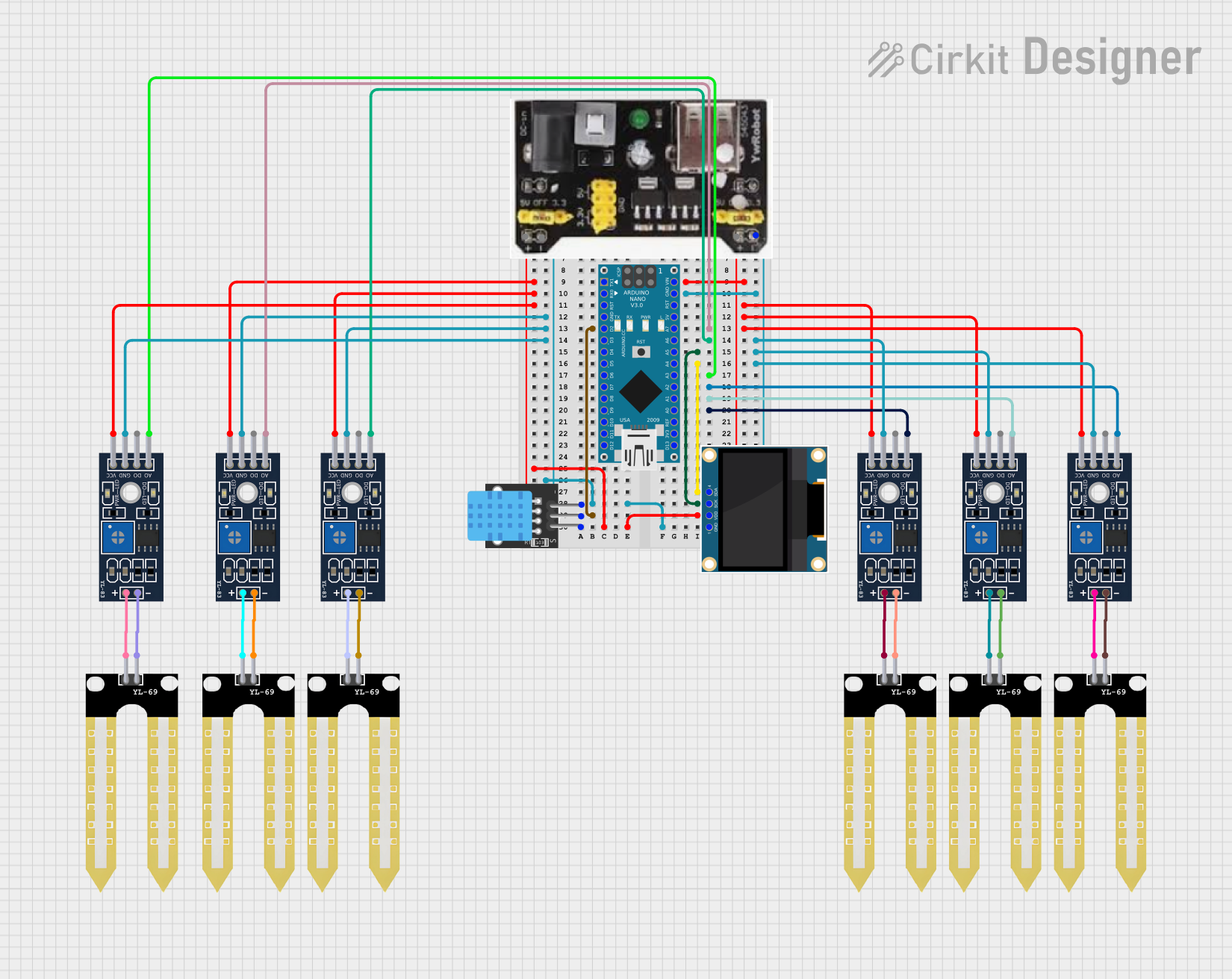
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer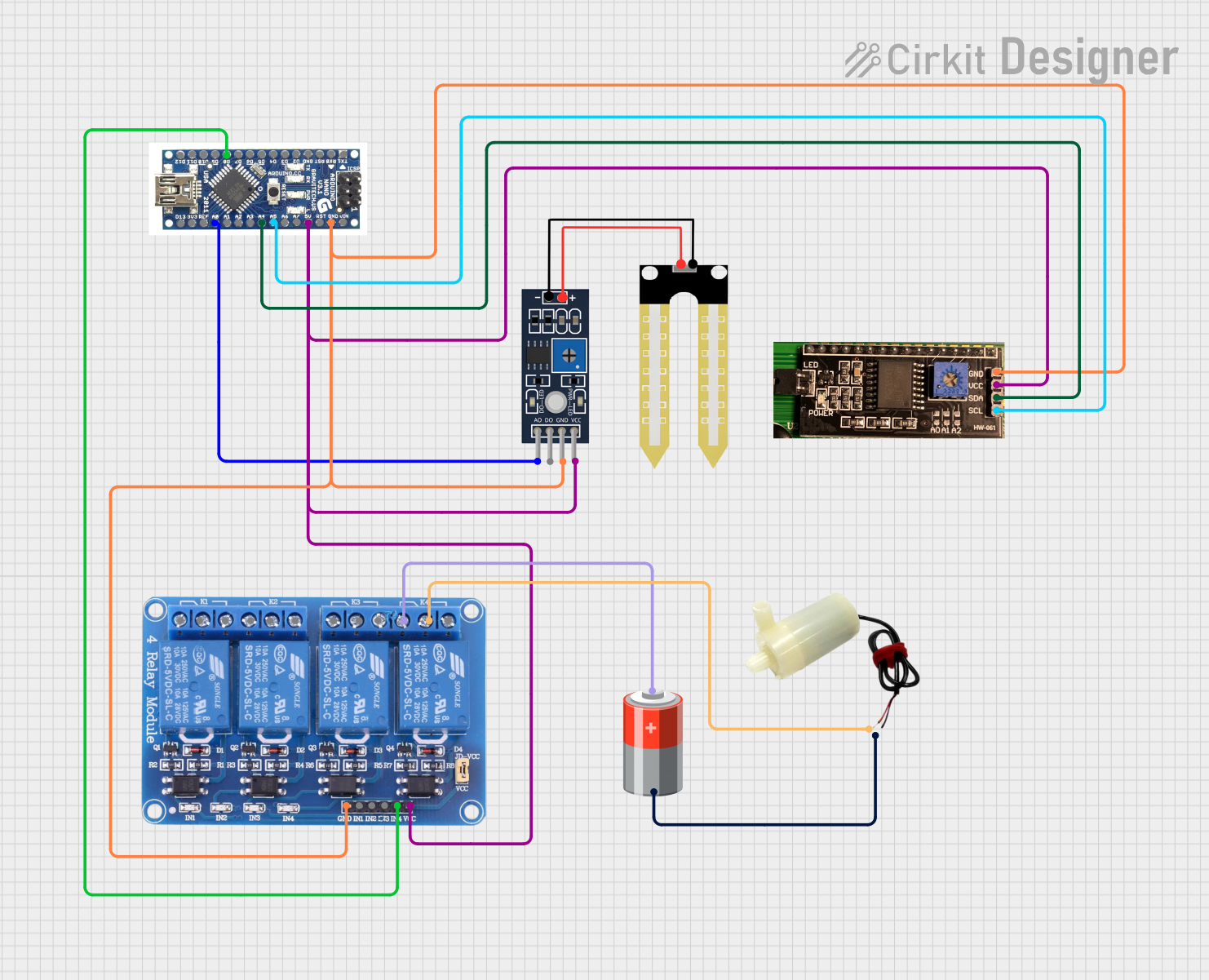
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer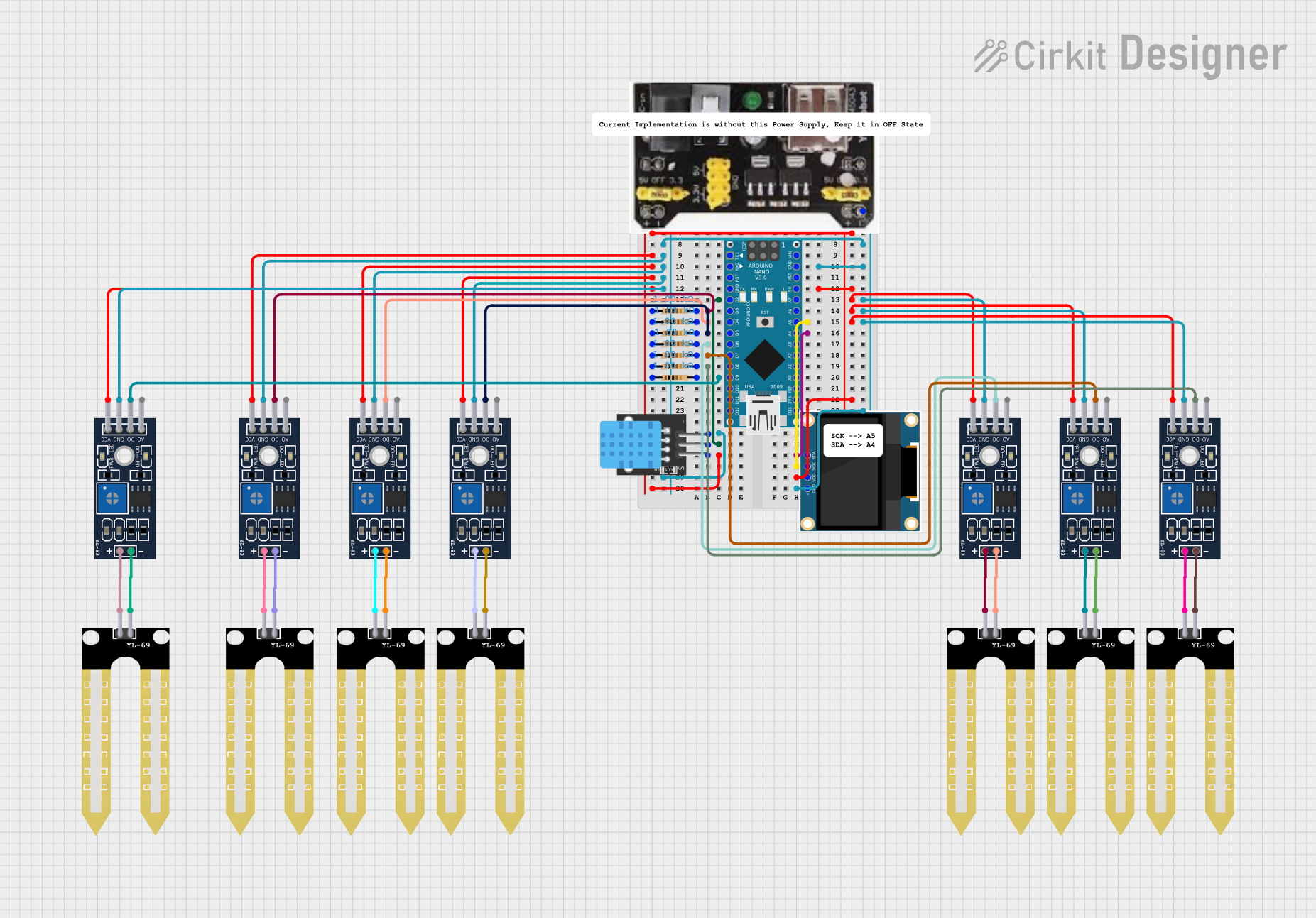
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer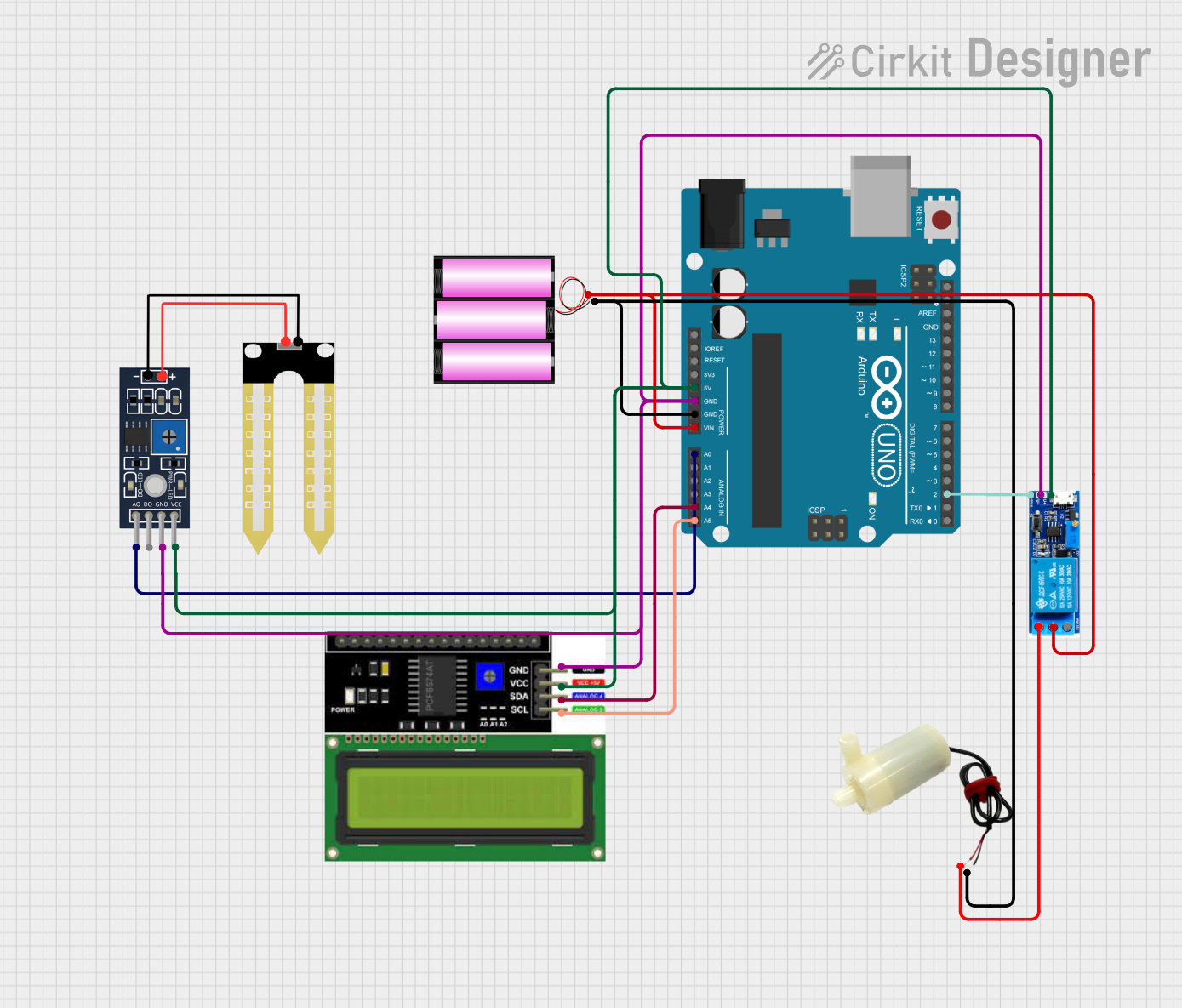
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Humidity YL-69

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automated irrigation systems
- Soil moisture monitoring in agriculture
- Environmental sensing in smart gardens
- Educational projects related to soil science
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V
- Output Voltage: 0V to 4.2V
- Current: 35mA (typical)
- Sensitivity: Adjustable via onboard potentiometer
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V to 5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | AOUT | Analog output voltage |
| 4 | DOUT | Digital output (threshold set by onboard potentiometer) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the VCC pin to the power supply (3.3V to 5V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power supply.
- Connect the AOUT pin to an analog input pin on your microcontroller to read the analog moisture level.
- Optionally, connect the DOUT pin to a digital input pin on your microcontroller if you want to use the digital threshold feature.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid submerging the sensor completely in water or exposing it to corrosive chemicals.
- Calibrate the sensor by adjusting the onboard potentiometer to set the threshold for the digital output.
- Use a pull-up resistor if you are using the digital output.
- To extend the life of the sensor, power it only when a reading is needed.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the sensor analog pin
const int sensorPin = A0;
void setup() {
// Begin serial communication at 9600 baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the value from the sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Convert the analog reading to a voltage
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Voltage: ");
Serial.println(voltage);
// Wait for a second before taking another reading
delay(1000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Inconsistent Readings: Ensure that the sensor is not moving and is properly inserted into the soil. Check for any corrosion on the sensor's probes.
- No Readings: Verify that the sensor is correctly powered and that all connections are secure. Check the microcontroller's analog pin with a known good sensor.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- If the sensor provides inconsistent readings, recalibrate the onboard potentiometer.
- Clean the sensor probes with distilled water and dry them if corrosion or soil buildup is present.
- Ensure that the sensor is not exposed to water for prolonged periods to prevent oxidation.
FAQs
Q: Can the YL-69 sensor be used to measure water content in substances other than soil? A: Yes, but the sensor is calibrated for soil moisture and may require recalibration for other materials.
Q: How do I prevent the sensor from corroding? A: Minimize the time the sensor is powered on, and avoid leaving it in wet soil for extended periods. Clean and dry the sensor after use.
Q: Is it possible to use the sensor with a 3.3V system? A: Yes, the sensor can operate at 3.3V, but the output voltage range will be lower, affecting the sensor's resolution.
Q: How do I interpret the analog voltage reading? A: The voltage reading is proportional to the moisture level. A higher voltage indicates more moisture. Calibration is required to correlate voltage to specific moisture levels.