
How to Use VL53LXX-V2: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with VL53LXX-V2 in Cirkit Designer
Design with VL53LXX-V2 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The VL53LXX-V2 is a time-of-flight (ToF) distance sensor manufactured by Arduino. It utilizes advanced laser technology to measure distances with high accuracy and speed. This sensor is capable of measuring distances ranging from 30 mm to 2 meters, making it ideal for applications requiring precise and reliable distance measurements.
Explore Projects Built with VL53LXX-V2
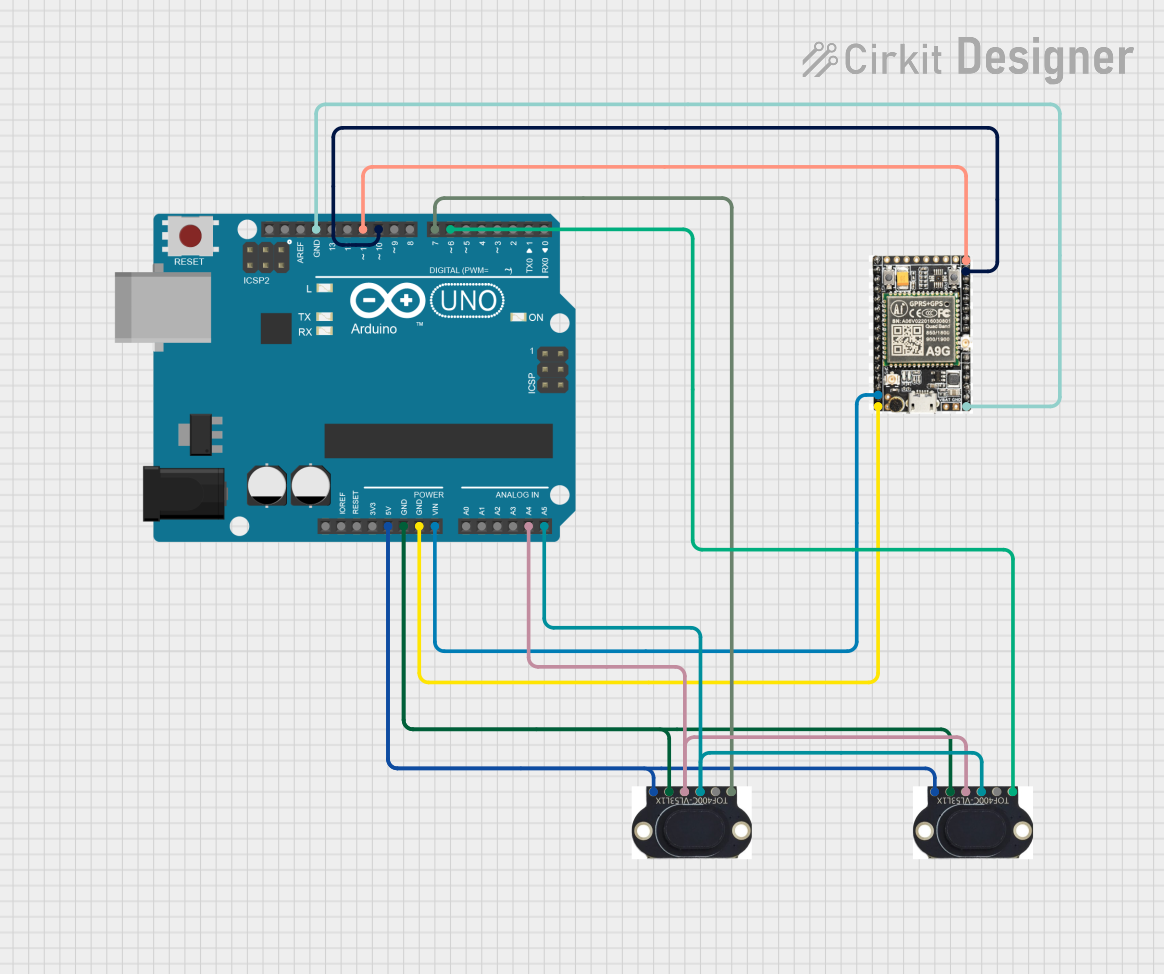
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer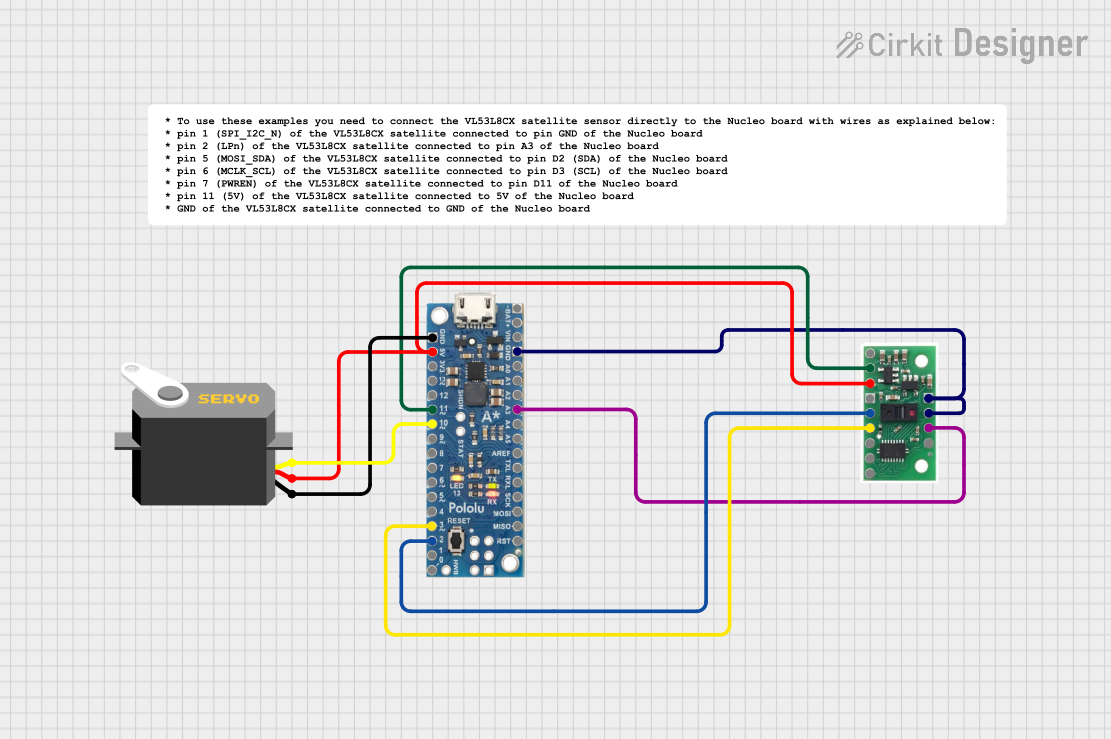
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer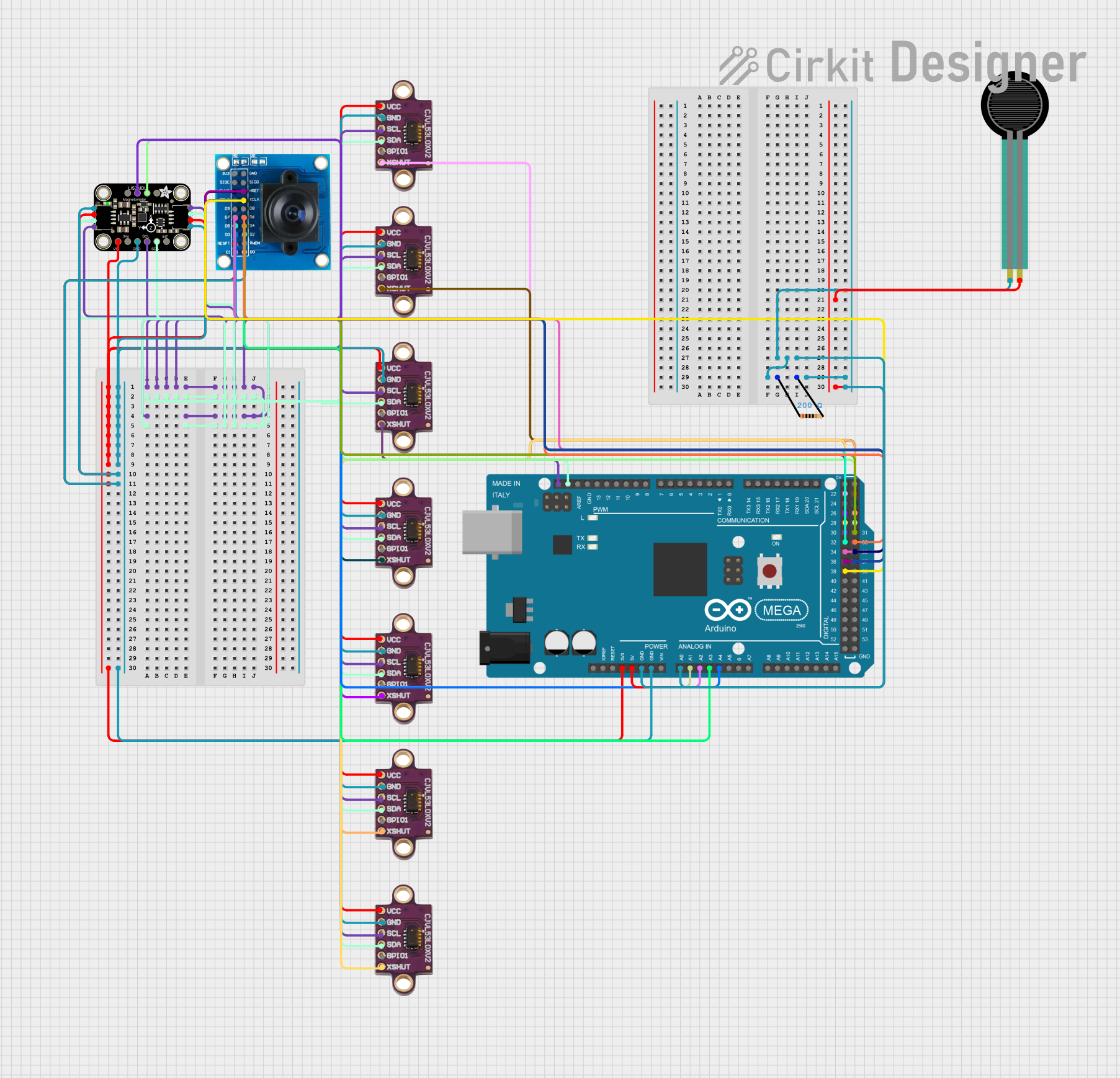
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with VL53LXX-V2

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics for obstacle detection and navigation
- Drones for altitude measurement and collision avoidance
- Industrial automation for object detection
- Consumer electronics for gesture recognition
- Smart home devices for proximity sensing
Technical Specifications
The VL53LXX-V2 is designed to deliver high performance in a compact form factor. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 2.6 V to 3.5 V |
| Communication Interface | I2C |
| Measurement Range | 30 mm to 2000 mm |
| Accuracy | ±3% |
| Field of View (FoV) | 27° |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +85°C |
| Power Consumption | 20 mW (typical) |
| Dimensions | 4.4 mm x 2.4 mm x 1.0 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The VL53LXX-V2 sensor module typically comes with the following pinout:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Power supply input (2.6 V to 3.5 V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| SDA | I2C data line |
| SCL | I2C clock line |
| XSHUT | Shutdown pin (active low, used to reset the sensor) |
| GPIO1 | Interrupt output (optional, configurable) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the VL53LXX-V2 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VIN pin to a 3.3 V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- I2C Communication: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- Optional Connections:
- Use the XSHUT pin to reset the sensor if needed.
- The GPIO1 pin can be used for interrupt-based applications.
- Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure that the I2C lines (SDA and SCL) have appropriate pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ambient Light: Avoid exposing the sensor to direct sunlight or strong ambient light, as it may affect accuracy.
- Reflective Surfaces: Highly reflective or transparent surfaces may cause measurement errors.
- Mounting: Ensure the sensor is mounted securely and aligned properly for accurate measurements.
- I2C Address: The default I2C address is 0x29. If using multiple sensors, you must configure unique addresses for each.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the VL53LXX-V2 with an Arduino UNO:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_VL53L0X.h> // Library for VL53LXX sensors
Adafruit_VL53L0X lox = Adafruit_VL53L0X();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
while (!Serial) {
delay(10); // Wait for Serial Monitor to open
}
Serial.println("VL53LXX-V2 Distance Sensor Test");
if (!lox.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize VL53LXX-V2 sensor!");
while (1) {
delay(10); // Stay in loop if initialization fails
}
}
}
void loop() {
VL53L0X_RangingMeasurementData_t measure;
lox.rangingTest(&measure, false); // Perform a distance measurement
if (measure.RangeStatus != 4) { // Check if measurement is valid
Serial.print("Distance (mm): ");
Serial.println(measure.RangeMilliMeter);
} else {
Serial.println("Out of range");
}
delay(100); // Wait before the next measurement
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Sensor Not Detected on I2C Bus:
- Ensure the SDA and SCL connections are correct.
- Verify that pull-up resistors are present on the I2C lines.
- Check the sensor's power supply voltage.
Inaccurate Distance Measurements:
- Avoid using the sensor in environments with strong ambient light.
- Ensure the target surface is not too reflective or transparent.
- Verify that the sensor is properly aligned with the target.
Out of Range Errors:
- Ensure the target is within the sensor's measurement range (30 mm to 2 m).
- Check for obstructions in the sensor's field of view.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the VL53LXX-V2 with a 5V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you will need a logic level shifter to safely interface the 3.3V I2C lines with the 5V microcontroller.
Q: How do I use multiple VL53LXX-V2 sensors on the same I2C bus?
A: Use the XSHUT pin to reset each sensor individually and assign a unique I2C address to each.
Q: What is the maximum update rate of the sensor?
A: The VL53LXX-V2 can achieve an update rate of up to 50 Hz, depending on the configuration.
Q: Can the sensor measure through glass?
A: The sensor may work through glass, but accuracy can be affected due to reflections and refractions.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the VL53LXX-V2 into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.