
How to Use Reed switch: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Reed switch in Cirkit Designer
Design with Reed switch in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Reed switch is an electromagnetic switch that opens and closes in response to a magnetic field. It consists of two ferromagnetic contacts sealed in a small glass tube. When a magnetic field is applied, the contacts close, completing the circuit. When the magnetic field is removed, the contacts open, breaking the circuit.
Reed switches are widely used in various applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and low power consumption. Common use cases include:
- Door and window sensors in security systems
- Position and proximity sensing
- Speed sensing in bicycles and treadmills
- Liquid level detection in tanks
- Automotive applications, such as brake or gear position sensing
Explore Projects Built with Reed switch
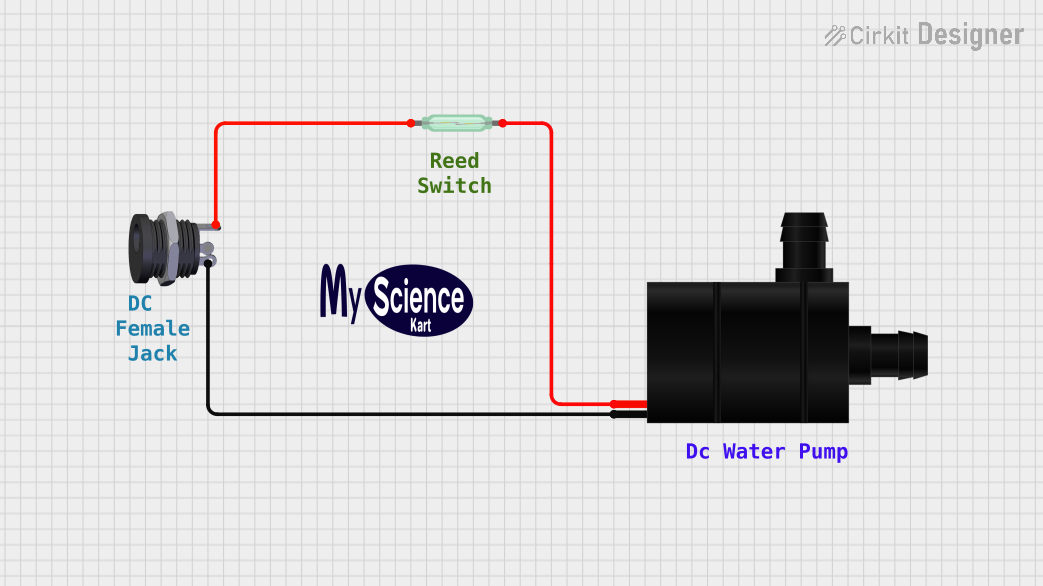
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer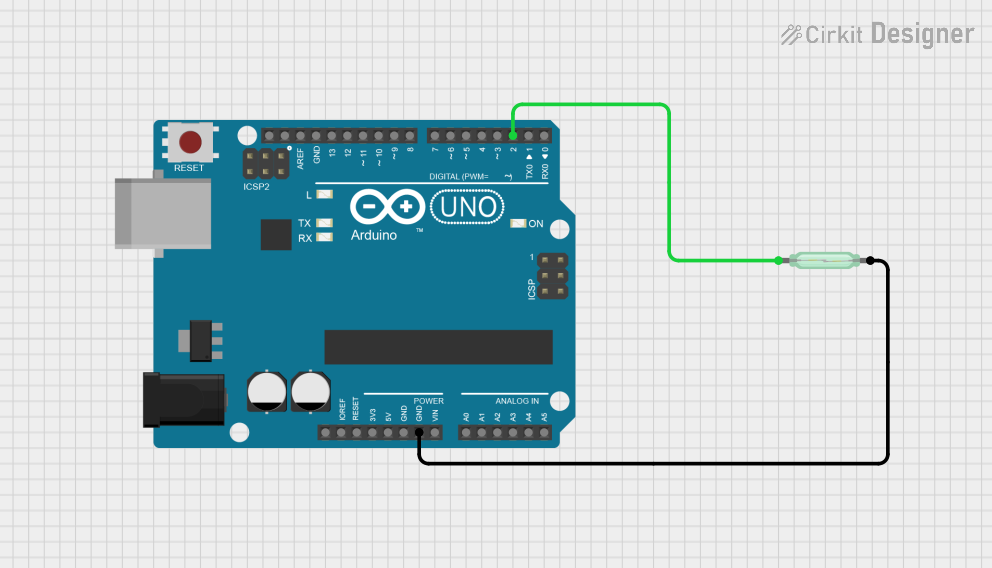
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer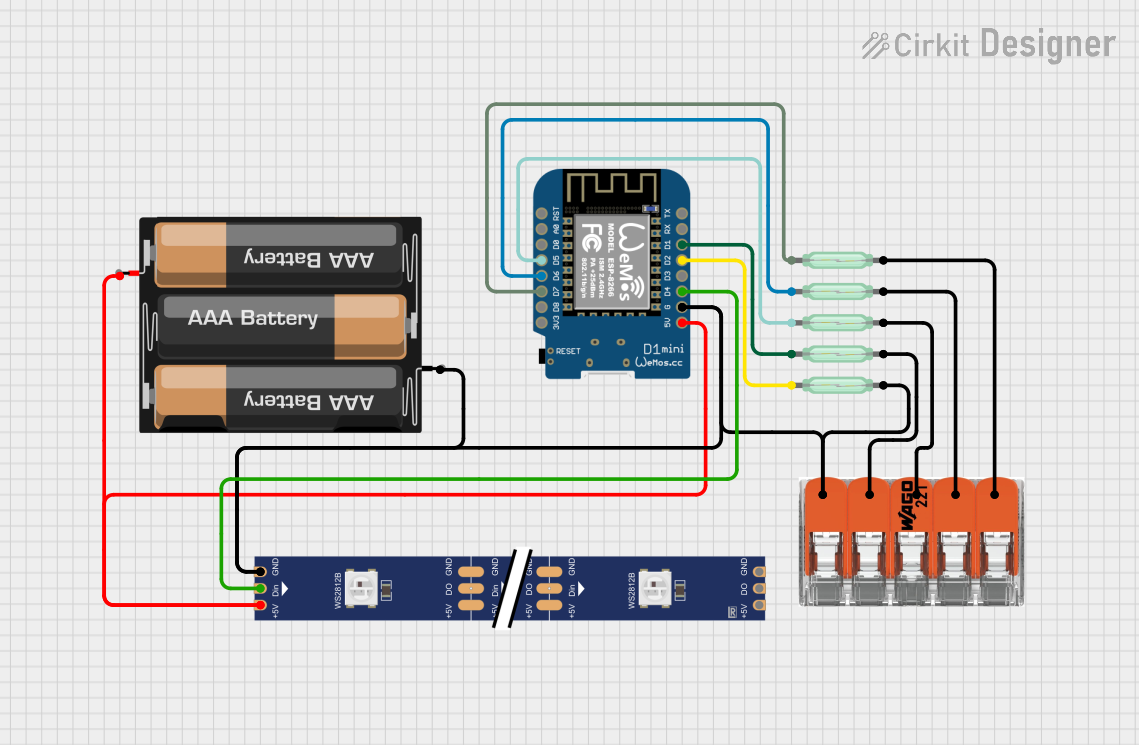
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer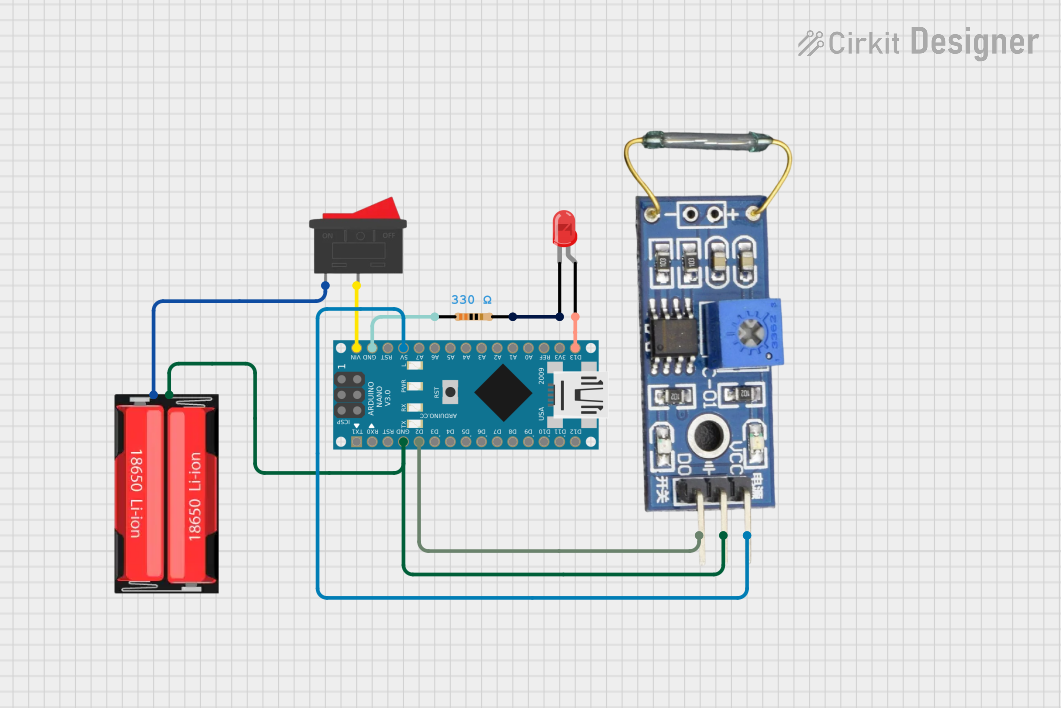
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Reed switch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical Reed switch. Note that specifications may vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Contact Form | SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) |
| Switching Voltage | 3V to 250V DC/AC |
| Switching Current | 10mA to 3A |
| Contact Resistance | 50 mΩ to 200 mΩ |
| Insulation Resistance | >10⁹ Ω |
| Operate Time | 0.5 ms to 2 ms |
| Release Time | 0.1 ms to 1 ms |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Glass Tube Dimensions | Typically 10mm to 50mm in length |
Pin Configuration and Description
Reed switches are simple two-terminal devices. The terminals are connected to the ferromagnetic contacts inside the glass tube.
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Contact terminal 1 (input/output) |
| 2 | Contact terminal 2 (input/output) |
Note: The Reed switch does not have polarity, so the terminals can be connected in either orientation.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Reed Switch in a Circuit
Basic Circuit Connection:
- Connect one terminal of the Reed switch to the positive side of the power supply.
- Connect the other terminal to the load (e.g., an LED with a current-limiting resistor) and then to the ground.
- Place a magnet near the Reed switch to close the circuit and activate the load.
Interfacing with a Microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO):
- Connect one terminal of the Reed switch to a digital input pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the other terminal to the ground.
- Use a pull-up resistor (10kΩ) between the digital input pin and the 5V supply to ensure a stable signal.
Example Arduino Code
// Reed Switch Example with Arduino UNO
// This code reads the state of a Reed switch and turns an LED on or off
// based on the switch's state.
const int reedSwitchPin = 2; // Pin connected to the Reed switch
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(reedSwitchPin, INPUT_PULLUP); // Set Reed switch pin as input with pull-up
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int reedState = digitalRead(reedSwitchPin); // Read the state of the Reed switch
if (reedState == LOW) { // If the Reed switch is closed (magnet near)
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
Serial.println("Magnet detected!"); // Print message to serial monitor
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off the LED
Serial.println("No magnet detected."); // Print message to serial monitor
}
delay(100); // Small delay for stability
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Magnet Selection: Use a magnet with sufficient strength to reliably activate the Reed switch. The activation distance depends on the magnet's strength and the switch's sensitivity.
- Debouncing: Reed switches may produce noise or "bouncing" when switching states. Use hardware (capacitors) or software (debouncing code) to filter out false signals.
- Current Limiting: Ensure the current through the Reed switch does not exceed its rated switching current to prevent damage.
- Environmental Protection: While the glass tube is sealed, avoid exposing the Reed switch to excessive vibration, shock, or corrosive environments.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Reed Switch Not Activating:
- Cause: Magnet is too weak or too far from the switch.
- Solution: Use a stronger magnet or reduce the distance between the magnet and the switch.
Intermittent Operation:
- Cause: Contact bouncing or poor connections.
- Solution: Add a capacitor across the Reed switch terminals or implement software debouncing.
Switch Fails to Open/Close:
- Cause: Exceeding the rated current or voltage may weld the contacts.
- Solution: Replace the damaged switch and ensure the circuit operates within the specified ratings.
False Triggering:
- Cause: External magnetic interference.
- Solution: Shield the Reed switch from stray magnetic fields or reposition it.
FAQs
Q1: Can a Reed switch handle AC signals?
Yes, Reed switches can handle both AC and DC signals, provided the voltage and current are within the specified ratings.
Q2: How do I increase the activation distance?
Use a stronger magnet or a Reed switch with higher sensitivity.
Q3: Can I use a Reed switch in high-vibration environments?
Reed switches are sensitive to vibration, which may cause false triggering. Consider using a solid-state alternative, such as a Hall effect sensor, for such applications.
Q4: Is the Reed switch polarity-sensitive?
No, the Reed switch is not polarity-sensitive and can be connected in either orientation.