
How to Use Arduino Nano: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
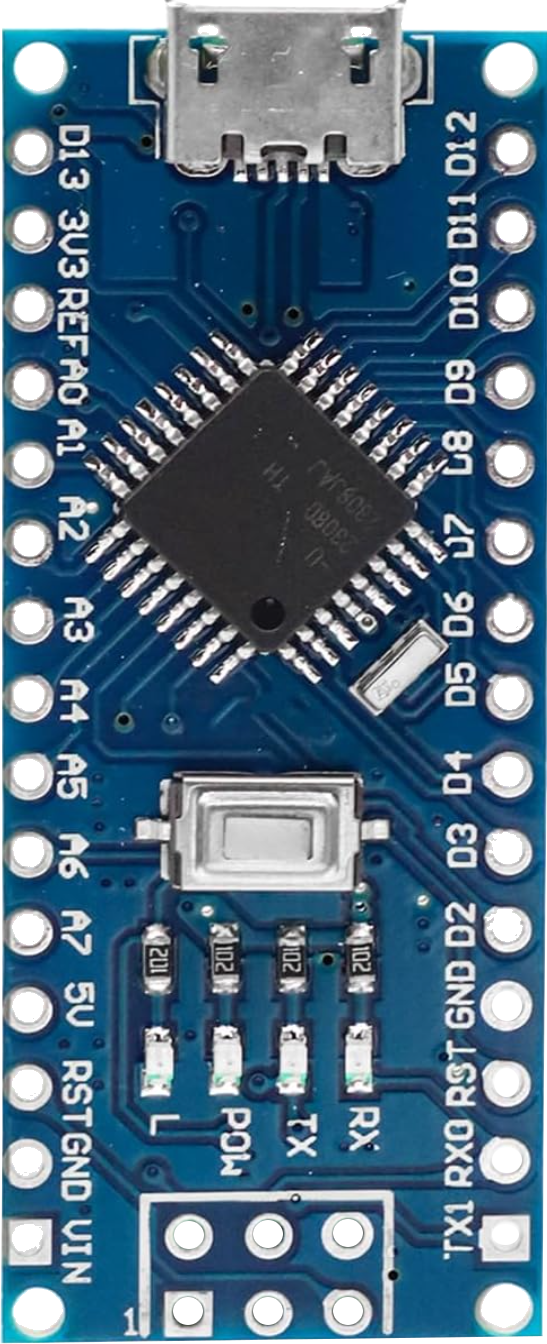
 Design with Arduino Nano in Cirkit Designer
Design with Arduino Nano in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Arduino Nano is a compact microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P microcontroller. It is designed for small-scale projects and prototyping, offering a balance of functionality and size. The Nano features 14 digital input/output pins, 8 analog input pins, USB connectivity for programming, and compatibility with the Arduino IDE. Its small form factor makes it ideal for embedding into projects where space is limited.
Explore Projects Built with Arduino Nano
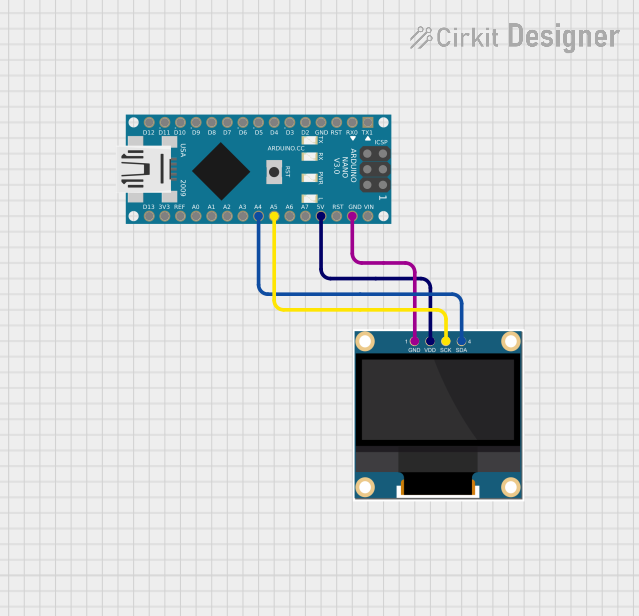
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer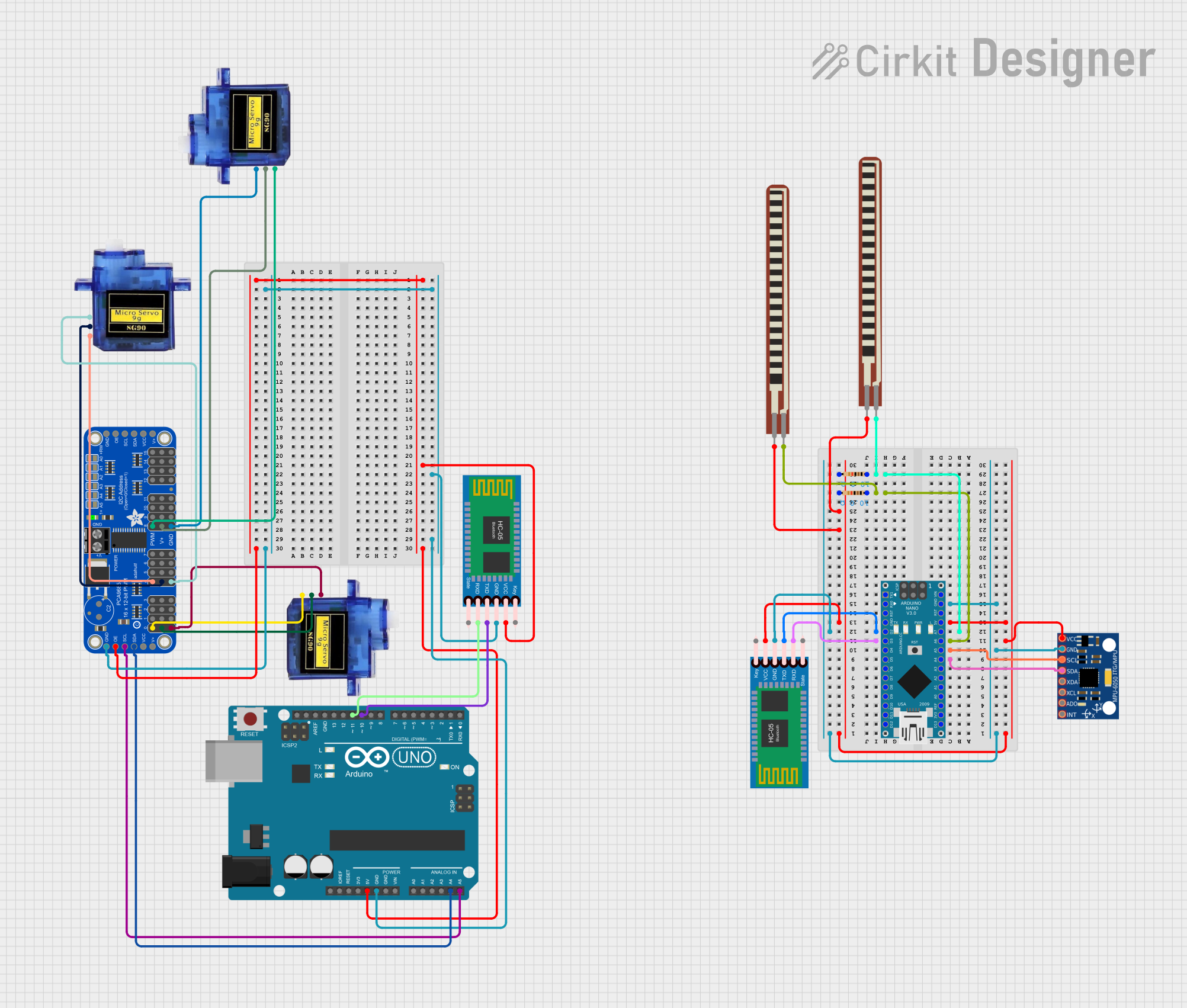
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Arduino Nano

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- DIY electronics and prototyping
- Robotics and automation
- Sensor data acquisition and processing
- Wearable technology
- IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Educational projects and learning microcontroller programming
Technical Specifications
The Arduino Nano is equipped with the following key features and specifications:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ATmega328P |
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V |
| Input Voltage (limit) | 6-20V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 (6 PWM outputs) |
| Analog Input Pins | 8 |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 40 mA |
| Flash Memory | 32 KB (2 KB used by bootloader) |
| SRAM | 2 KB |
| EEPROM | 1 KB |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| Dimensions | 18 x 45 mm |
| Weight | ~7 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Arduino Nano has a total of 30 pins, including power, digital, and analog pins. Below is a detailed description of the pin configuration:
Power Pins
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage to the board when using an external power source (7-12V recommended). |
| 2 | GND | Ground pins (multiple GND pins available). |
| 3 | 5V | Regulated 5V output from the onboard voltage regulator. |
| 4 | 3.3V | Regulated 3.3V output (limited to 50 mA). |
| 5 | AREF | Reference voltage for analog inputs. |
| 6 | RESET | Resets the microcontroller when pulled LOW. |
Digital Pins
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D0-D13 | Digital I/O | General-purpose digital input/output pins. Pins D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, and D11 support PWM. |
Analog Pins
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A0-A7 | Analog Input | Used for reading analog signals (0-5V). Can also be used as digital I/O pins. |
Communication Pins
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D0, D1 | RX, TX | Serial communication pins for UART. |
| D10-D13 | SPI | SPI communication pins (SS, MOSI, MISO, SCK). |
| A4, A5 | I2C | I2C communication pins (SDA, SCL). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Arduino Nano in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Use the USB Mini-B port to power the board and upload code from your computer.
- Alternatively, supply 7-12V to the VIN pin or 5V to the 5V pin for external power.
Connecting Components:
- Use the digital pins (D0-D13) for digital input/output operations.
- Use the analog pins (A0-A7) to read analog signals or as additional digital I/O pins.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Select "Arduino Nano" as the board type and choose the correct processor (ATmega328P).
- Connect the Nano to your computer via a USB cable and upload your code.
Example Code: Blinking an LED
The following example demonstrates how to blink an LED connected to pin D13:
// This example blinks an LED connected to pin D13 on the Arduino Nano.
// The LED will turn on for 1 second, then off for 1 second, repeatedly.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin D13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating (40 mA) for any I/O pin to prevent damage.
- Use appropriate resistors when connecting LEDs or other components to limit current.
- Ensure proper grounding when connecting external components to avoid noise or instability.
- When using the Nano with an external power source, ensure the voltage is within the recommended range (7-12V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The board is not detected by the computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
- Install the correct USB driver for the Arduino Nano.
Code upload fails with an error:
- Verify that the correct board and processor are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Check the COM port in the IDE and ensure it matches the one assigned to the Nano.
The board is not powering on:
- Check the power source and ensure the voltage is within the acceptable range.
- Inspect the USB cable or external power connections for faults.
Analog readings are unstable:
- Use a capacitor between the analog input pin and GND to filter noise.
- Ensure proper grounding for all connected components.
FAQs
Q: Can the Arduino Nano run on 3.3V?
A: The Nano operates at 5V, but it has a 3.3V output pin for low-power peripherals. Running the Nano itself on 3.3V is not recommended.
Q: How do I reset the Arduino Nano?
A: Press the onboard reset button or connect the RESET pin to GND momentarily.
Q: Can I use the Arduino Nano for wireless communication?
A: Yes, you can connect wireless modules like Bluetooth (HC-05) or Wi-Fi (ESP8266) to the Nano via UART or SPI/I2C.
Q: What is the difference between the Nano and the Uno?
A: The Nano is smaller and more compact, making it suitable for space-constrained projects. It has the same microcontroller (ATmega328P) as the Uno but lacks a standard USB-B port and uses a Mini-B USB connector instead.