
How to Use Dioda schottky: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Dioda schottky in Cirkit Designer
Design with Dioda schottky in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Dioda Schottky (Manufacturer: OOOT, Part ID: 90QE9Q) is a semiconductor device designed to allow current to flow in one direction with minimal forward voltage drop and high-speed switching capabilities. Its unique construction, utilizing a metal-semiconductor junction, makes it highly efficient for applications requiring low power loss and fast response times.
Explore Projects Built with Dioda schottky
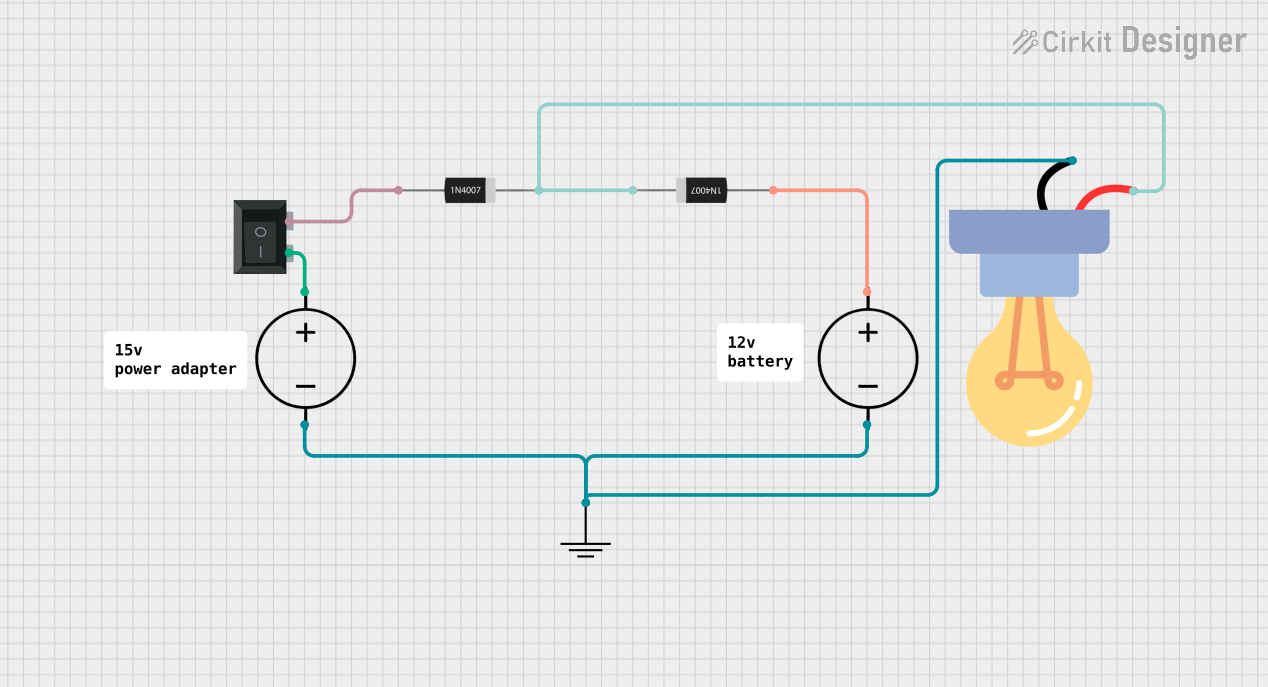
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer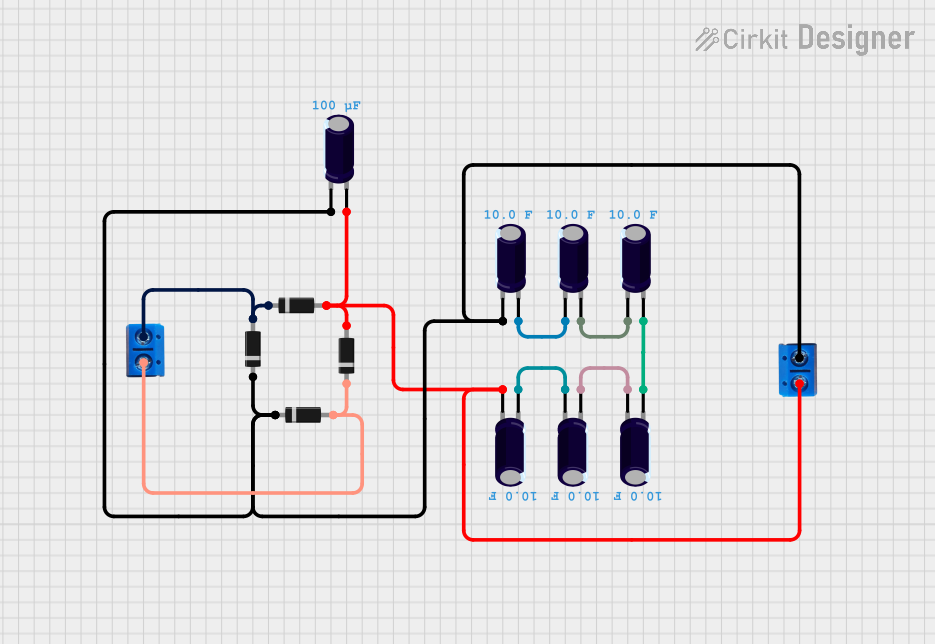
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer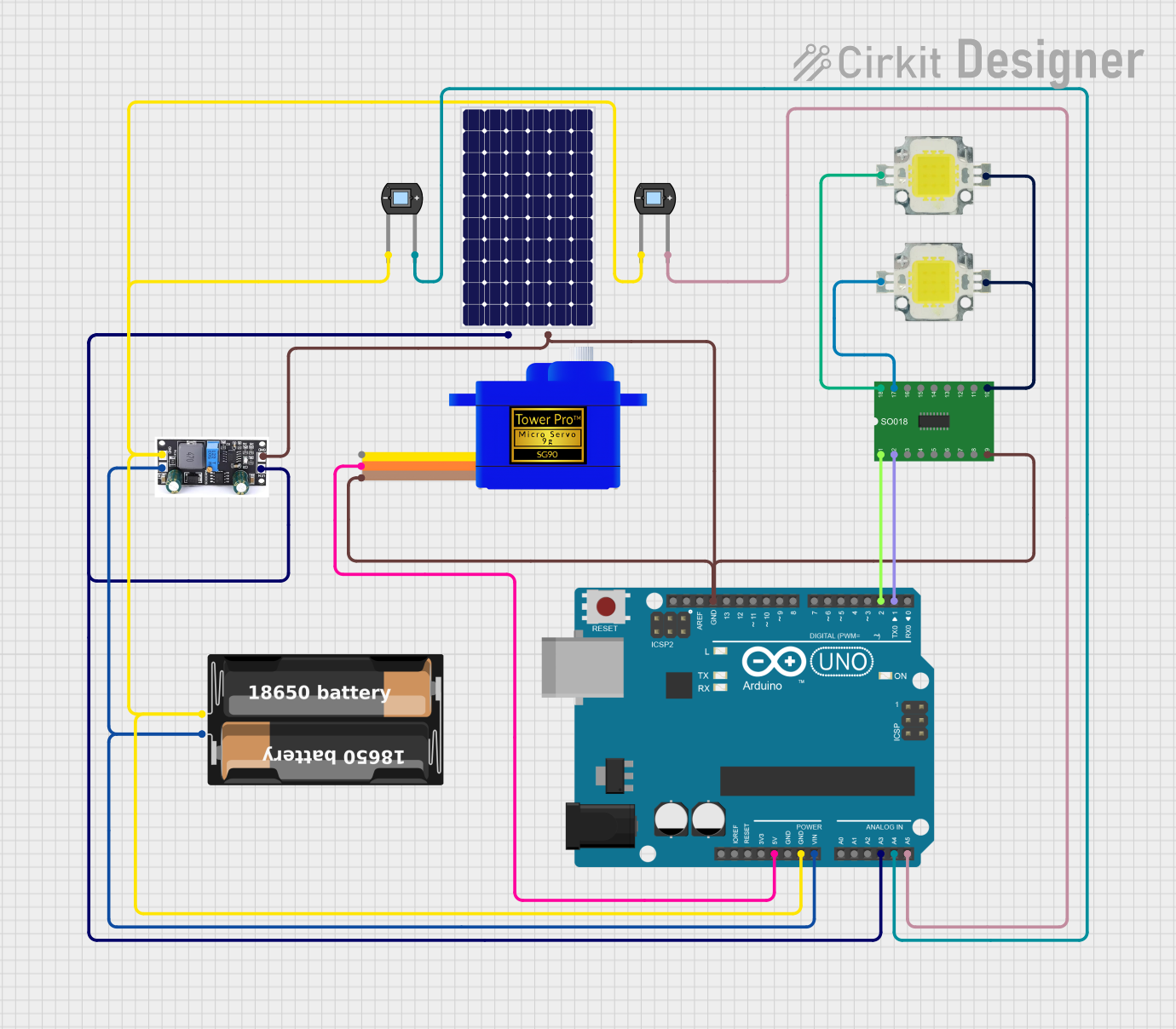
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer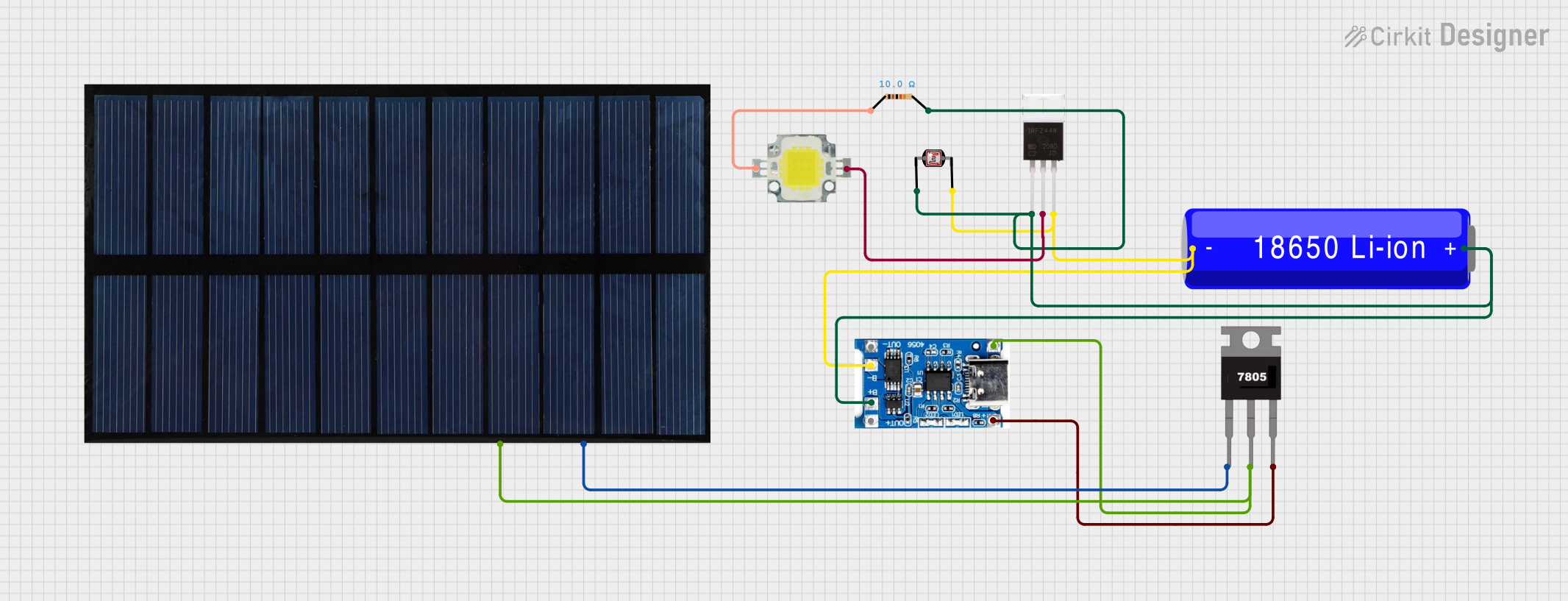
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Dioda schottky

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power rectification in power supplies
- High-frequency switching circuits
- Voltage clamping and protection
- RF and microwave applications
- Solar panel bypass diodes
- Low-voltage, high-efficiency DC-DC converters
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Forward Voltage Drop (Vf): 0.2V to 0.45V (typical, depending on current)
- Maximum Reverse Voltage (Vr): 90V
- Maximum Forward Current (If): 9A
- Reverse Leakage Current (Ir): ≤ 1mA at Vr = 90V
- Junction Temperature Range (Tj): -55°C to +150°C
- Switching Speed: < 10ns
- Package Type: TO-220
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Dioda Schottky (90QE9Q) is typically housed in a TO-220 package with three pins. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode | Positive terminal for current flow |
| 2 | Cathode | Negative terminal for current flow |
| 3 | Cathode (Tab) | Connected to the cathode, used for heat dissipation |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Polarity Matters: Ensure the anode is connected to the positive side of the circuit and the cathode to the negative side. Reversing the polarity will block current flow.
- Heat Dissipation: The TO-220 package includes a metal tab for heat dissipation. Use a heatsink if the diode operates at high currents to prevent overheating.
- Voltage Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum reverse voltage (90V) to avoid breakdown.
- Current Ratings: Ensure the forward current does not exceed 9A to prevent damage.
- Bypass Applications: In solar panels, connect the diode in parallel with the panel to prevent reverse current during low light conditions.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
The Dioda Schottky can be used in an Arduino-based DC motor driver circuit to protect against back EMF. Below is an example:
Circuit Description
- The Schottky diode is placed across the motor terminals to prevent voltage spikes from damaging the Arduino or motor driver.
Code Example
// Example code for controlling a DC motor with Arduino UNO
// The Schottky diode protects against back EMF from the motor.
const int motorPin = 9; // PWM pin connected to motor driver
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motor pin as output
}
void loop() {
analogWrite(motorPin, 128); // Run motor at 50% speed
delay(5000); // Run for 5 seconds
analogWrite(motorPin, 0); // Stop motor
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Thermal Management: Always monitor the diode's temperature during operation. Use a heatsink or thermal paste if necessary.
- Parasitic Capacitance: In high-frequency circuits, consider the diode's parasitic capacitance, as it may affect performance.
- Parallel Operation: When using multiple diodes in parallel, ensure proper current sharing by adding small resistors in series with each diode.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Diode overheating | Exceeding current or poor heat dissipation | Use a heatsink or reduce the current load. |
| No current flow in the circuit | Incorrect polarity connection | Verify the anode and cathode connections. |
| High reverse leakage current | Operating near maximum reverse voltage | Reduce the reverse voltage or check for damaged diode. |
| Circuit not functioning as expected | Faulty or damaged diode | Test the diode with a multimeter and replace if necessary. |
FAQs
Can I use the Dioda Schottky for AC rectification?
- Yes, but ensure the reverse voltage rating is sufficient for the peak AC voltage.
What makes a Schottky diode different from a regular diode?
- Schottky diodes have a lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speeds compared to regular silicon diodes.
How do I test if the diode is working?
- Use a multimeter in diode mode. Connect the positive lead to the anode and the negative lead to the cathode. A forward voltage drop of ~0.2V to 0.45V indicates a functional diode.
Can I use this diode in high-frequency circuits?
- Yes, the Dioda Schottky is ideal for high-frequency applications due to its fast switching speed.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Dioda Schottky (90QE9Q) into your electronic projects for efficient and reliable performance.